Steam is one of the largest marketplaces for gaming. It hosts thousands of games from publishers all over the world. If you’ve ever been into gaming, then Steam is definitely a name you’ve heard.
In addition to the awesome online marketplace, Steam also offers a dedicated client for easier management of games. For Linux, however, Steam is more than that. Steam is the leading platform for supporting Linux as a viable gaming platform. Thanks to Steam client and Proton, a big portion of Steam games can run on Linux.
In this guide, check out how to install Steam on Fedora Linux.
Steam on Fedora Linux
Steam offers an official desktop client for multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, macOS, etc. By default, Steam offers a DEB package for Debian/Ubuntu-based systems. For Fedora, however, the installation is a bit different.
Install Steam from RPM Fusion repo
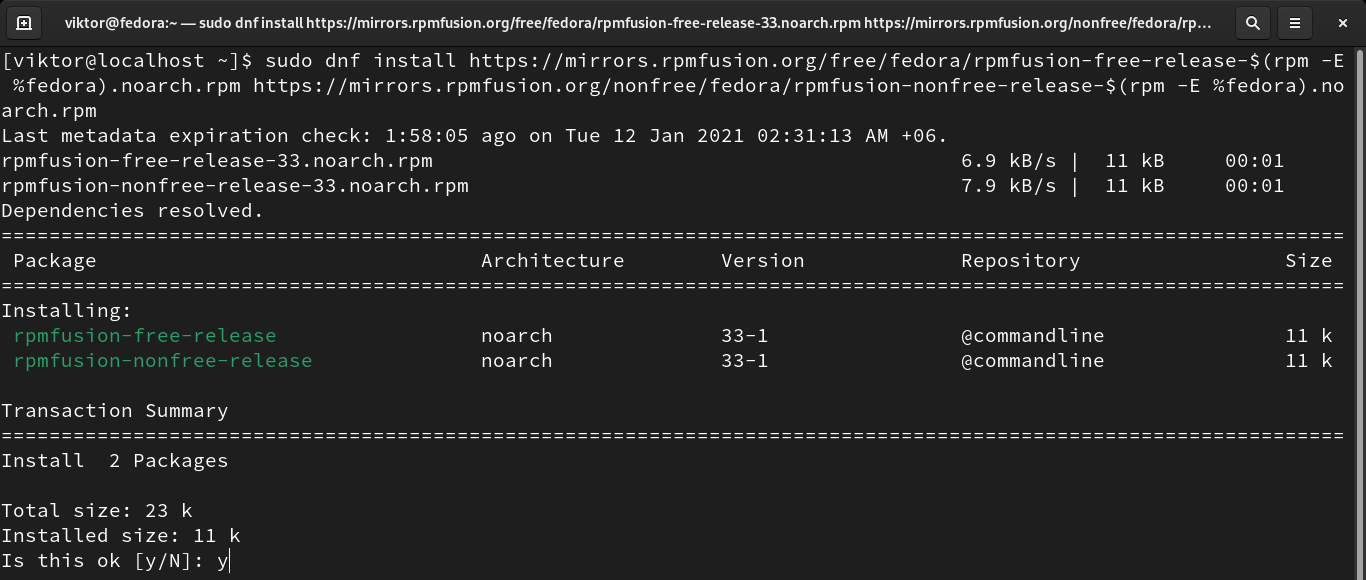
RPM Fusion is a 3rd-party repository for apps that Red Hat and Fedora Project don’t ship. The software comes in pre-compiled RPM packages for all current Fedora versions and RHEL or clone versions. RPM Fusion works with YUM, DNF, and PackageKit, etc.
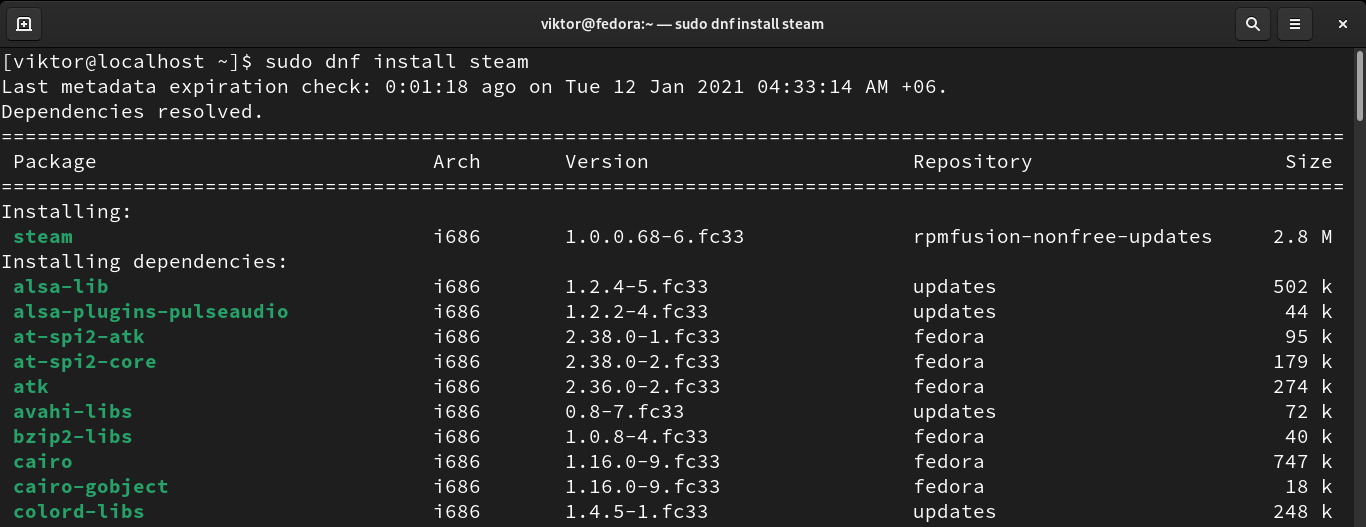
Note that Steam for RPM Fusion is available only for 32-bit architecture. However, it should work fine under Fedora 64-bit system.
