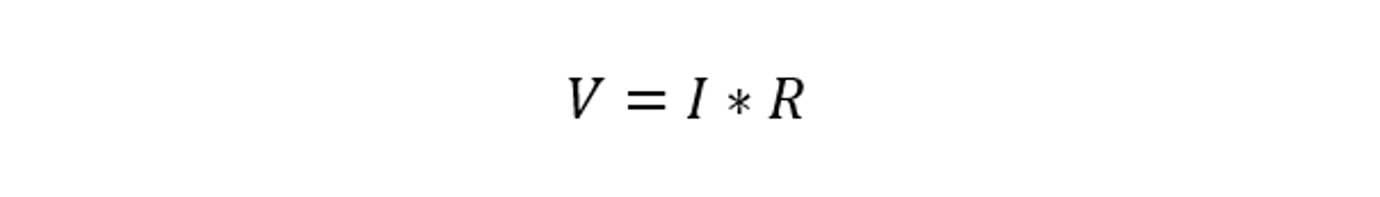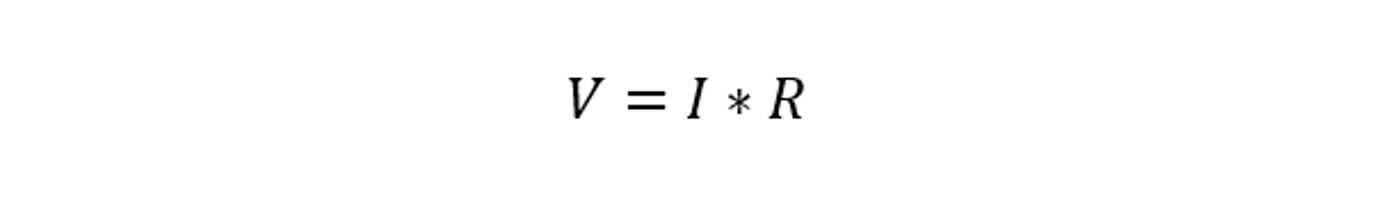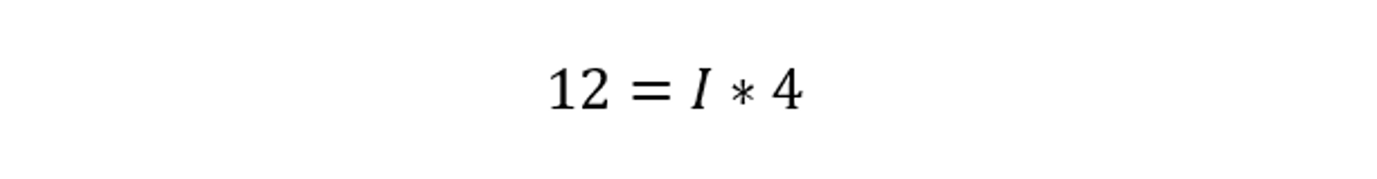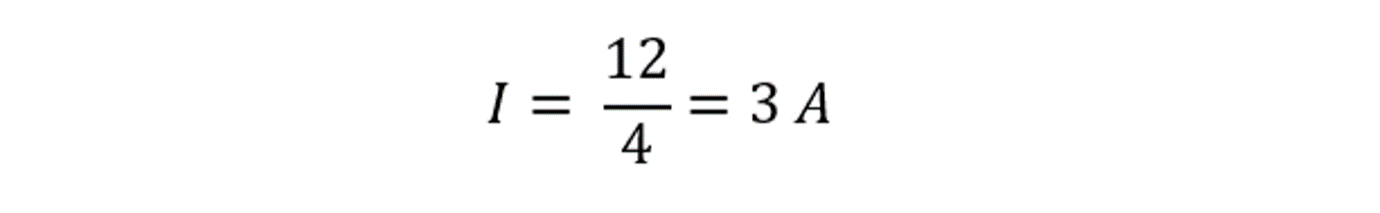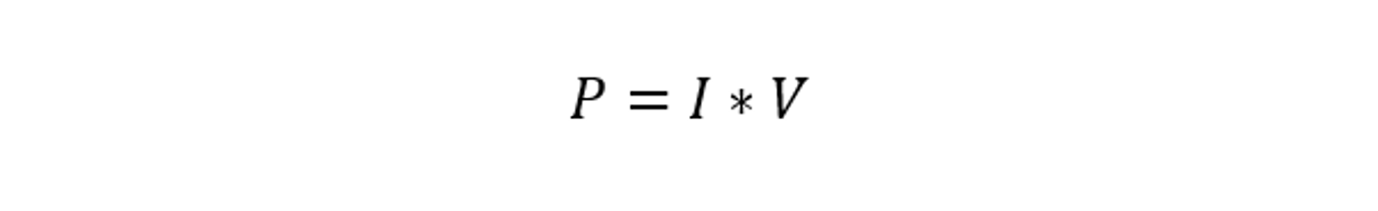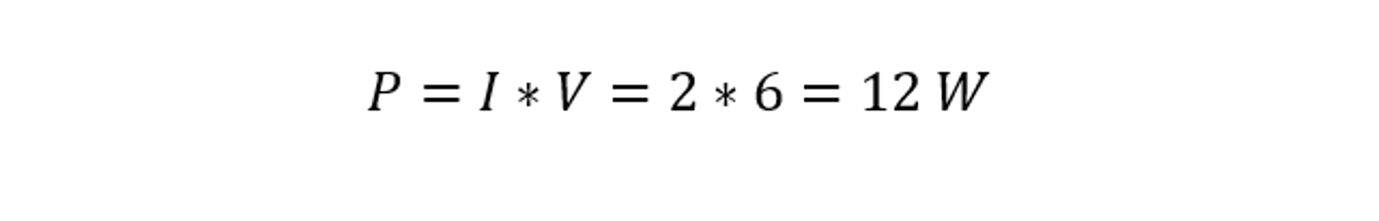Ohm’s Law holds significant importance in electrical engineering as a fundamental concept, providing valuable insights into the behavior of electrical circuits. By comprehending Ohm’s Law, you can unlock the ability to calculate voltage, current, resistance, and power in a circuit. In this tutorial, we will delve into the principles of Ohm’s Law and explore how power is related to electrical circuits.
