Fiddling with NVIDIA drivers and CUDA versions on your computer may cause problems like the NVIDIA drivers not working or leaving you with a black/blue screen of death. It’s always a good idea to leave your system as it is and make changes in an isolated environment like the Docker containers. This keeps your main computer clean (of unnecessary development tools).
In this article, we will show you how to install the Docker CE and NVIDIA docker on Debian 11 so that you can access the NVIDIA GPU of your computer from the Docker containers and run the CUDA programs on your NVIDIA GPU.
Table of Contents:
- Checking If the Official NVIDIA GPU Drivers Are Installed on Debian 11
- Installing the Docker CE Dependencies on Debian 11
- Installing the Docker CE GPG Keys on Debian 11
- Installing the Docker CE Repository on Debian 11
- Installing the Docker CE on Debian 11
- Adding the Debian 11 Login User to the Docker Group
- Checking If the Docker CE Is Installed Correctly on Debian 11
- Installing the NVIDIA Container Toolkit GPG Keys on Debian 11
- Installing the NVIDIA Container Toolkit Repository on Debian 11
- Installing the NVIDIA-Docker Drivers on Debian 11
- Checking If the NVIDIA GPU Is Accessible from the Docker Containers on Debian 11
- Conclusion
- References
Checking If the Official NVIDIA GPU Drivers Are Installed on Debian 11
Before you get started, run the following command to verify that you have an NVIDIA GPU installed on your computer:
In this case, we have the NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti GPU installed on our computer. You will most likely have a different NVIDIA GPU installed on your computer.
Also, make sure that you have the official NVIDIA drivers installed on your Debian 11 operating system with the following command:
If the official NVIDIA drivers are installed on your Debian 11 operating system, you will see the following outputs:
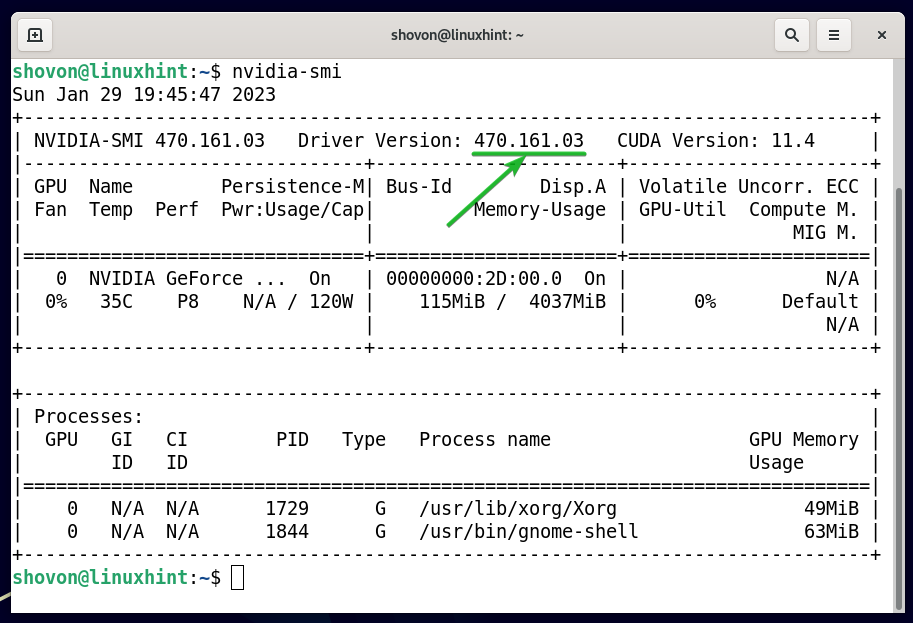
Also, check if the official NVIDIA GPU drivers are working with the following command:
If the official NVIDIA GPU drivers are working, you will see the following outputs. As you can see, we have the official NVIDIA GPU Driver version 470.161.03 installed on our Debian 11 machine:
If you don’t have the official NVIDIA GPU drivers installed on your Debian 11 machine and you need any assistance with that, check the article on How to Install the NVIDIA Drivers on Debian 11.
Installing the Docker CE Dependencies on Debian 11
Before you can install the Docker CE on Debian 11, you need to install the required Docker CE dependency packages on Debian 11.
First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
The APT package repository cache should be updated.
