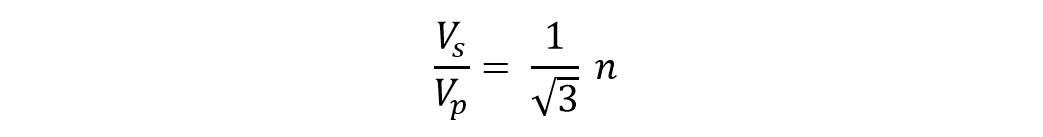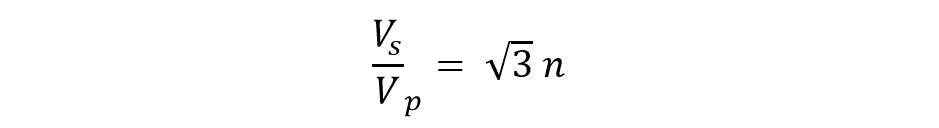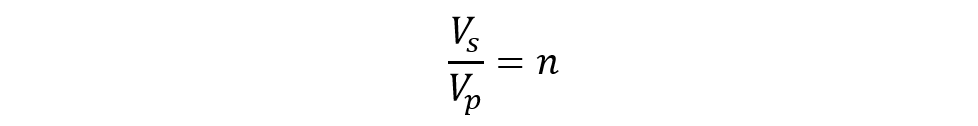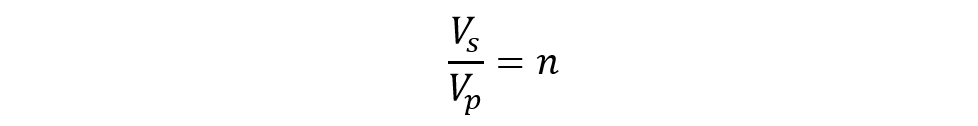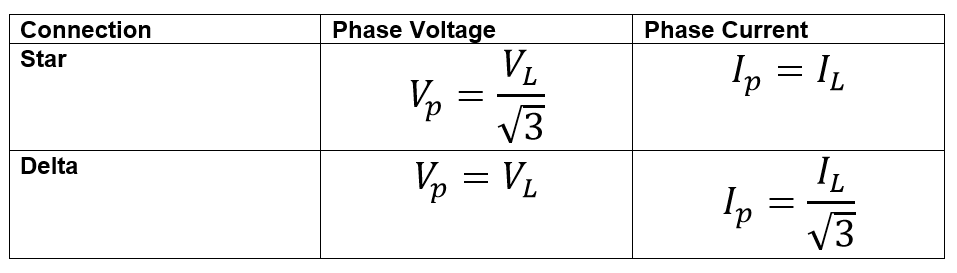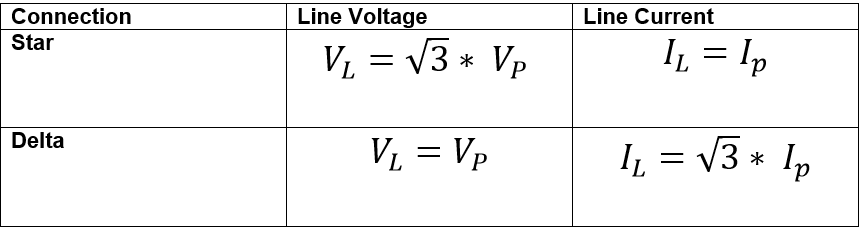Three Phase Transformer
Three-phase transformers are the anchors of power transmission and distribution because they can efficiently transmit power over long distances. Three-phase transformers are manufactured by three primary windings and three secondary windings. These windings can be connected in different configurations that are explained below in the construction and connection of the three-phase transformer.
Assembly of Three Phase Transformer
Three-phase transformers can have two different assemblies, as mentioned below.
