Installing TFTP Server:
TFTP server package is available in the official package repository of CentOS 8. So, you can easily install it on CentOS 8.
First, update the CentOS 8 package repository cache with the following command:
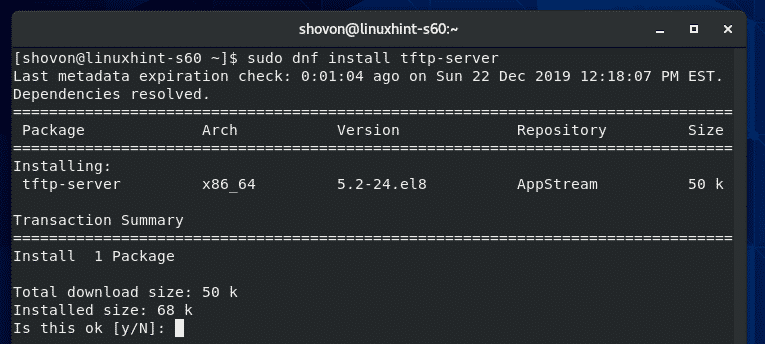
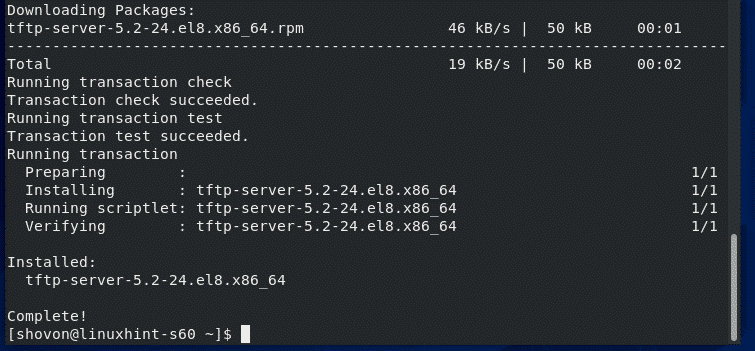
Now, install TFTP server package with the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
TFTP server package should be installed.
Configuring TFTP Server Service:
The default systemd service configuration of TFTP does not work correctly on CentOS 8. So, you have to create your own version of systemd service for TFTP server.
First, copy the default /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.service file to /etc/systemd/system/tftp-server.service with the following command:
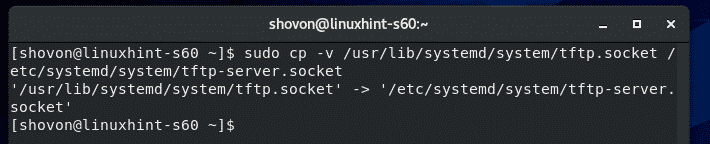
Then, copy the default /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket file to /etc/systemd/system/tftp-server.socket with the following command:
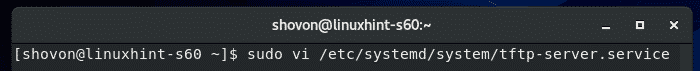
Now, edit the /etc/systemd/system/tftp-server.service file with the following command:
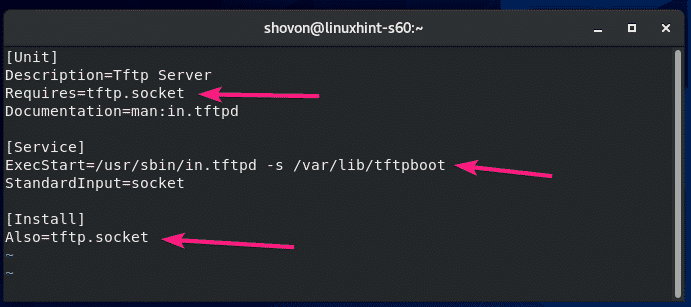
The default content of the tftp-server.service file is as follows. You have to change the lines as marked in the screenshot below.
Change Requires=tftp.socket to Requires=tftp-server.socket, change ExecStart=/usr/sbin/in.tftpd -s /var/lib/tftpboot to ExecStart=/usr/sbin/in.tftpd -c -p -s /var/lib/tftpboot and change Also=tftp.socket to Also=tftp-server.socket.
Here, ExecStart=/usr/sbin/in.tftpd -c -p -s /var/lib/tftpboot is used to run the TFTP server daemon. Here, the -c option is used to allow new files to be created in the TFTP server. The -p option is used to solve many of the file and directory permission issues. The -s option is used to set the TFTP server’s root directory. In this article, the TFTP root directory is /var/lib/tftpboot.
Once you change these lines, the tftp-server.service file should look as shown in the screenshot below.
You also have to add a new line WantedBy=multi-user.target after the [Install] line.
The final tftp-server.service file should look as shown in the screenshot below.
Now, edit the /etc/systemd/system/tftp-server.socket file with the following command:
The default tftp-server.socket file should look as shown in the screenshot below.