Ohm’s Law
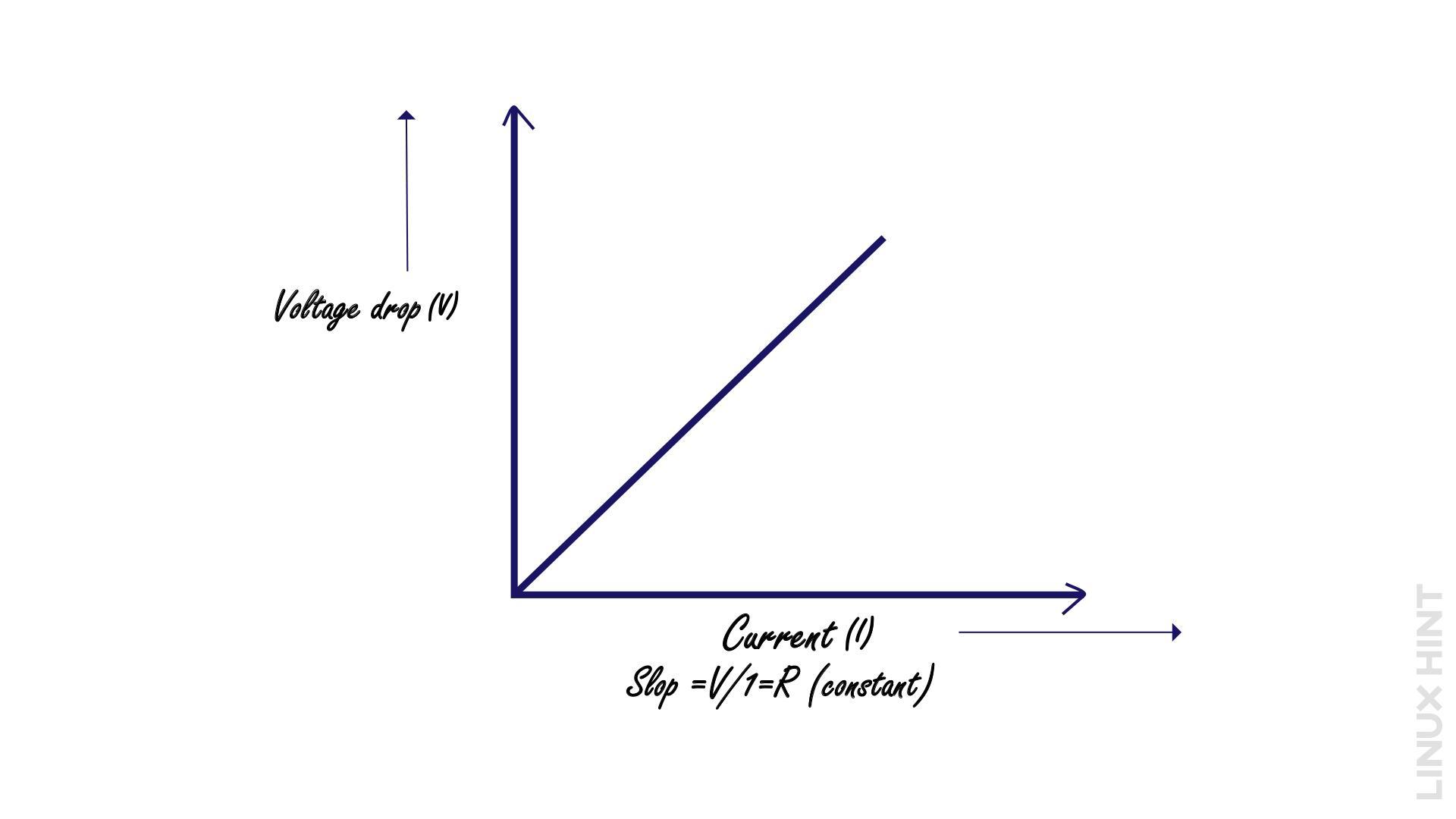
According to Ohm’s law, a conductor connecting two points will have a current flow that is directly correlated to the voltage around those points and inversely correlated to the conductor’s resistance. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
In this equation, V represents the voltage measured in volts, I denotes the current measured in amperes, and R signifies the resistance measured in ohms. This mathematical relationship highlights the interconnection between voltage, current, and resistance. According to Ohm’s law, an increase in voltage across a