- Single Unit Three Phase Transformer or Three Phase Core Type Transformer
- Three Phase Transformer Banks or Three Phase Shell Type Transformer
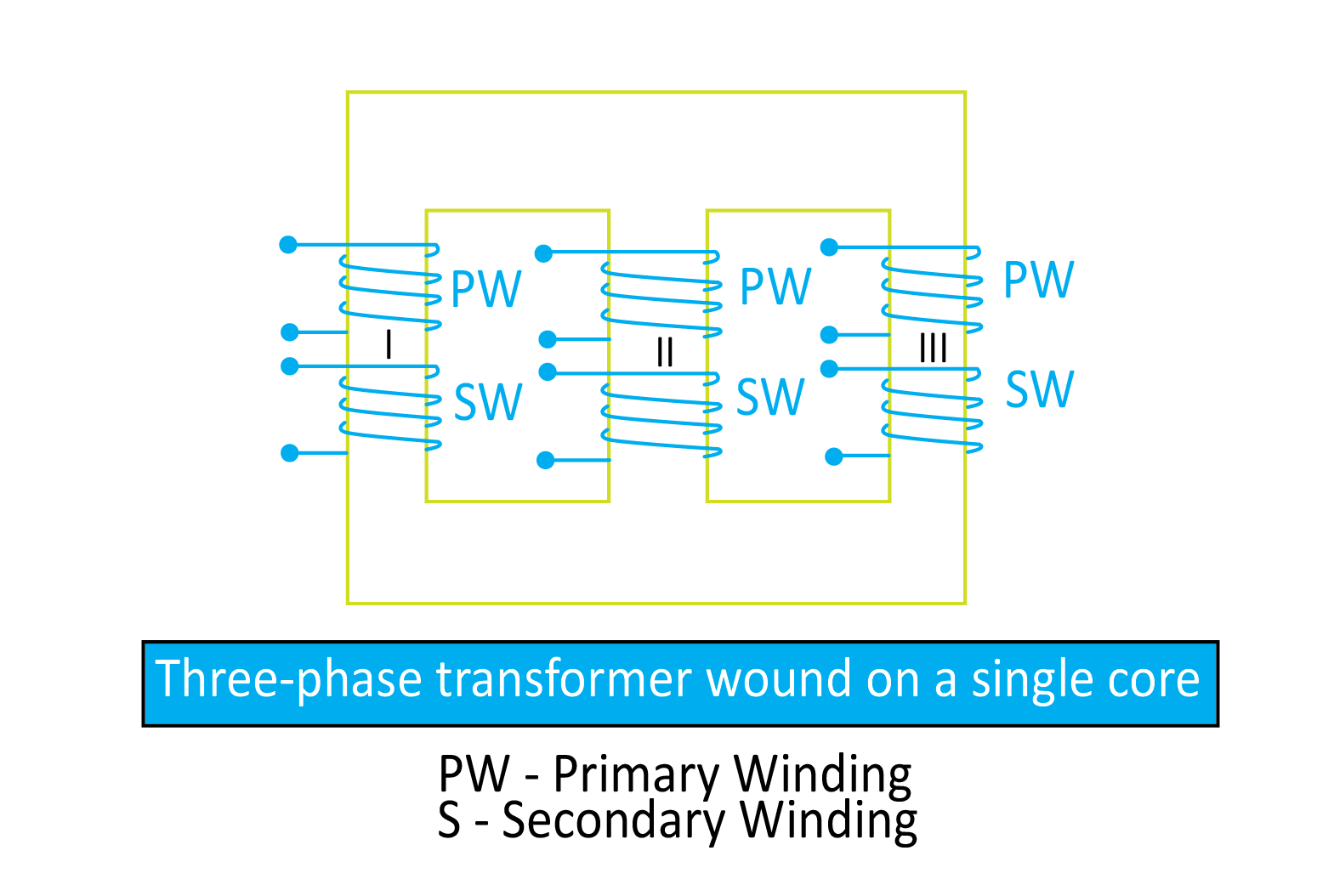
Single Unit Three Phase Transformer
This construction of a three-phase transformer consists of a single core with three different legs. Each leg of the single core of the transformer has both primary and secondary winding. In this configuration, low-voltage windings are connected below high-voltage windings. This construction of a three-phase transformer is also called a three-phase-core-type transformer. It is more compact and simpler than transformer banks; therefore, it is mostly preferred.
