What is a Sensor?
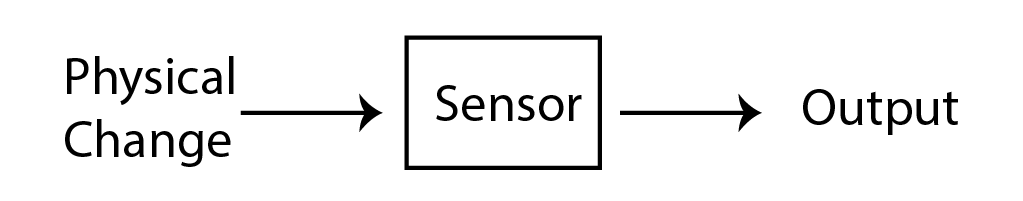
A sensor is an input device that senses physical quantities and gives output in the form of electrical signals. Sensors can sense different types of physical quantities such as light, temperature, pressure, humidity, distance, speed, and sound. These quantities are converted to electrical signals when passed through the system or controller and are shown as output-on-output devices or actuators.
Types of Sensors
1. Analog Sensors
The analog sensor as the name suggests gives analog outputs, which means that output is varying with time and does not have a discrete value. It gives the output signal that is proportional to the input signal.
For example, a temperature sensor, either a thermometer or thermocouple, is an analog sensor. When the temperature of the object changes, the voltage across the diode changes by 10mV/°C. Therefore, as the temperature changes, the output voltage also changes proportionally.
2. Digital Sensors
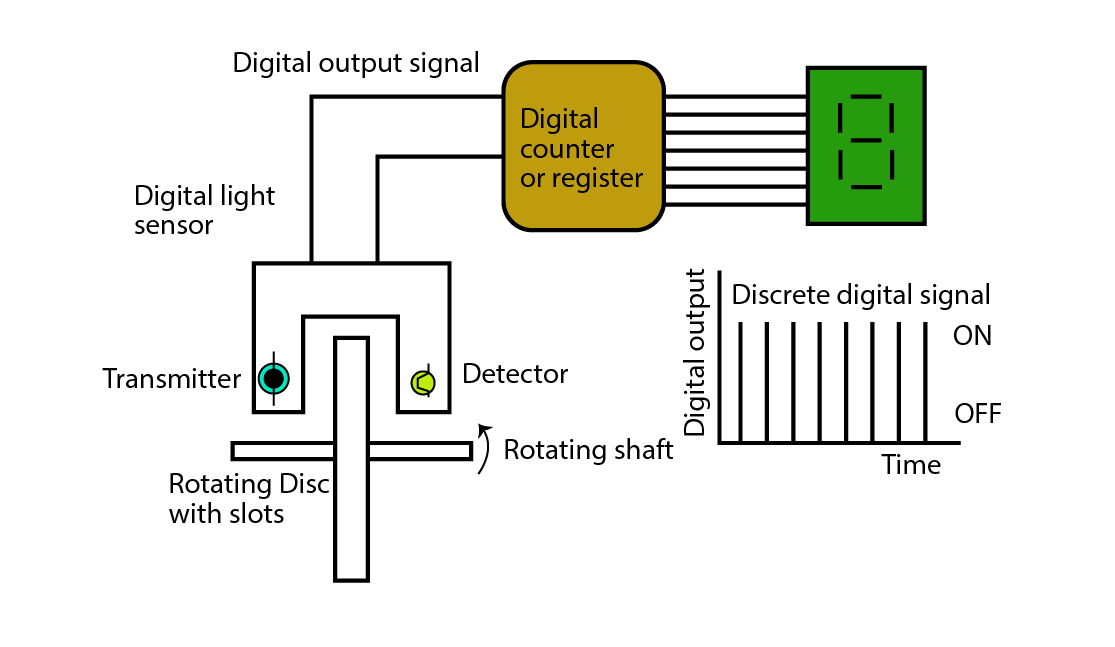
A digital sensor, unlike an analog signal, gives a discrete value of output, usually Logic 0 or 1, or we can say two states, either ON or OFF. For example, the Light sensor gives output 0 or 1, according to the absence or presence of light, respectively. Given below is the light sensor, which has transparent slots on the rotating shaft. The digital light sensor sends signals according to the availability of light.
Generally, the accuracy of digital sensors is higher than that of analog sensors.
3. Active Sensors
Active sensors are those sensors that require a power supply or energy to work. They need to be energized through an excitation signal in order to give output. Active sensors change their properties according to the external power they have received. For example, if the external voltage applied increases from 5V to 20V, then the current through the sensor may also increase correspondingly. A suitable example of an active sensor is a strain gauge which works according to the pressure applied to it.
4. Passive Sensors
Unlike active sensors, passive sensors do not need external power sources to excite them. They generate output signals themselves, such as the temperature sensor generating voltage by itself when it senses heat difference. Passive sensors can also be called direct sensors due to this property.
Commonly Used Sensors
Light Sensing
Light Dependent Resistors (LDR), photodiodes, and solar cells are some light sensors.
Temperature Sensing
Thermistors, thermocouples, thermostats, and Temperature sensing ICs are commonly used temperature sensors.
Position Sensing
For position sensing, potentiometer and proximity sensors are the most commonly used sensors.
