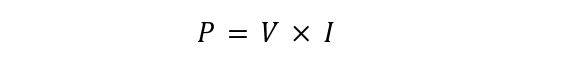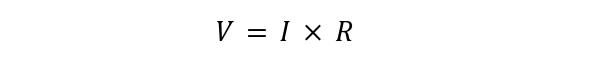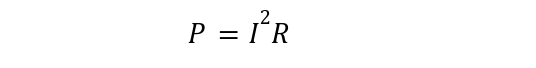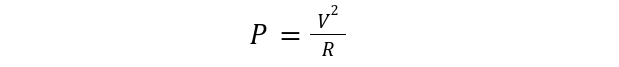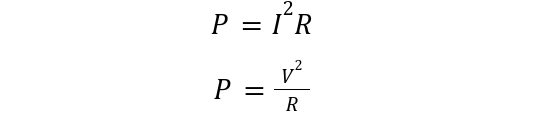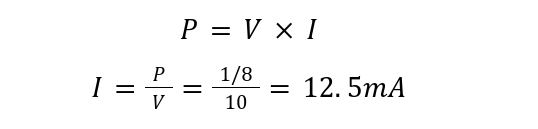Power Rating of Resistor
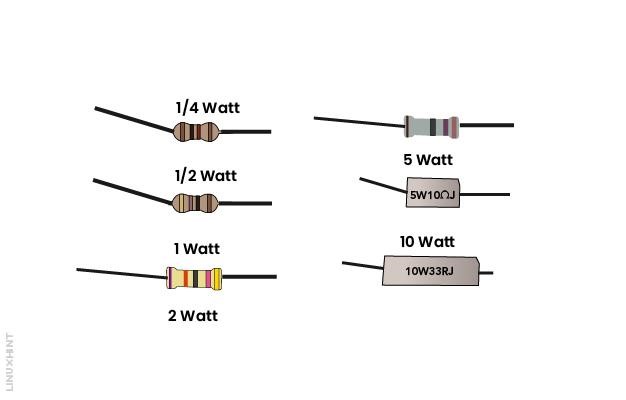
The maximum amount of allowed energy that can be dissipated from a resistor is called power rating. Power is expressed in watts. Therefore, the power rating is also called the wattage rating of the resistor. The below figure shows different power ratings of resistors. The maximum power that should be connected with these resistors shall not exceed their wattage ratings. A ¼ watt resistor shall be connected with a power supply not more than ¼ watt otherwise it will burn out.
Calculation of Power Ratings
To calculate the power rating of a resistor, the formula used to calculate the power can be used which is given below:
Here ‘V’ denotes voltage across the resistor while ‘I’ denotes current through it.
Using Ohms’ law:
Substituting in the above formula, we get two expressions:
Measurement of Power Ratings
The two of the power equations listed above are used for the measurement of the power ratings of the resistor:
By knowing the maximum current and resistor size or voltage ratings, the power rating of resistors can be calculated from the above equations.
Size Chart
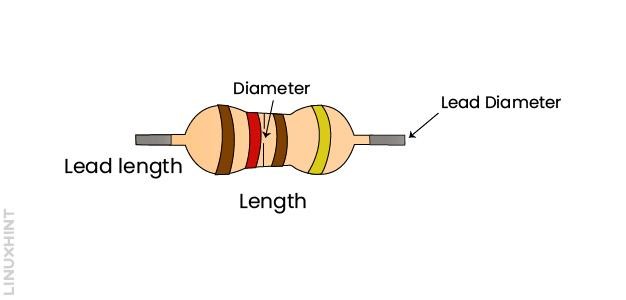
The size of resistors is defined by their diameter, length, lead length, and lead diameters as shown below:
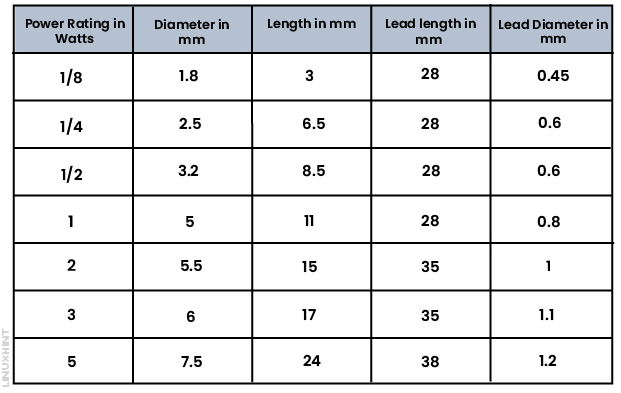
A resistor size chart provides a standard resistor’s physical dimensions with different power ratings. Generally, the size of resistors increases with the increase in power ratings:
In the above chart, power ratings corresponding to the diameter and lengths of resistors have been shown. The current ratings can be easily calculated using Ohm’s law if the supply voltage is known. Considering the supply voltage is 10V for ⅛ watt resistors, the current is given by:
Thus, a ⅛ watt resistor can pass a maximum current of 12.5mA across it if a 10V supply is connected across it.
Conclusion
The need for finding the power ratings is to find out how much power a resistor can handle, or in other words its power capacity. With increased power rating requirements, a high-size resistor is required. The power ratings are also called the wattage ratings of resistors.