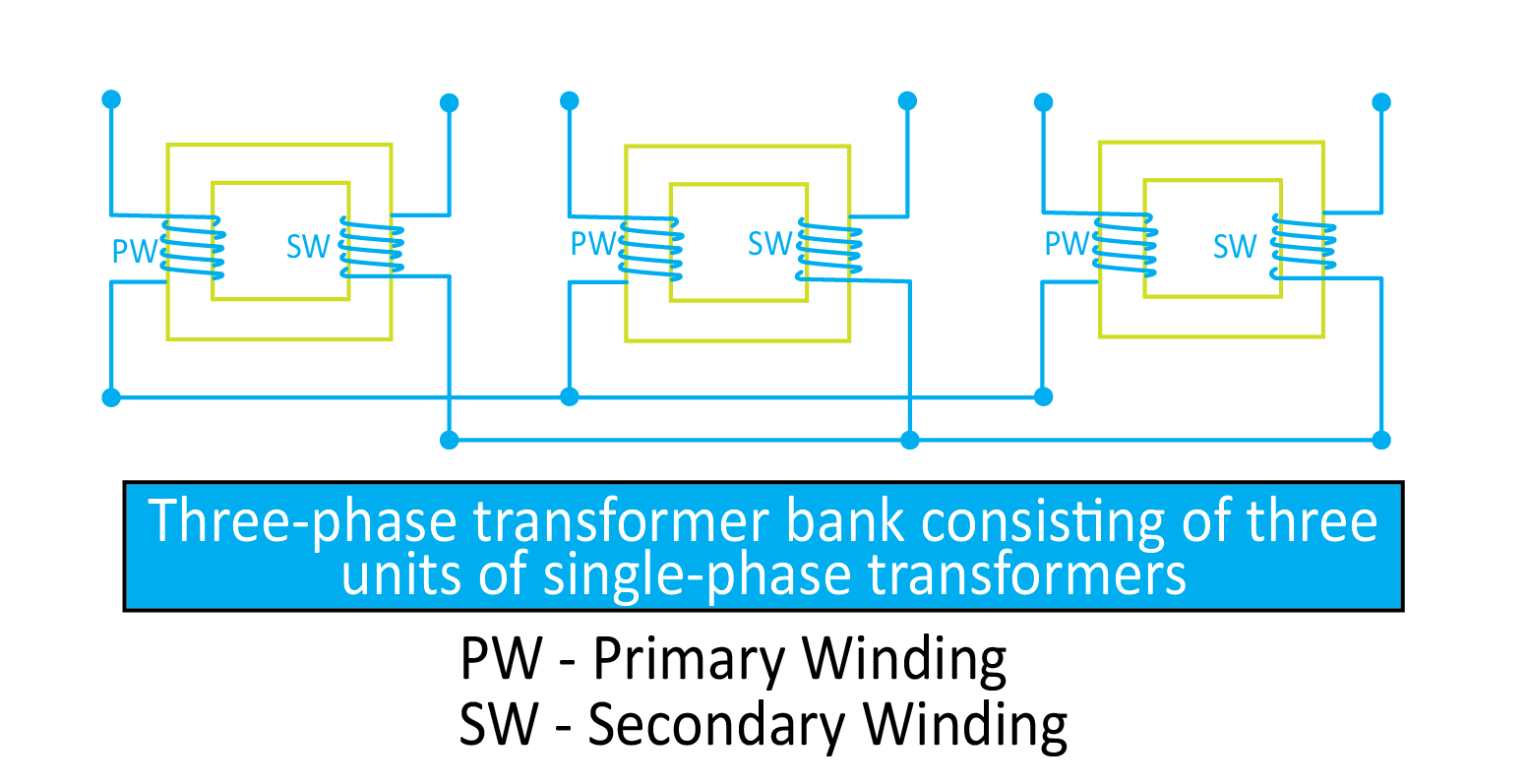
Three-Phase Transformer Bank
In this type of construction of a three-phase transformer, three different cores are combined in a single shell. Therefore, it is also called a three-phase shell-type transformer. Each core inside the shell has primary and secondary windings like single-phase transformers. This construction is rarely used because it is less compact and occupies more space.
