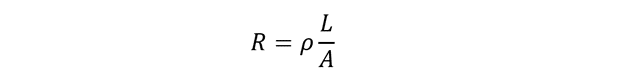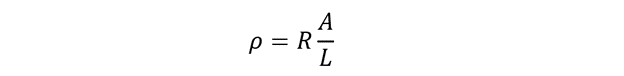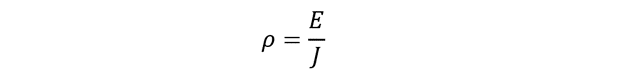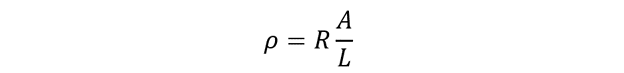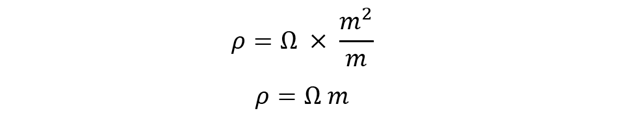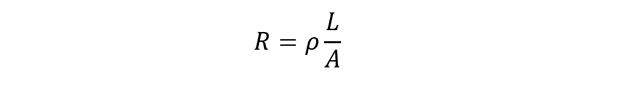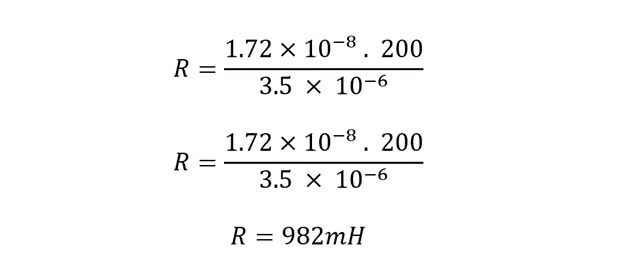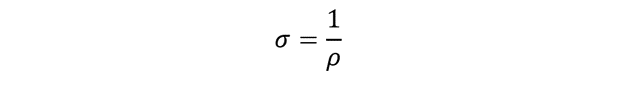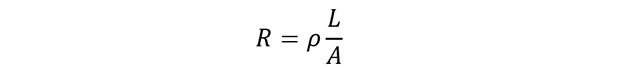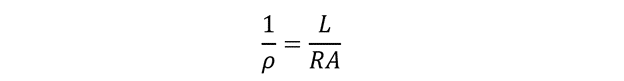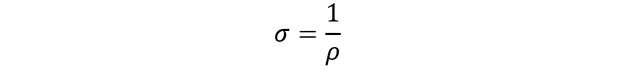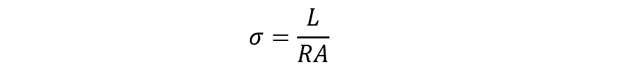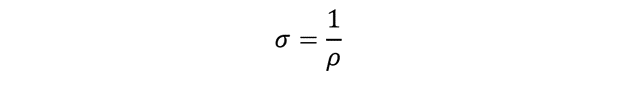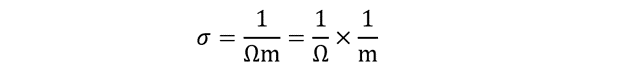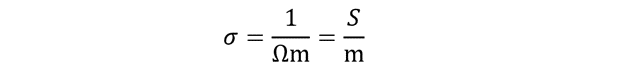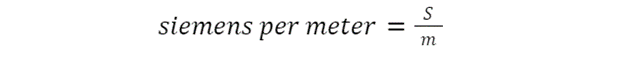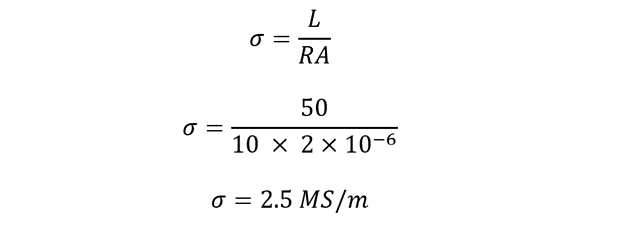Electrical Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is the ability of a material to resist the flow of electric current through a resistor. Some materials have a greater tendency to resist the flow of current than others. It means that resistivity can be greater for some materials than others.