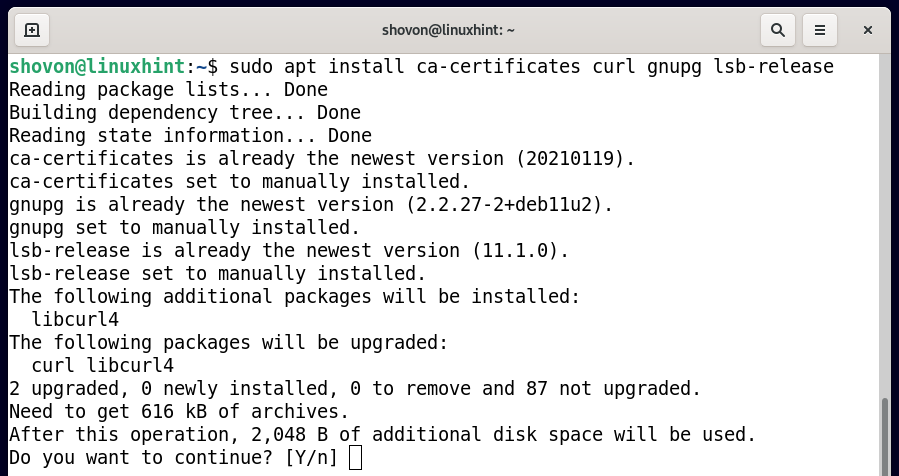
To install the required dependency packages of Docker CE, run the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
The required Docker CE dependency packages should be installed.
Installing the Docker CE GPG Keys on Debian 11
In this section, we will show you how to install the GPG key of the Docker CE package repository on Debian 11.
First, create a new /etc/apt/keyrings folder with the following command:
To install the GPG key of the Docker CE package repository on Debian 11, run the following command:
Installing the Docker CE Repository on Debian 11
To install the Docker CE package repository on Debian 11, run the following command:
Update the APT package repository cache for the changes to take effect.
Installing the Docker CE on Debian 11
To install the latest version of the Docker CE on Debian 11, run the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
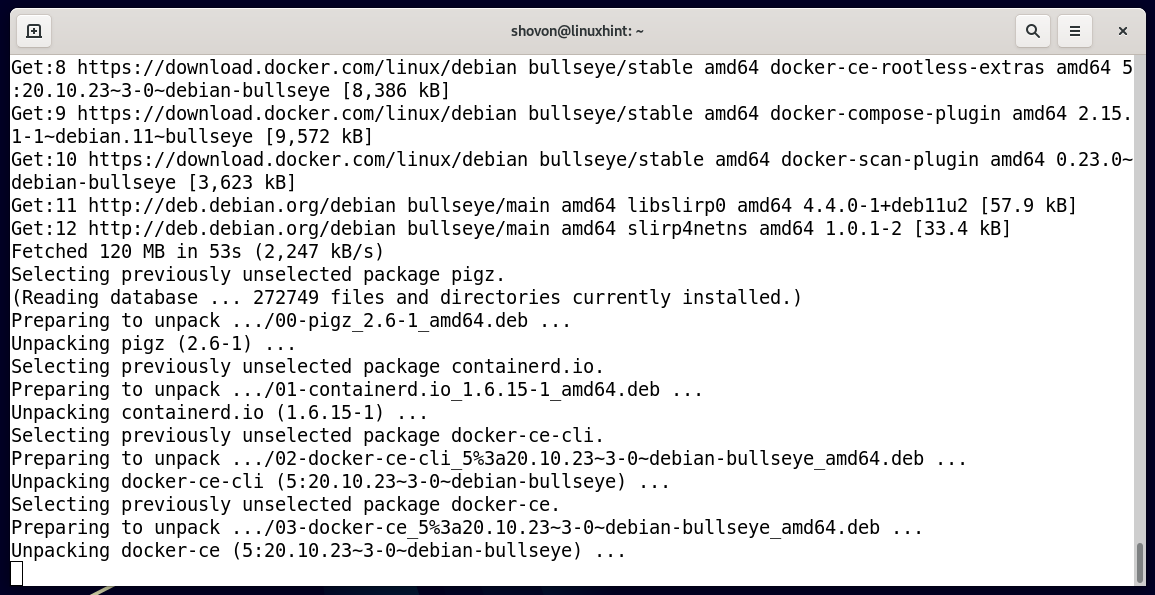
The Docker CE and the required dependency packages are being downloaded. It takes a while to complete.