Connections of Three-Phase Transformer
Three-phase transformers may have distinct connections according to the connections of their primary windings and connections of secondary windings. There are mainly four connection configurations of three-phase transformers, as given below.
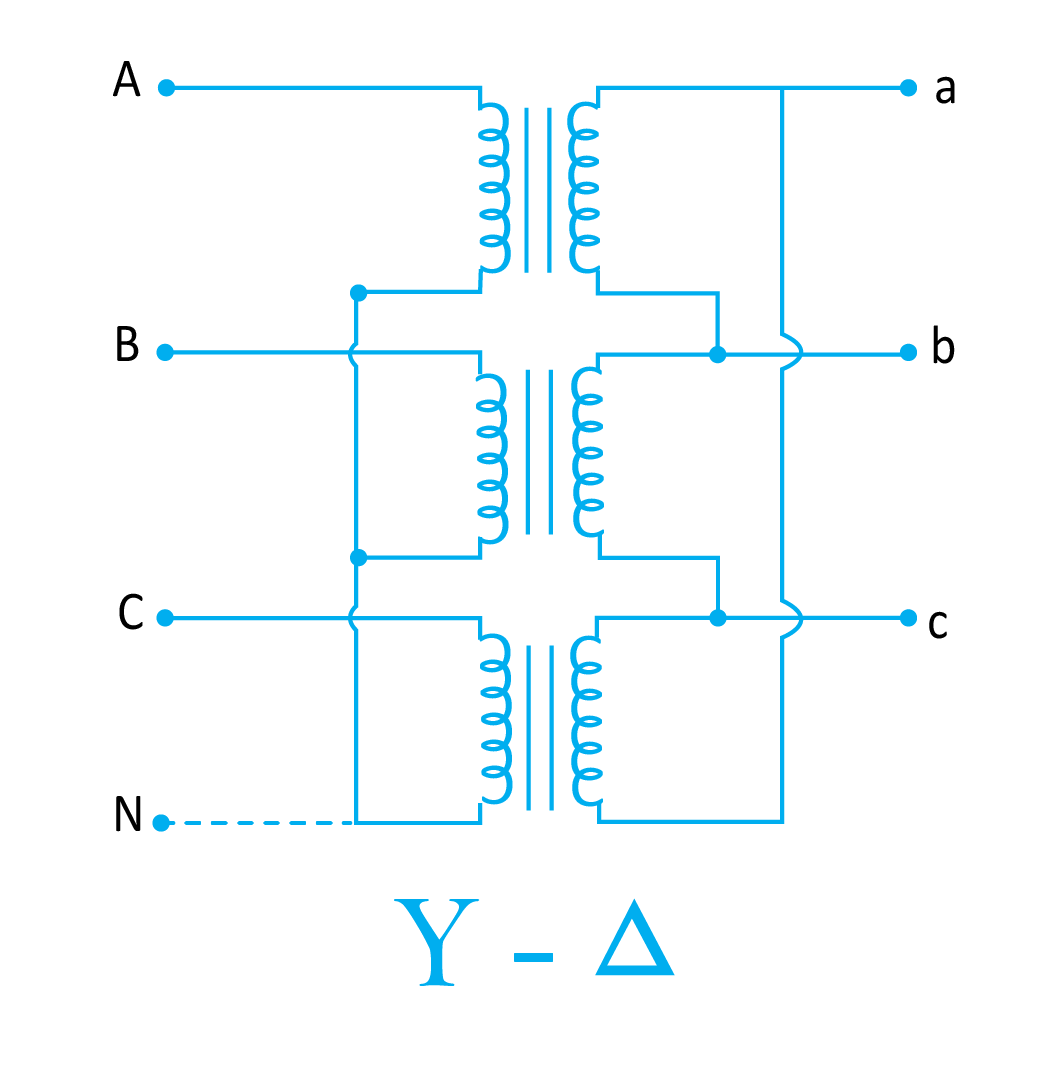
Star to Delta Connection
As the name indicates, the star-to-delta connection of a three-phase transformer means that star connected is primary windings and delta connected is secondary windings. The star-connected primary windings have a neutral wire that is grounded.
