Prerequisites
The following set of programs must be present on your system to start using delete cascade:
- A Postgres database installed and functioning properly:
- Make sure the delete cascade keyword is embedded properly in a table:
How Postgres delete cascade works
The delete cascade operation is practiced deleting the records association in multiple tables. The delete cascade is a keyword that allows DELETE statements to perform deletion if any dependencies occur are present. The delete cascade is embedded as a property of the column during the insert operation. We have provided a sample of delete cascade keyword that how it is used:
Let’s say, we have used employee_id as a foreign key. When defining the employee_id in the child table, the delete cascade is set to ON as shown below:
employee_id INTEGER REFERENCES employees (id) ON delete cascade
The id is being fetched from the employees table and now, if the Postgres DELETE operation is applied on the parent table, the associated data will be deleted from respective child tables too.
How to use Postgres delete cascade
This section guides you to apply delete cascade on a Postgres database. The following steps will create parent and child tables and then apply delete cascade on them. So, let’s start:
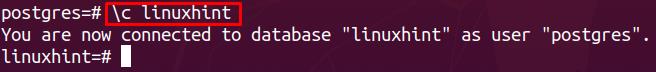
Step1: Connect to database and create tables
The following command leads us to connect with the Postgres database named linuxhint.
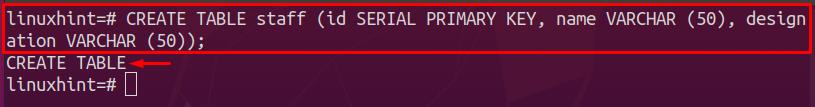
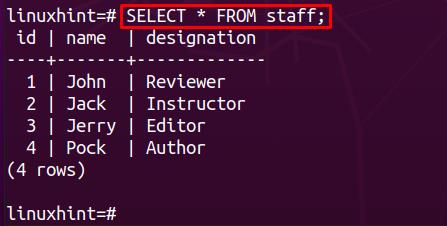
Once the database is connected successfully, we have created a table named staff and the following lines of code are executed to create several columns in the staff table. The staff table will act as a parent table here:
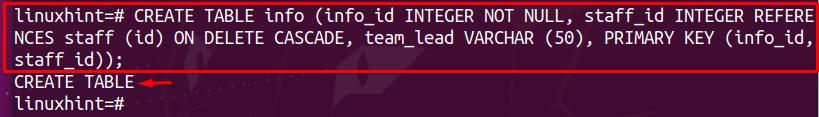
Now, we have created another table named info by using the command stated below. Among the tables, the info table is referred to as the child, whereas the staff table is known as the parent. Here the key addition would be the delete cascade mode set to ON. The delete cascade is used in the foreign key column named (staff_id) as this column acts as a primary key in the parent table.
Step 2: Insert some data into tables
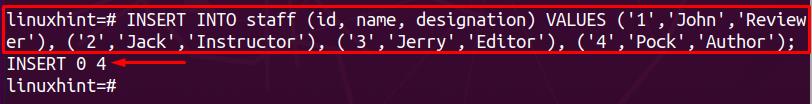
Before digging into the deletion process, insert some data into the tables. So, we have executed the following code that inserts data into the staff table.
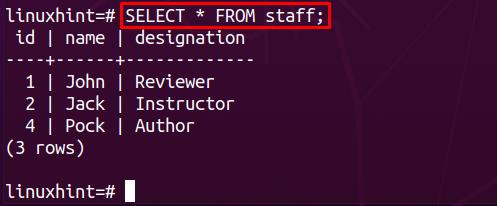
Let’s have a look at the content of the staff table by using the command provided below:
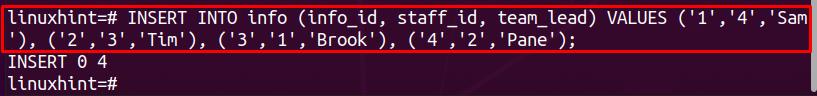
Now, add some content to the child table. In our case, the child table is named info and we have executed the following lines of Postgres statements to insert data into the info table:
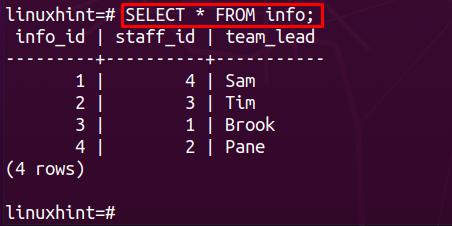
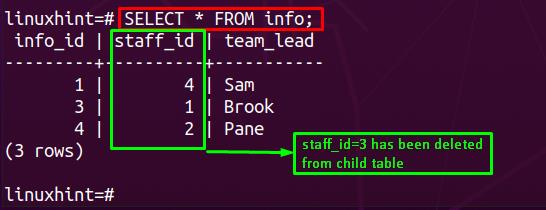
After successful insertion, use the SELECT statement to get the content of info table:
Note: If you do have the tables already and the delete cascade is set to ON inside a child table then you may skip the first 2 steps.
Step 3: Apply DELETE CASCADE operation
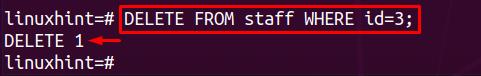
Applying the DELETE operation on the staff table’s id field (primary key) will also delete all its instances from the info table. The following command assisted us in this regard:
Once the deletion is performed successfully, verify the delete cascade is applied or not. To do so, get the content from both parent and child tables:
On retrieving the data from the staff table, it is observed that all the data of id=3 is deleted:
After that, you must apply the SELECT statement on the child table(In our case, it is info). Once applied, you would observe that the field associated with staff_id=3 is deleted from the child table.
Conclusion
Postgres supports all the operations that can be carried out to manipulate the data inside a database. The delete cascade keyword allows you to delete the data associated with any other table. Generally, the DELETE statement will not allow you to do so. This descriptive post provides the working and usage of Postgres delete cascade operation. You would have learned to use the delete cascade operation in a child table, and when you apply the DELETE statement on the parent table, it will also delete all its instances from the child table.