circuit results in a corresponding increase in current, given that the resistance remains constant. Similarly, if the resistance increases, the current decreases for a given voltage.
Calculating Voltage, Current, and Resistance
Consider an example to demonstrate the practical application of Ohm’s law. A circuit with a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms and by utilizing Ohm’s law, we can calculate the current flowing through the circuit:
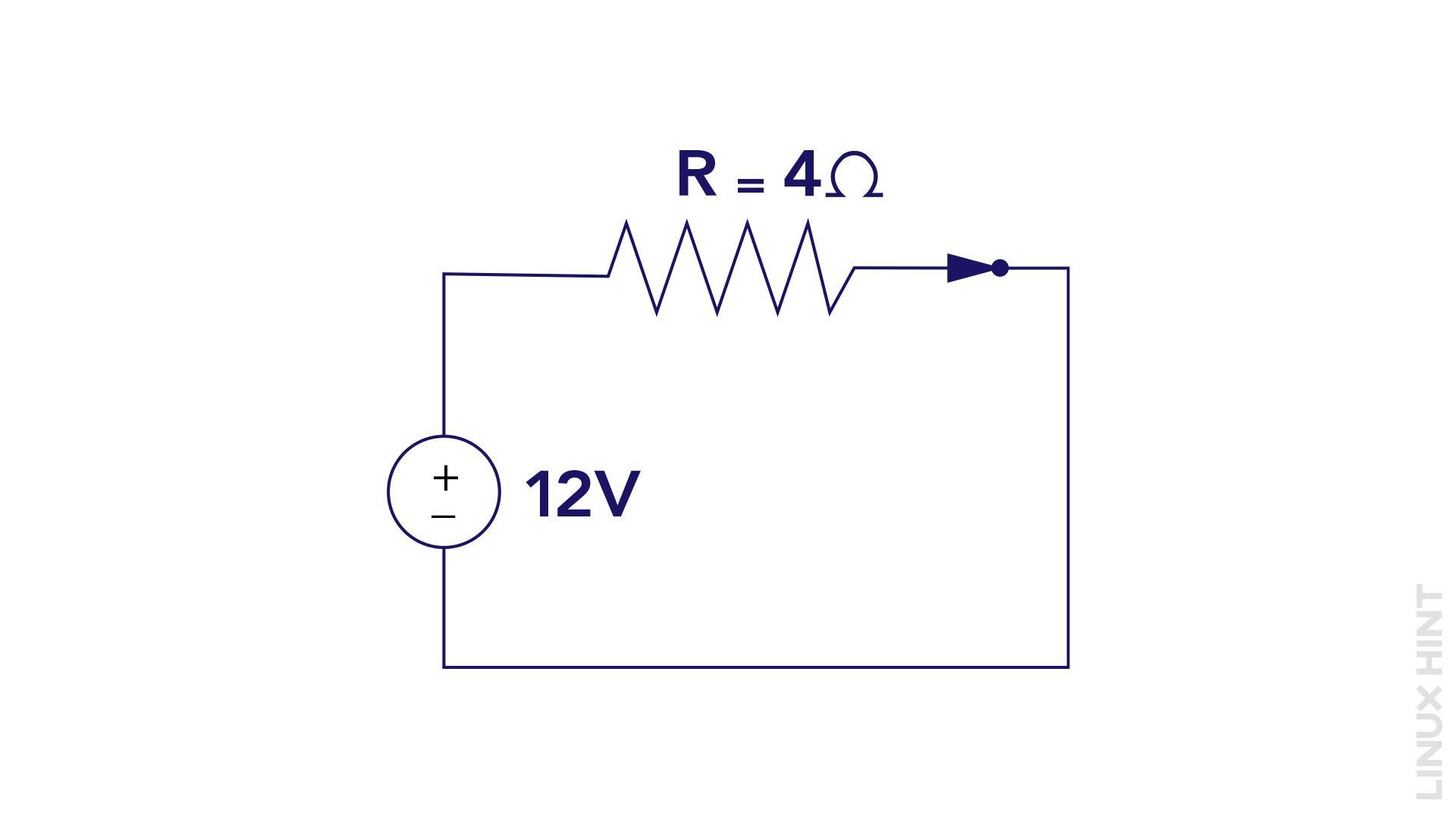
To find the value of current (I), we divide both sides of the equation by 4:
Hence, in this example, the current flowing through the circuit is 3 amperes.
Power in Electrical Circuits
Power holds significant importance in electrical circuits, as it signifies the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or transferred, playing a crucial role in understanding circuit behavior. The power (P) in an electrical circuit can be calculated using the following equation:
Here, P is the power that is measured in watts:
The equation demonstrates that power is the product of current and voltage. This implies that the power consumed by a device or component in a circuit is directly proportional to both the current flowing through it and the voltage across it.
