Although this can be useful when working with a few commands, it can quickly become tiresome and challenging to manage when working with multiple commands or copies of the same Jenkins pipeline.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to eliminate such a problem by adding our commands in a shell script, whether a PowerShell script or a Bash script. We will then discuss how we can tell Jenkins to load the shell script and execute the commands that are defined in the file.
Requirements
For this tutorial, we use the following:
- A Jenkins controller that is running on Windows.
- A Jenkins Agent labeled “debian” that is running on Debian 11.
Step 1: Prepare Your Shell Script
The first step is to ensure that you have your shell script ready on the Jenkins agent. Next, we create a simple shell script for this tutorial on the Debian 11 agent.
Login into your Jenkins agent:
Once logged in, we need to create a shell script that we wish to use in our Jenkins pipeline.
$ touch myscript.sh
Edit the shell script and add the function of your Shell script. For this tutorial, we get the list of files and directories using awk.
We can then add the script as shown in the following:
ls -la | awk '{print $9}'
The previous script is a simple script that calls the ls -la command and passes the output to awk. AWK then prints the value at the specified position.
The next step is to ensure that the shell has execute permissions. We can do this by running the following chmod command:
Before running the script on the Jenkins pipeline, you can execute the script on the local machine to ensure that the script is working as expected.
Step 2: Setting Up a Jenkins Job
Once we are done, let us return to the Jenkins controller and configure a job that uses the defined script.
Select “New Item” on the Jenkins dashboard to create a new job. Give the job a name and select the job type as “Pipeline”.
Navigate to the pipeline section and add a pipeline script as shown in the following:
agent {label 'debian'}
stages {
stage('Run Script') {
steps {
sh '/home/debian/myscript.sh'
}
}
}
}
Click on “Save” to apply the script and select “Build Now” on the left pane to allow Jenkins to build the job.
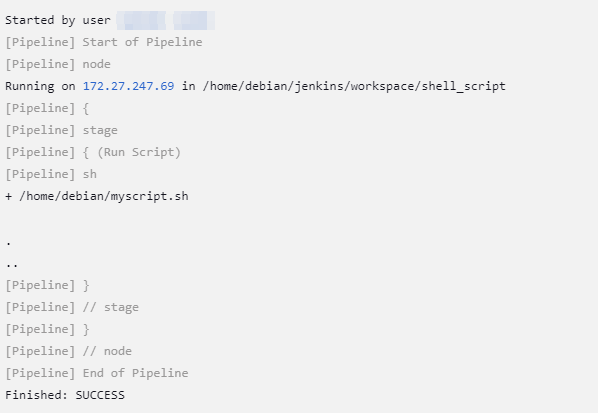
On the build number, select the console output to see the build process for the invoked job.
Conclusion
You have now successfully learned how to invoke a shell script from a Jenkins pipeline in a few steps.