In C# we use “Int32” which is the type that the “.NET framework” has provided. It is primitive in nature and represents the 32-bit signed integer. Its minimum range is “-2,147,483,648” and the maximum range of “Int32” is “+2,147,483,648”. These minimum and maximum ranges are constant. We use “Int32” because it provides different methods which allow us to perform different mathematical operations on it.
The “Int32.MaxValue” field in C# will be covered in this article with examples.
Int32.MaxValue Field in C# with Examples
This field represents the largest value of “Int32” which is always “2,147,483,648” and we cannot change it. The syntax of the “Int32.MaxValue” field is:
Here is a simple program that shows the value of this field:
public class Int32_example
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine ("The maximum value of Int32 is: "+Int32.MaxValue);
}
}
In the above program:
-
- We use the “System” namespace as the “Int32” is included in the “System” namespace.
- Then, we declare a public class “Int32_example”.
- Inside the “Int32_example” class we have a static “Main()” method.
- Finally, inside the “Main()” method we have shown the value of the “Int32.MaxValue” field by calling it.
Output
The above-given output shows the maximum value.
Now, let’s modify the code to see how we can use the “Int32.MaxValue” field:
public class Int32_example
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
long[] a = { 123, -123, 1234567, 7162539988766655355 };
Console.WriteLine ("The maximum value of Int32 is: "+Int32.MaxValue);
Console.WriteLine ("The minimum value of Int32 is: "+Int32.MinValue);
foreach (long n in a)
{
if (n >= Int32.MinValue && n <= Int32.MaxValue)
{
Console.WriteLine($"The number {n} can be converted to Int32. The number after conversion is: "+Convert.ToInt32(n));
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"The number {n} can not be converted to Int32.");
}
}
}
}
According to the above-stated code:
-
- We use the “System” namespace and declare a class “Int32_example”.
- Inside the “Main()” method of this class, we have declared an array “a” of type “long” that contains “{ 123, -123, 1234567, 7162539988766655355 }”.
- To display the maximum and minimum range, we first printed the maximum and minimum values of the “Int32.MaxValue” field.
- Then, we use a “foreach” loop to check whether each element of this array “a” lies between this range or not.
- If an element of array “a” lies in this range then it will be converted to “Int32” and printed on the screen.
- Otherwise, if the element does not lie in the range of “Int32” the message will be displayed that “The number cannot be converted to Int32”.
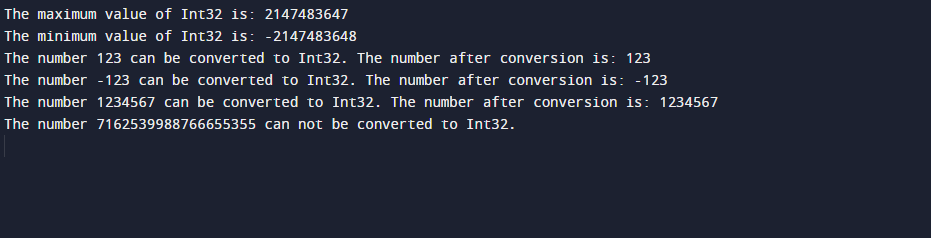
Output
In this output:
-
- We can see that the first two lines show the maximum and minimum values of “Int32”.
- The third line checks “123” which lies within this range so it is converted to “Int32”.
- The fourth line checks “-123” which also lies within the given range so it is converted to “Int32”.
- The fifth line checks “1234567” which is also in the given range so its value is converted to “Int32”.
- The last line checks “7162539988766655355” which is greater than the given range so its value is not converted to “Int32”.
Using code examples, we went through the “Int32.MaxValue” property in C#.
Conclusion
“Int32” is provided by the “.NET framework” and is primitive in nature. It is a 32-bit signed value. The “Int32.MaxValue” field is the maximum range that cannot be changed as it is constant in nature. We can use this field to check whether a number lies in the “Int32” range or not. This guide described the “Int32.MaxValue” field in C#.