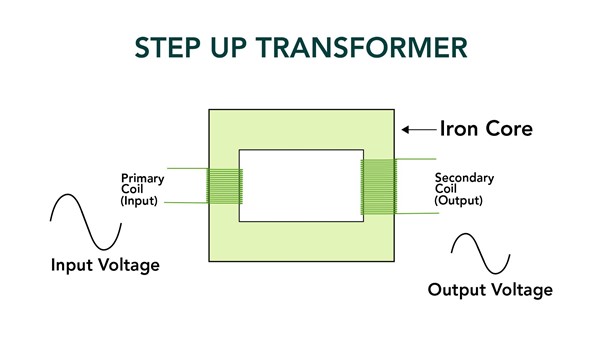
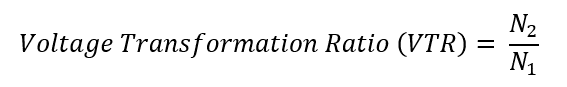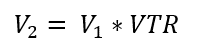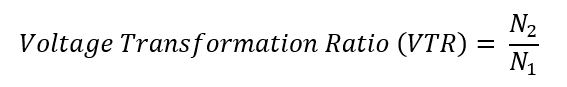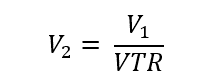What is a Step-Up Transformer?
An increase in voltage from the input (primary) side to the output (secondary) side is the goal of a step-up transformer. It is made up of two or more coils twisted around a laminated iron core. The coil is linked with the input side is the primary and the one linked with the output side is the secondary coil.
Working of a Step-Up Transformer
The iron core creates a magnetic field when an alternating current (AC) passes through the primary coil. A voltage or electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the secondary coil as a result of this magnetic field, by Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
The ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil (N1) to the number of turns in the secondary coil (N2) determines the voltage transformation ratio. Mathematically, this ratio is represented as:
The voltage output (V2) of a step-up transformer is higher than the voltage input (V1) because the secondary coil’s (N2) number of turns is greater than the primary coil’s (N1) number of turns.
Step-up transformers are widely used in power transmission systems to increase the voltage level for efficient long-distance transmission, reducing power losses along the way.
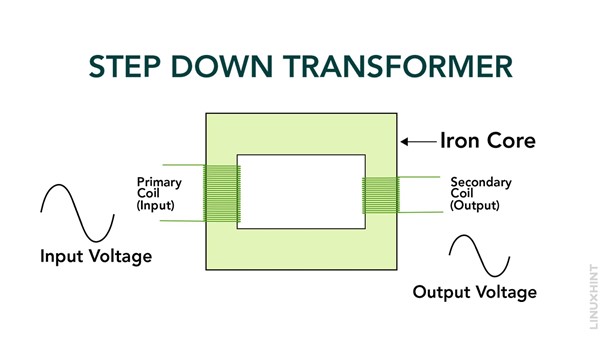
What is a Step-Down Transformer?
The voltage level from the input (primary) side to the output (secondary) side is reduced by a step-down transformer. It follows the same construction principle as a step-up transformer with a primary coil, secondary coil, and an iron core.
Working of a Step-Down Transformer
An alternating magnetic field generates in the iron core when an AC flows through the primary coil. This magnetic field induces an EMF or voltage in the secondary coil however, in a step-down transformer, the secondary coil’s (N2) amount of turns is less than the primary coil’s (N1) amount of turns.
The voltage transformation ratio (VTR) for a step-down transformer is calculated as:
According to the VTR equation, the voltage output (V2) is lower than the voltage input (V1) because the secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary coil.
Difference Between Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers
Here is a brief comparison between the two types of transformers that will help in better understanding the working of the two:
| Aspects | Step -Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Input voltage is lower than output voltage. | Input voltage is higher than output voltage. |
| Core Construction | Consists of laminated iron core with primary and secondary coils. | Consists of laminated iron core with primary and secondary coils. |
| Power relationship | Step-up transformers reduce the current and increase the voltage. | Step-down transformers decrease voltage and increase current. |
| Voltage Equation | V2 = V1 * VTR (VTR > 1) | V2 = V1 / VTR (VTR < 1) |
| Turns Ratio | The amount of turns in secondary coil is greater than the amount of turns in primary coil. | The amount of turns in secondary coil is less than amount of turns in primary coil. |
| Applications | Used for long-distance power transmission, where high voltage is required to minimize power losses. | Used in electrical appliances and devices to provide a safe and usable voltage level. |
Conclusion
Step-up and step-down transformers are essential components in electrical systems, facilitating voltage transformations for efficient power transmission and diverse applications. By utilizing electromagnetic induction, these transformers enable the transfer of electrical energy between circuits with varying voltage levels.