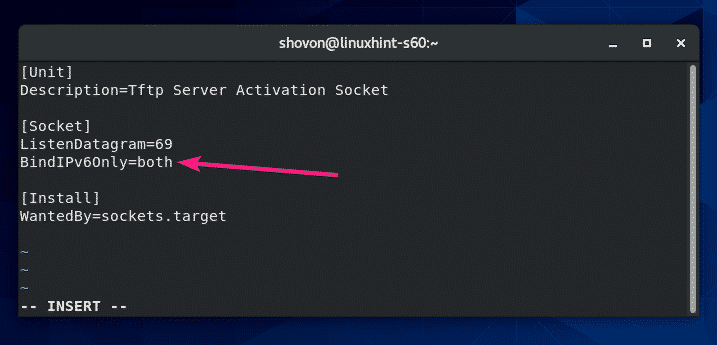
You have to add a new line BindIPv6Only=both after the ListenDatagram=69 line.
The final tftp-server.socket file should look as shown in the screenshot below.
Now, check the status of the tftp-server service that you’ve just created with the following command:
As you can see, the tftp-server service is inactive (not running) and disabled (won’t automatically start on system boot).
Now, start the tftp-server service with the following command:
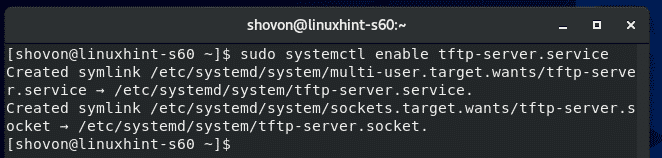
Also, add the tftp-server service to the system startup of your CentOS 8 machine with the following command:
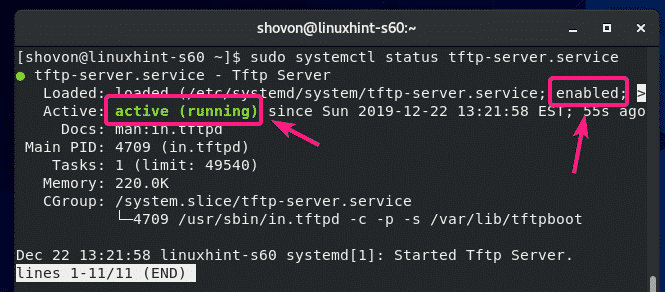
The tftp-server service should be active (running) and enabled (will automatically start on system boot).
If you have SELinux enabled, allow anonymous write access to the TFTP server with the following command:
NOTE: setsebool command may not be available on your CentOS 8 machine. If that’s the case, install the policycoreutils-python package with the following command:
Now, allow read, write and execute permission to the TFTP root directory /var/lib/tftpboot from any user with the following command:
Configuring the Firewall:
TFTP server runs on the UDP port 69.
If you have firewall configured on your CentOS 8 machine (which is very likely), you have to allow access to the UDP port 69 with the following command:
For the changes to take effect, run the following command:
Using the TFTP Server:
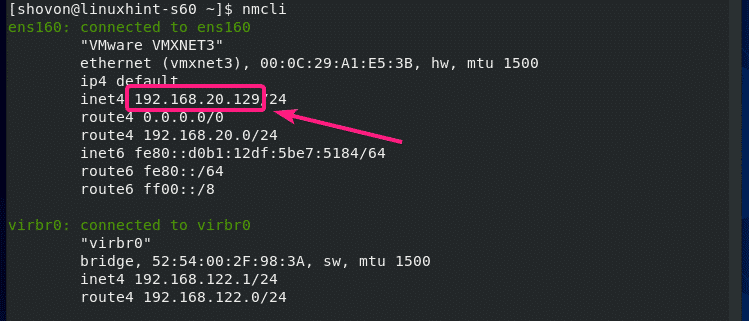
In order to access the TFTP server, you must know the IP address of your CentOS 8 machine.
You can find the IP address of your CentOS 8 machine with the following command:
In my case, the IP address is 192.168.20.129. It will be different for you. So, make sure to replace it with yours from now on.
In order to access the TFTP server, you must have a TFTP client program installed on the computer from where you want to access it.
On CentOS 8/RHEL 8, you can install the TFTP client program with the following command:
On Ubuntu/Debian and other Ubuntu/Debian based Linux distributions, you can install the TFTP client program with the following command:
In order to upload files to your TFTP server or download files from your TFTP server, you have to navigate to the directory where the file/files you want to upload to the TFTP server is available, or where you want to store the downloaded file/files from the TFTP server.
Let’s say, you want to upload some file/files from the /etc directory and also download and store some file/files to the /etc directory. So, navigate to the /etc directory with the following command:
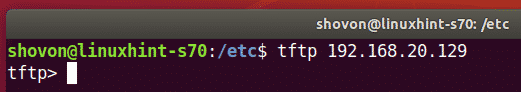
To connect to the TFTP server, run the following command:
You should be connected.
You can check the status of your connection with the following command:
You can enable verbose mode with the following command:
To upload a file fstab (let’s say), run the following command:
If you want to download and store file/files to your /etc directory, you will have to run the tftp client program with sudo privileges.
To download the hosts file and store it to the /etc directory, run the following command:
This is how you configure TFTP server on CentOS 8 and use it. Thanks for reading this article.