The Docker CE and the required dependency packages are being installed. It takes a while to complete.
The Docker CE and the required dependency packages should be installed at this point.
Adding the Debian 11 Login User to the Docker Group
To create the Docker containers and manage them without using sudo or without logging in as root user, you have to add your login user to the Docker group.
To add the login user of your Debian 11 to the Docker group, run the following command:
For the changes to take effect, restart your computer with the following command:
Checking If the Docker CE Is Installed Correctly on Debian 11
Once your computer starts, run the following command to verify that you can access the Docker without superuser privileges:
If everything works, you should see the following outputs.
As you can see, we are running the Docker version 20.10.23 – the latest version of Docker CE at the time of this writing.
Installing the NVIDIA Container Toolkit GPG Keys on Debian 11
In this section, we will show you how to install the GPG key of the NVIDIA Container Toolkit package repository on Debian 11.
To install the GPG key of the NVIDIA Container Toolkit package repository on Debian 11, run the following command:
Installing the NVIDIA Container Toolkit Repository on Debian 11
In this section, we will show you how to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit package repository on Debian 11.
First, create a new APT source file nvidia-container-toolkit.list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory as follows:
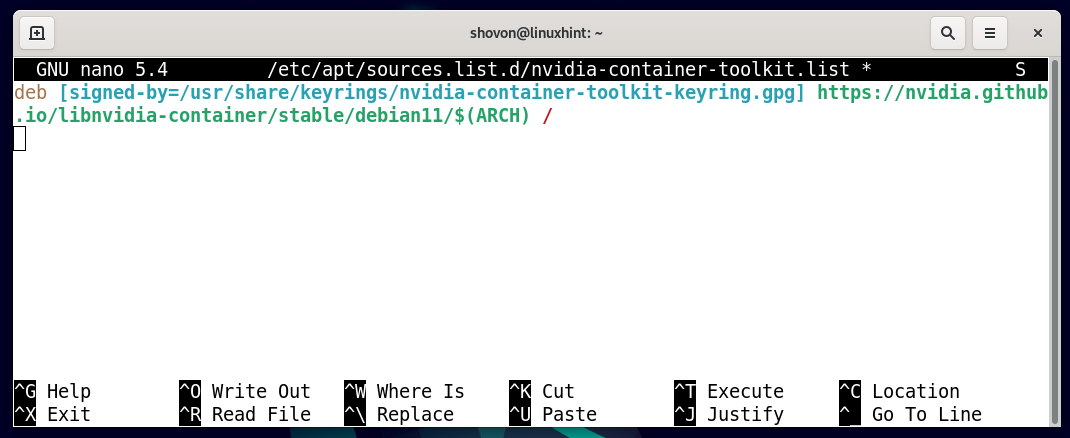
In the nvidia-container-toolkit.list file, add the following line and press <Ctrl> + X followed by Y and <Enter> to save the file:
For the changes to take effect, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
Installing the NVIDIA-Docker Drivers on Debian 11
To install the NVIDIA Docker drivers on Debian 11, run the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
The NVIDIA docker drivers should be installed.
For the changes to take effect, restart your computer with the following command:
Checking If NVIDIA GPU Is Accessible from the Docker Containers on Debian 11
In this section, we will show you how to create an NVIDIA CUDA Docker container and verify that the container can access the NVIDIA GPU from your computer.
To create an NVIDIA CUDA 12 Docker container based on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS and run the nvidia-smi command in it once it’s created to verify whether it can access the NVIDIA GPU from your computer, run the following command:
Docker is pulling the nvidia/cuda:12.0.0-base-ubuntu20.04 image from the Docker Hub. It takes a while to complete.
Once the NVIDIA CUDA docker image is pulled and a container is created, the nvidia-smi command runs on it and prints the output on the console as you can see in the following screenshot:
The Docker container uses the NVIDIA GPU driver 525.78.01[1] and the CUDA version 12.0[2]. If you see some similar outputs, the Docker container can access the NVIDIA GPU of your computer.
If you need to use the older versions of CUDA, check the nvidia/cuda image at the Docker Hub.
Conclusion
We showed you how to install the Docker CE package repository on Debian 11. We also showed you how to install the latest version of the Docker CE on Debian 11. We showed you how to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit package repository on Debian 11 as well as how to install the NVIDIA Docker driver on Debian 11. Finally, we showed you how to access the NVIDIA GPU of your computer from a Docker container.