Configuring RPM Fusion is quite simple. Just run this long command.
Now, update the DNF cache.
Finally, install Steam.
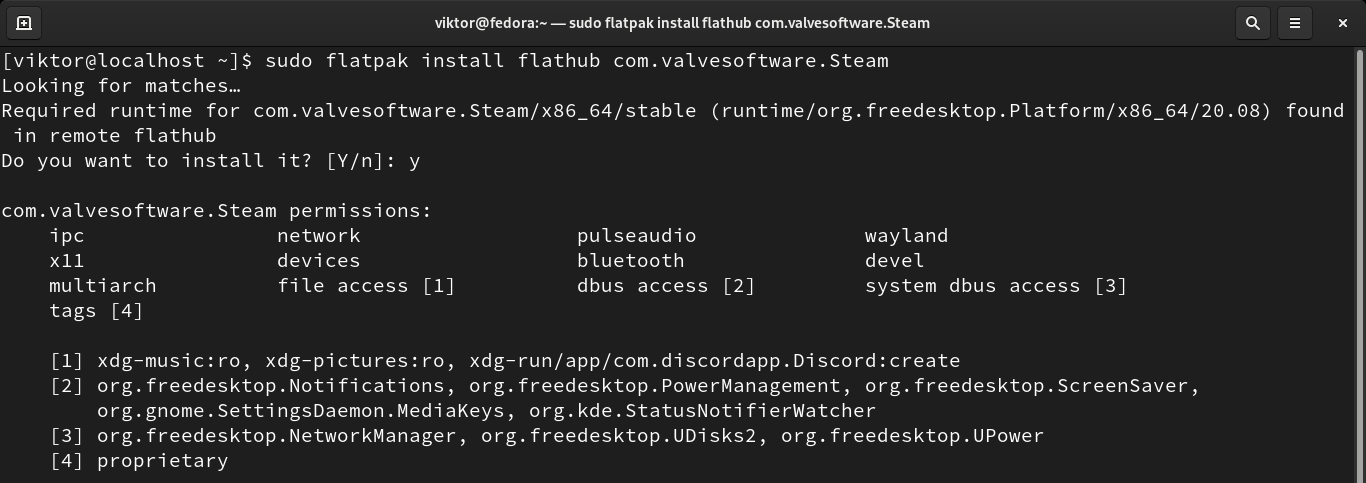
Install Steam flatpak
Flatpak is an interesting type of Linux package. Given the support for the platform, a flatpak package can run on any Linux distro. All it requires is having the flatpak package manager installed. Steam is available as a flatpak package. This method is less troublesome than the previous one.
