In this guide, we will illustrate the LINQ Aggregate() functions in C# and also discuss its different methods and implement it in a single program.
What are LINQ Aggregate() Functions in C#?
In C#, LINQ Aggregate() functions are a collection of methods that enable users to carry out calculations in multiple items while returning a single result. The syntax of the LINQ Aggregate() function in C# is provided below:
In the above syntax, collection refers to the series of data that is being processed. While function is a parameter passed to the “Aggregate()” function that refers to the mathematical operation being done. The outcome will be saved into the “result” variable.
Usage of LINQ Aggregate Methods in C#
LINQ “Aggregate()” functions perform mathematical operations. As follows:
Aggregate() Method
The “Aggregation()” function is applied to all the elements of the source sequence and calculates a collection of values that considers the return value of each function call. The syntax of the LINQ Aggregate() function is mentioned below:
Here, the “Aggregate()” function used lambda expression (n1, n2) => n1 * n2 where (n1, n2) are the parameters and n1*n2 is the operation to be done on the parameters.
Average() Method
It computes the collection’s average for the numeric elements. The syntax for LINQ aggregate function Average() is stated below:
Count() Method
It counts all the number of elements in the source sequence, just those that meet a predicate function. As follows:
In the above syntax, an array is the collection of items and the value of the total number of elements of the array will be stored in the result variable.
Max() Method
It determines the collection’s largest value from the array. The general syntax for LINQ aggregate function “Max()” is described below:
In the above syntax, the array is the combination of elements, and the “Max()” method will retrieve the maximum value among the elements of the array and then store it in the “my_result” variable.
Min() Method
It is used to retrieve the collection of the smallest values:
Sum() Method
The “Sum()” method is used to find the sum of all the given values of the array:
Example: Implementation of LINQ Aggregate Functions
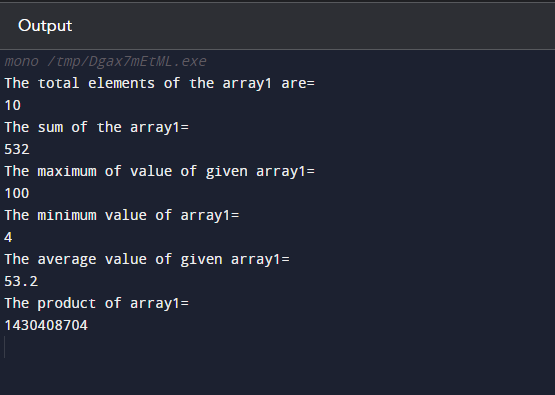
The LINQ aggregate functions are used in the below-provided code. Here, we are calculating the total number of elements, sum, minimum value, maximum value, product(with the help of aggregate function), and the average of the provided values of an array:
using System.Linq;
public class Sum {
static public void Main() //main method
{
int[] array1 = {5, 10, 50, 68, 90, 100, 99, 4, 57, 49};
// finding total elements of the array1
Console.WriteLine("The total elements of the array1 are= ");
int result6 = array1.Count();
Console.WriteLine("\n"+result6);
Console.WriteLine("The sum of the array1= ");
// Finding sum of the given array
int result1 = array1.Sum();
Console.WriteLine("\n"+result1);
Console.WriteLine("The maximum of value of given array1=");
// Finding the maximum value of the given array1
int result2 = array1.Max();
Console.WriteLine("\n"+result2);
// Finding the minimum value of the given array1
Console.WriteLine("The minimum value of array1= ");
int result3 = array1.Min();
Console.WriteLine(result3);
// Finding the average of all the values of the given array1
Console.WriteLine("The average value of given array1= ");
double result4 = array1.Average();
Console.WriteLine(result4);
// Finding product of the given array1 using aggregate function
Console.WriteLine("The product of array1= ");
double result5 = array1.Aggregate((n1,n2 ) => n1*n2);
Console.WriteLine(result5);
}
}
Output
That’s all! We have described the LINQ aggregate functions in C#.
Conclusion
In C#, LINQ aggregate functions are used for performing mathematical operations on data sequences. Developers may acquire important insights into their data by using different techniques, such as “Sum()”, “Min()”, “Max()”, “Average()”, and “Count()”. In this tutorial, we have illustrated the LINQ aggregate functions in C#.