Pressure Sensing
Strain gauges and pressure switches are commonly used examples.
Sound Sensing
A microphone is the major input device or sound sensor that is mostly used.
Speed Sensing
Techo-Generator and Doppler Effect Sensors are used for speed sensing.
What is a Transducer?
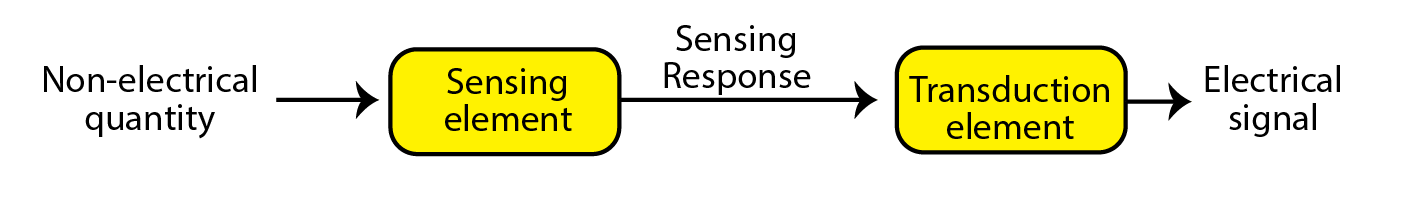
A transducer is an electronic element or device which is utilized for interconversion of forms of energy. Transducer is a collective term for sensors and actuators. Sensors work as input devices, whereas actuators work as output devices. It can also convert physical quantities to electrical quantities. The process through which this conversion takes place is called transduction. The input devices sense physical quantity and send a signal to the controller or processing device, which performs an operation on the signal, and the output is displayed on the actuator. Transducers can interconvert electrical, mechanical, light, and electromagnetic energy.
Commonly Used Transducers
Light Sensing
The output of light sensors is displayed through Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), Monitor displays and Fiber Optics.
Temperature Sensing
Thermostats and thermocouples are used to convert electrical energy into heat energy and give output through Heaters and Fans
Position Sensing
After sensing position through potentiometers or proximity sensors, panel meters are used to display output and motors convert electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Pressure Sensing
Lifts and Jacks perform lifting operations after sensing through pressure sensors.
Sound Sensing
Electrical Signals from the microphone are converted to sound energy through the Loudspeaker. A bell and Buzzer are also output devices for sound.
Speed Sensing
Brakes are applied when speed exceeds the limit that is sensed through speed sensors.
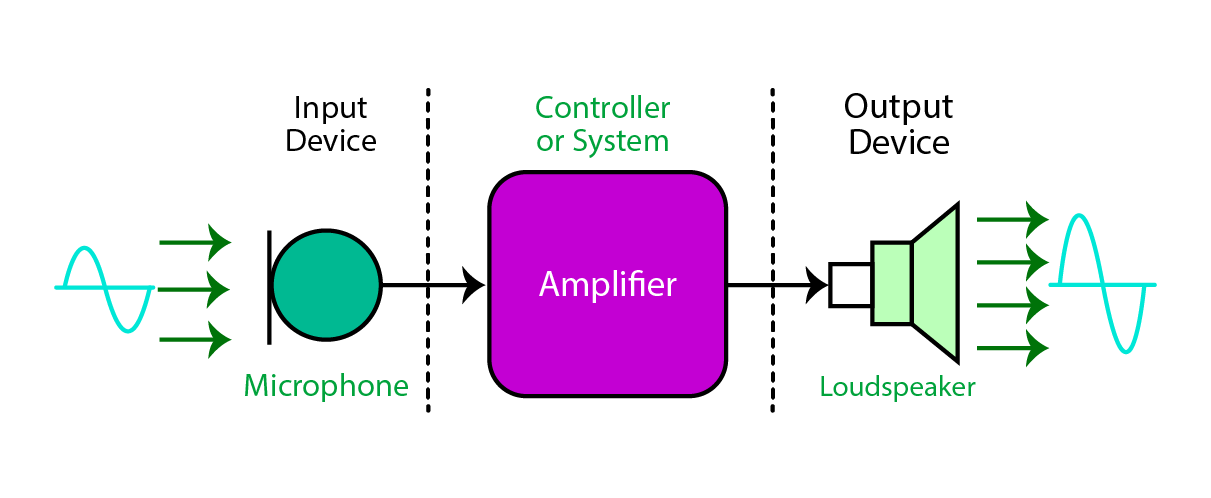
A Simple System of Transducers
The above diagram shows a simple system where an input device or sensor gives a signal to a controller or system that converts energy to the required form, and then it is transmitted through an actuator or output device.
Distinguishing Features of Sensors and Transducers
| Transducer | Sensor |
| They perform interconversion of energy. | They sense physical changes. |
| Sensors and actuators combine to form transducers | Sensors are a part of transducers |
| It is slightly more complicated than sensors | It is a simple device |
| It may work by giving feedback to input | It does not give feedback. |
Conclusion
Sensors and transducers are the most important part of modern-day electronics. Without them, electronic devices cannot be made. Sensors are constituents of transducers; however, both are incomplete without each other. Input devices and output devices are always dependent on each other to perform the whole function.