This configuration is largely used in step-down transformers placed at the end of transmission lines or distribution stations.
Moreover, the ratio of secondary line voltage and primary line voltage can be given as:
Where ‘n’ is the transformation ratio calculated through the number of turns in primary and secondary windings. Owing to the difference in connections of primary and secondary windings, a phase shift of 30° is also observed between primary line voltage and secondary line voltage.
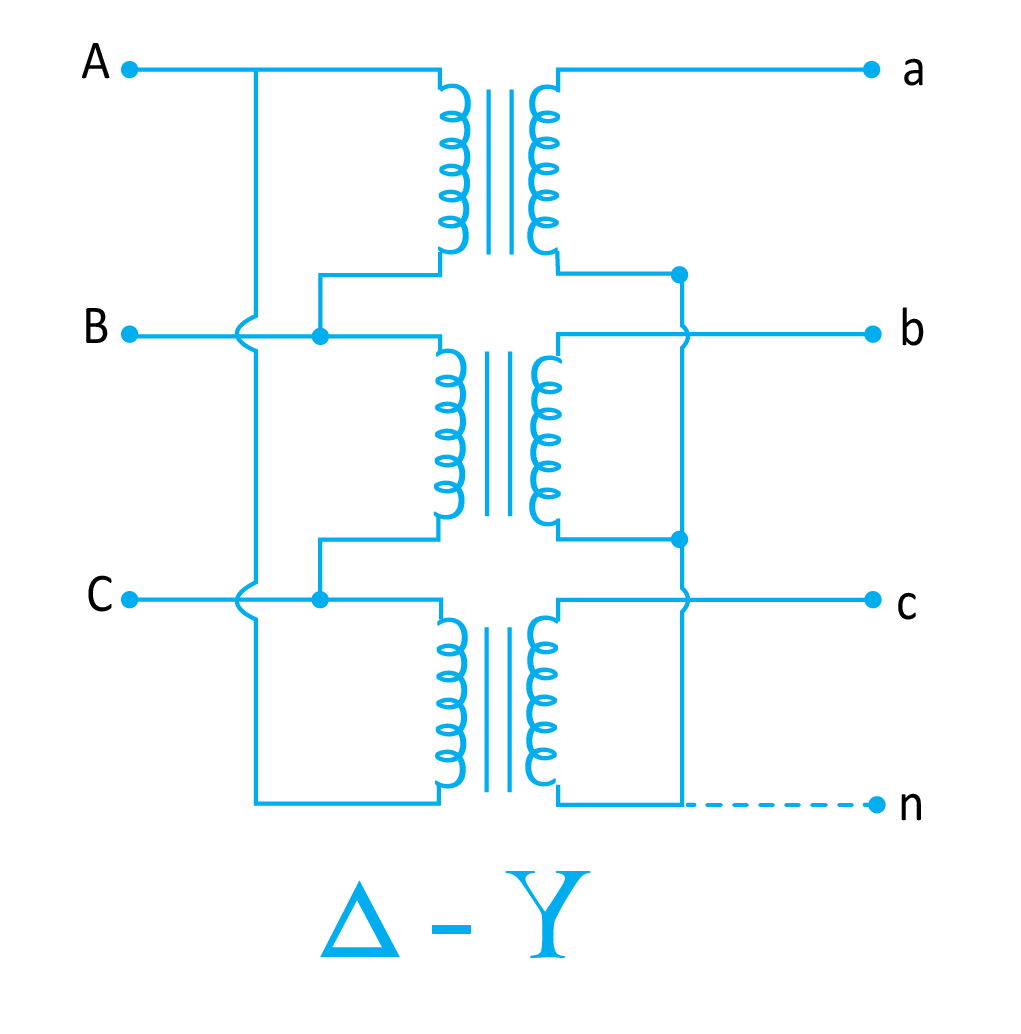
Delta to Star Connection
This kind of configuration is opposite to the star-delta configuration. Here, primary windings are delta connected whereas secondary windings are star connected. In the star connection of secondary windings, all three windings have a common ground that makes it a three-phase-four wire system.