Mathematical Expression
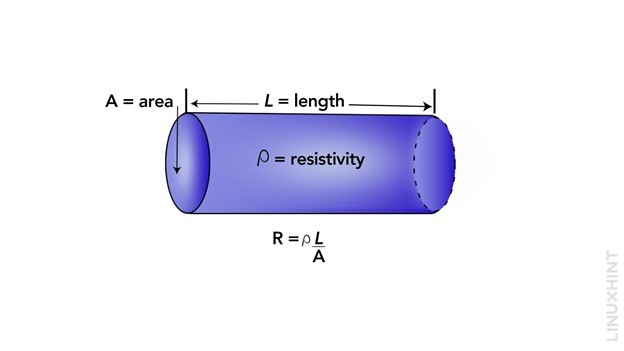
The mathematical expression for electrical resistance for a conductor is given by:
Here ‘R’ represents electrical resistance, ‘L’ represents length of conductor, ‘A’ represents area of cross-section and ρ represents electrical resistivity.
The mathematical expression for electrical resistivity can be evaluated as below:
Resistivity can also be evaluated in terms of electric field and current density through following expression:
Where ρ is electrical resistivity of a material, ‘E’ is electrical field and ‘J’ is electric current density. Although the above expressions may relate to resistivity. The above expression mostly helps in the unit’s evaluation for resistivity. But resistivity is fixed and constant. It means it would not change for different values of resistance, area, or length of conductor. Whenever the area or length of conductor is changed, the resistance adjusts its value to keep resistivity exactly at the same values.
SI Units of Resistivity
The SI units of electrical resistivity can be figured out from the above resistance formula:
Substituting units:
The SI units of electrical resistivity is Ωm.
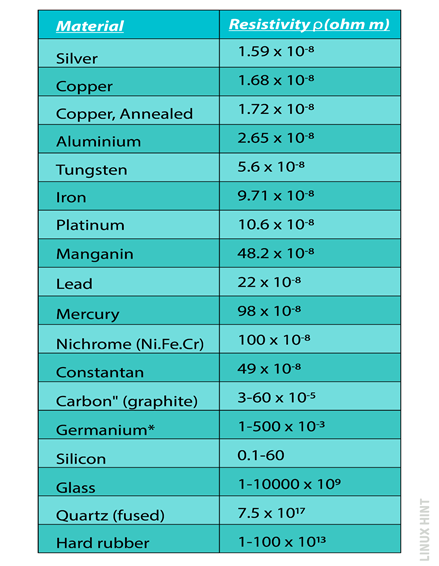
Resistivity of Materials
The resistivity values are pre-calculated for a variety of materials. These materials can include conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. The pre-calculated and standardized values of resistivity for different electrical materials are listed below:
Example: Calculating the Resistance of Copper Wire
If resistivity of copper is estimated at 1.72 x 10-8 Ωm. what will be the dc resistance of 200m meter 3.5mm2 copper wire.
Electrical resistance in terms of resistivity is expressed as:
Electrical Conductivity
Conductivity is defined as the measure of ease with which an electric current will flow through a material. It is exactly the inverse of the resistivity. It is expressed mathematically as a reciprocal of resistivity.
Mathematical Expression
The standard expression for electrical resistance is given by:
Electrical conductivity σ is given by:
Therefore, the expression for electrical conductivity is derived as.
SI unit for Conductivity
The SI units of conductivity can therefore be found as:
But 1/Ω is unit of conductance which is also represented through siemens, S.
The SI unit of electrical conductivity is:
Example: Calculating the Conductivity of Cable
Calculate conductivity of 50m cable length with resistance of 10 ohms and area 2mm2.
Electrical conductivity is expressed as:
Conclusion
Electrical resistivity is the measure of the ability of any electrical material to hinder the flow of current, while electrical conductivity is the measure of easiness any material offers to flow of current. Both parameters are opposite to each other in terms of both definitions and characteristics.