Calculating Power in Electrical Circuits
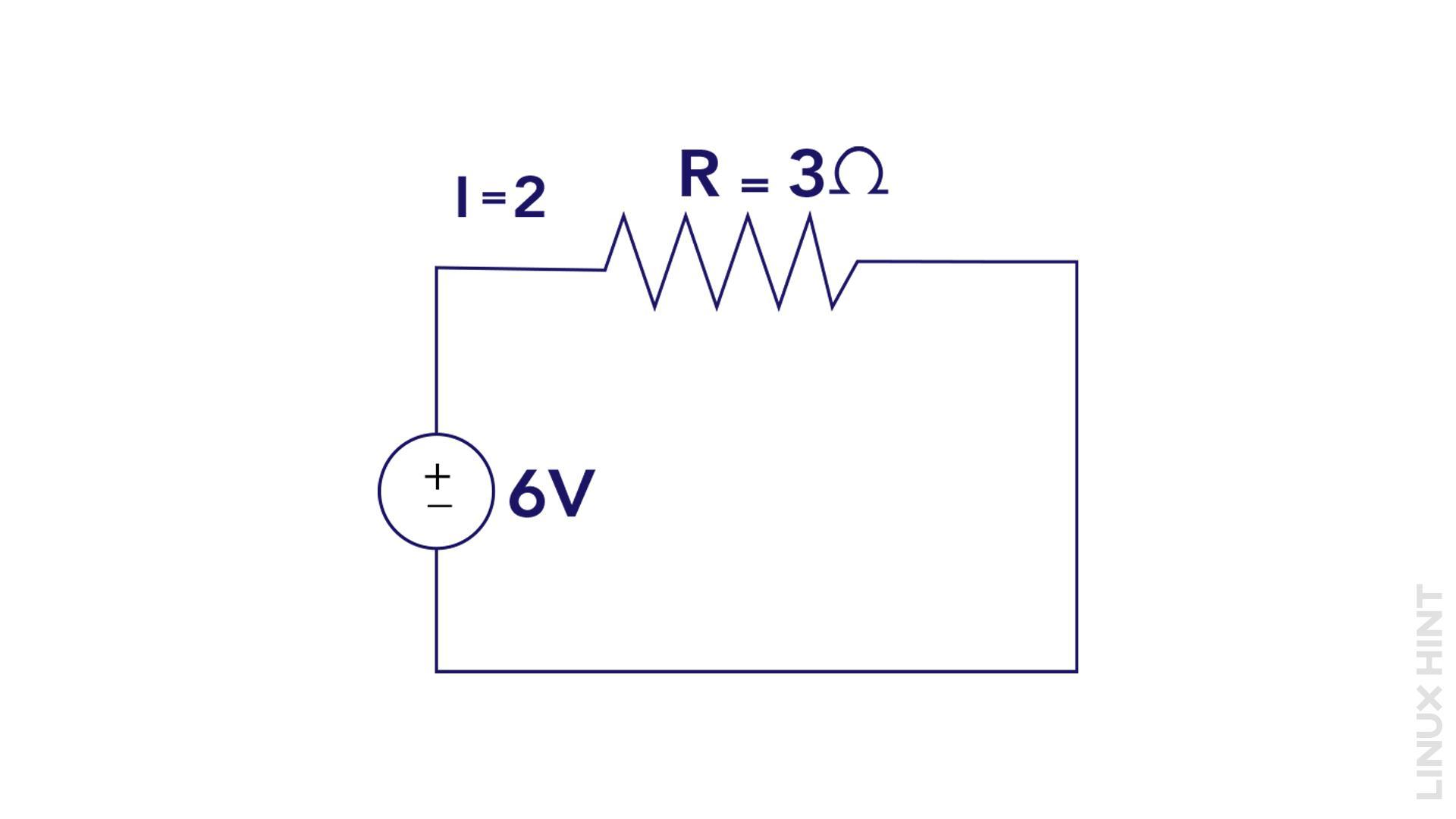
Now, to calculate the power consumed by a device in a circuit. Suppose we have a circuit with a current of 2 amperes and a voltage of 6 volts, and we want to determine the power then:
Therefore, the power consumed by the device in this example is 12 watts.