This type of configuration is largely used in step-up transformers at the origination of transmission lines.
Moreover, the ratio of secondary line voltage and primary line voltage can be given as:
Where ‘n’ is the transformation ratio calculated through the number of turns in primary and secondary windings. There also exists a 30° phase shift within primary and secondary line voltages.
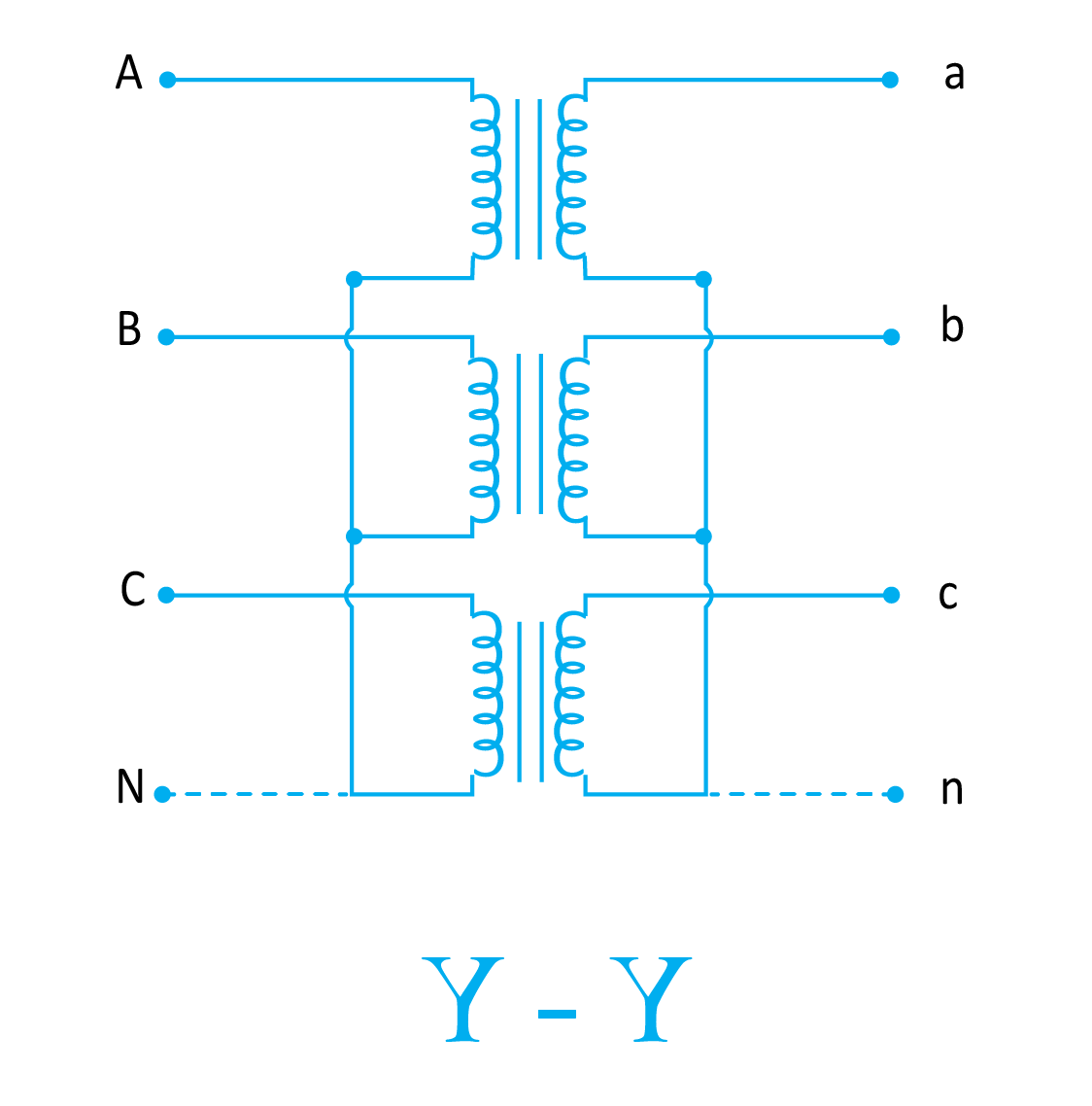
Star to Star Connection
As the name suggests, this configuration is based on star-connected primary as well as secondary voltages. The benefit of this configuration is that the number of turns per phase in primary and secondary windings is reduced. It happens because the phase voltage is 1/√3 times the line voltage in the star connection. Therefore, less insulation is required to segregate the windings.
This configuration is largely used in areas where the load is balanced and does not fluctuate much. If an unbalanced load is connected to the star-star configuration of the three-phase transformer, then the phase voltages are disturbed severely.
Here, the ratio of primary line voltages and secondary line voltages is similar to the turns ratio or transformation ratio.
Where ‘n’ is the transformation ratio calculated through the number of loops in primary and secondary windings. The line voltages at the primary side and secondary side do not have any phase difference because of the same star configuration on both sides.
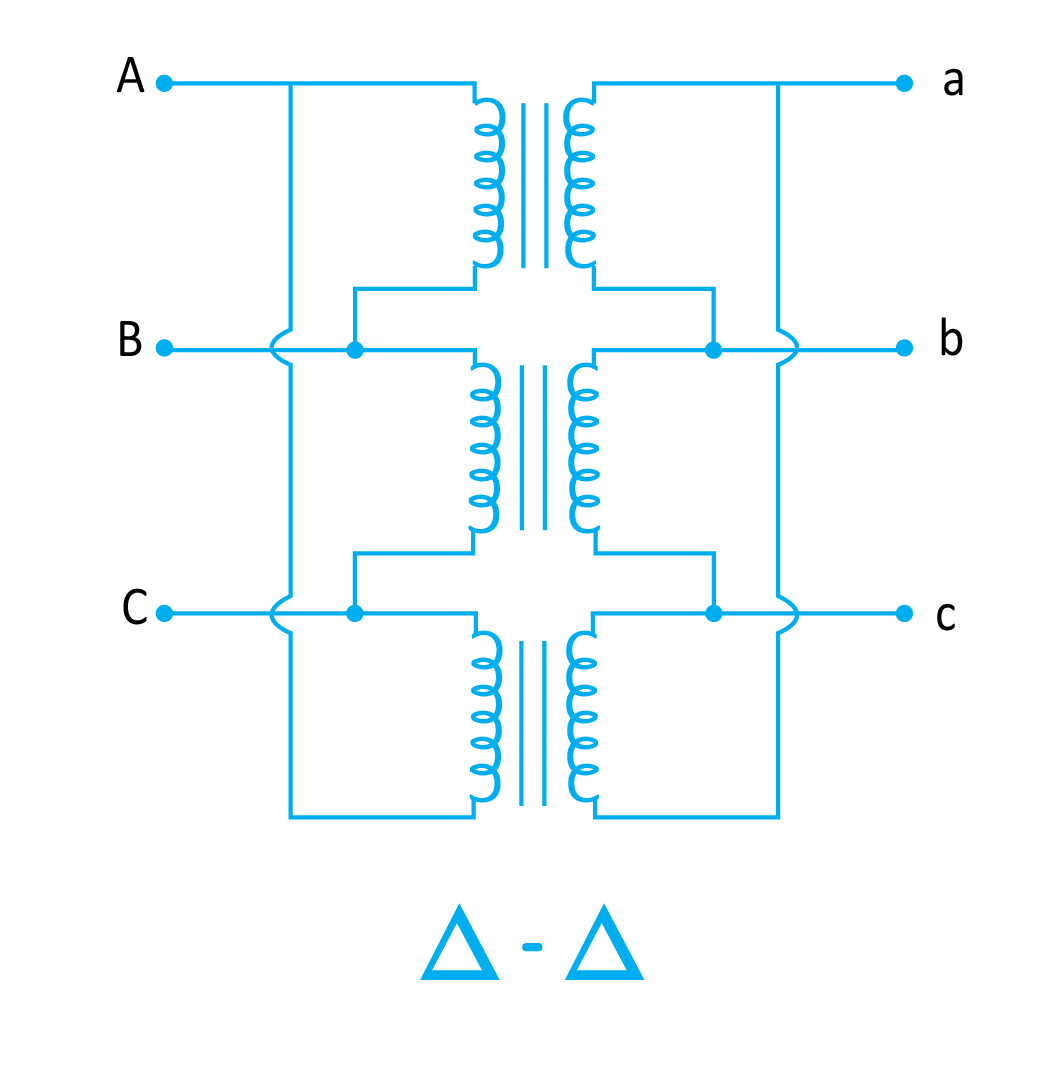
Delta to Delta Connection
This kind of configuration has delta-connected primary as well as secondary windings. It is opposite to the star-star connection. More turns per phase are required in this case, yet there can be two benefits of this configuration.
- It can handle an unbalanced load because phase voltages are equal to line voltages in a delta connection.
- Balanced loads can also be connected with delta-to-delta transformers.
- This configuration can operate even with an open delta connection if any of the phases or transformers fail to operate.
The disadvantage associated with this configuration is that it does not have a neutral wire.
Here, the ratio of primary line voltages and secondary line voltages is similar to the turn ratio or transformation ratio.
Where ‘n’ is the transformation ratio calculated through the number of loops in primary windings and secondary windings.
Phase Voltage and Phase Current
The table given below shows the relationship between phase voltage and line voltage, and phase current and line current, in both delta and star connections. It will give a better understanding of the relation between primary and secondary voltages of three-phase transformers in different configurations.
Line Voltage and Line Current
The table given below shows the relationship between phase voltage and line voltage, and phase current and line current, in both delta and star connections.
Applications of Three-Phase Transformer
Three-phase transformers are a very important kind of electrical machine that have applications in daily life. They are present in power generation, power transmission, and power distribution systems. Similarly, they are used as step-up and step-down transformers in industries such as mining, textile, automation, etc. They are also used with motors and rectifiers in high-power industrial loads.
Conclusion
Three-phase transformers are very useful electrical machines that can be constructed in two ways. One is a single unit three-phase transformer and the other is a transformer bank. A single unit is more compact and less costly than a transformer bank. The windings of three-phase transformers can be connected in four different configurations that are star to delta, delta to star, star to star, and delta to delta. Each of them has its usage. These transformers are used in almost every kind of industry where loads are to be managed.