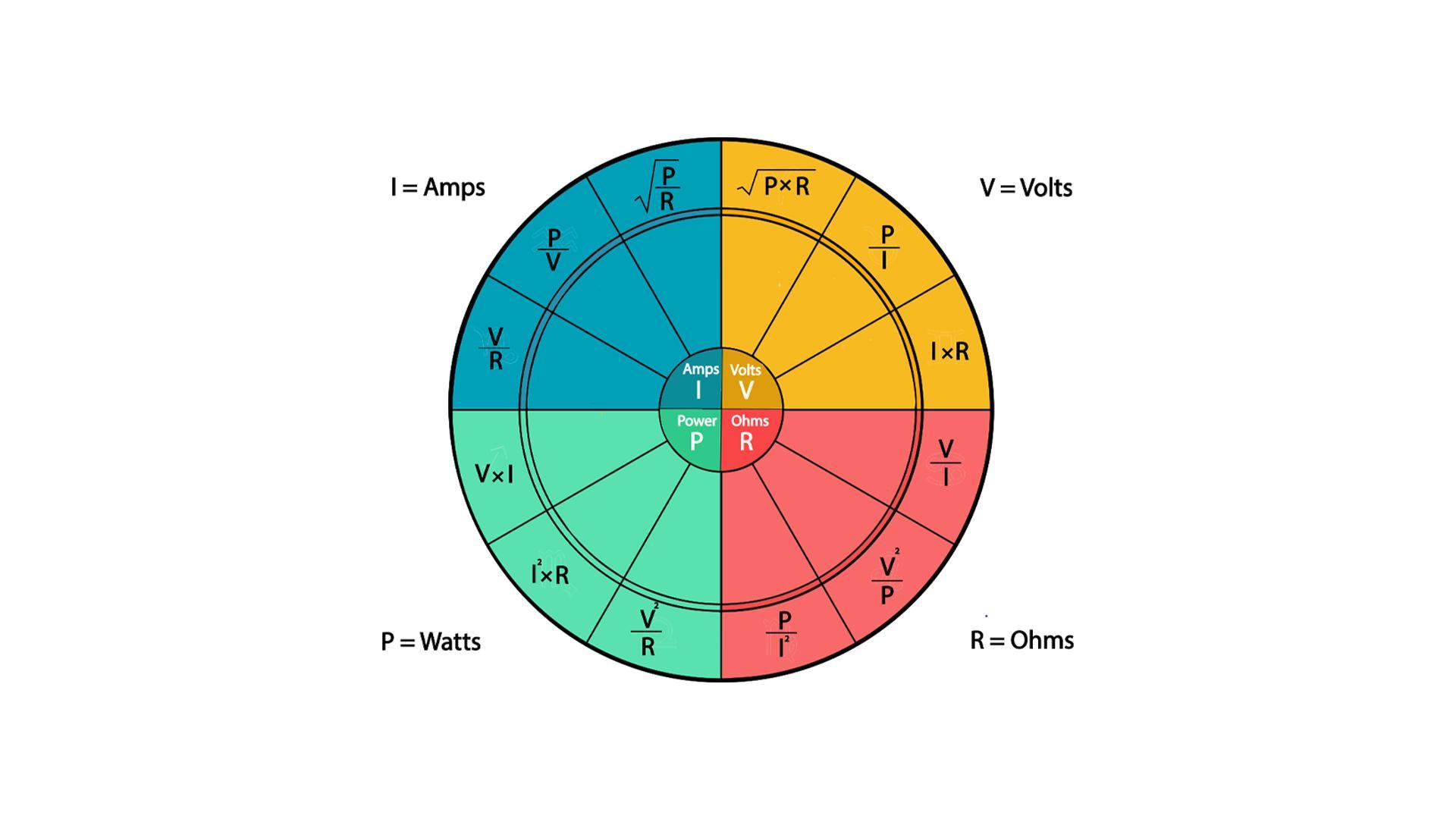
Ohm’s Law Formula Pie Chart
Below is the pie chart that displays all the formulas for calculating the current, resistance, voltage, and power of any circuit:
Conclusion
Ohm’s Law provides a fundamental relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, enabling accurate calculations and predictions in electrical circuits. Additionally, power calculations allow us to evaluate the energy consumption and efficiency of devices and components within a circuit.