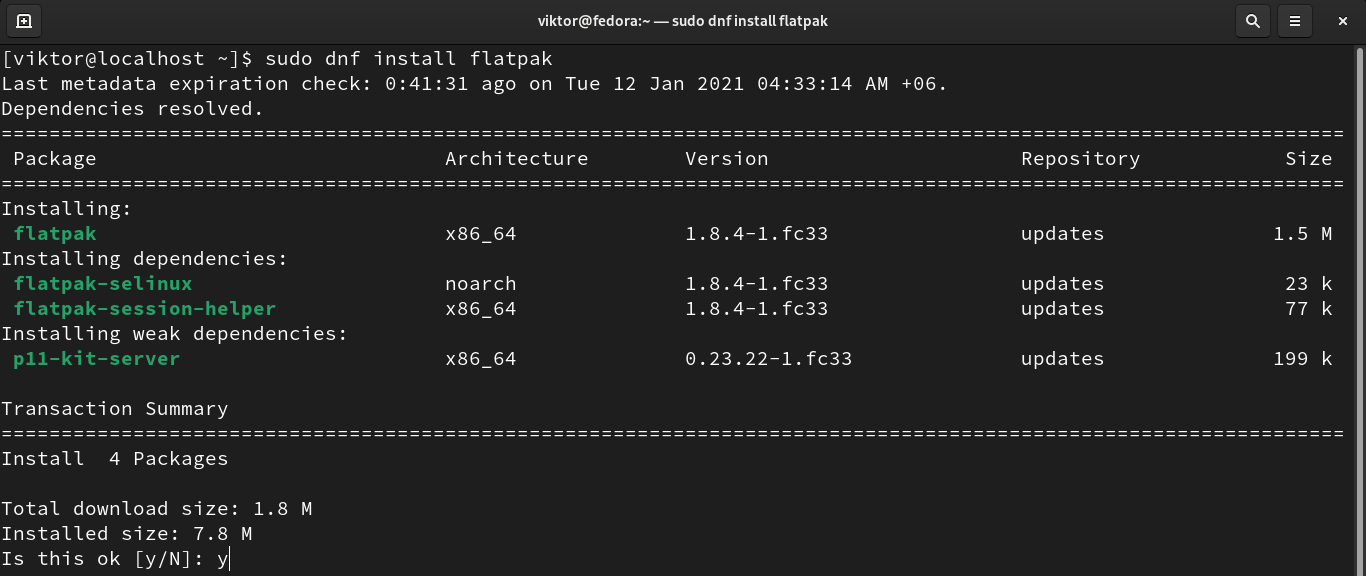
The flatpak package manager comes pre-installed with Fedora. So, there’s no need to install it again manually. However, if it’s missing, then run the following command to install it quickly.
Add the FlatHub repo to flatpak. FlatHub is basically the official flatpak app store.
Finally, install Steam flatpak.
Configuring Steam
Once the client is installed, it’s time to configure it. Launch the Steam client.
When launched for the first time, Steam will download the latest updates. It may take some time.
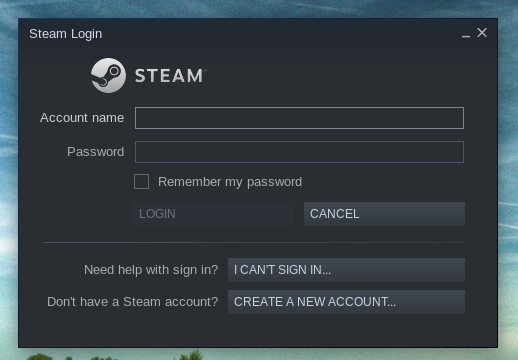
Steam is ready to go! Assuming you already have a Steam account, select “LOGIN TO AN EXISTING ACCOUNT”. If there’s no Steam account, then click “CREATE NEW ACCOUNT” and follow the instructions to create a new one.
Enter the necessary credentials.
Voila! Steam is up and running!
Configuring Proton
Proton is a powerful tool released by Valve Software (owner of Steam). It’s integrated with the Steam client. It’s the tool that offers to have a better experience playing Windows games on Linux. Under the hood, Proton is a combination of multiple tools like Wine and DXVK. It’s all installed and maintained automatically.
There’s also a big database to find out whether your desired game is stable under Proton. Check out ProtonDB.
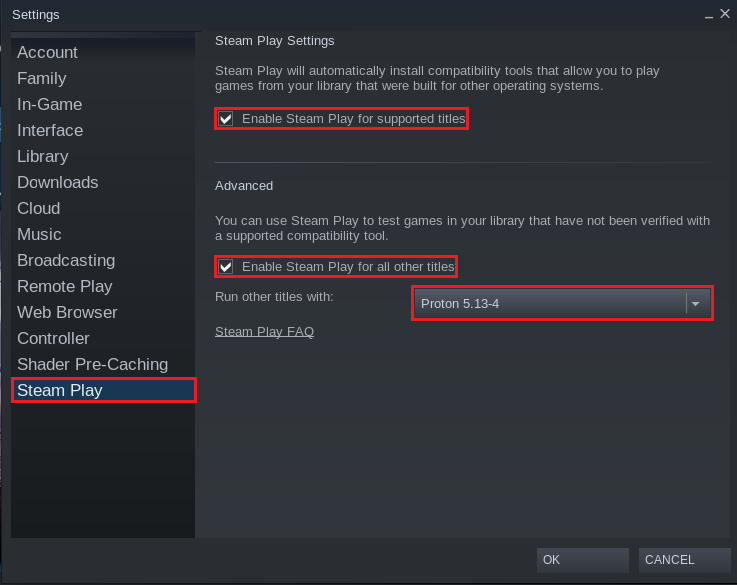
To enable Proton, go to Steam >> Settings.
From the “Settings” window, select “Steam Play” from the left panel.
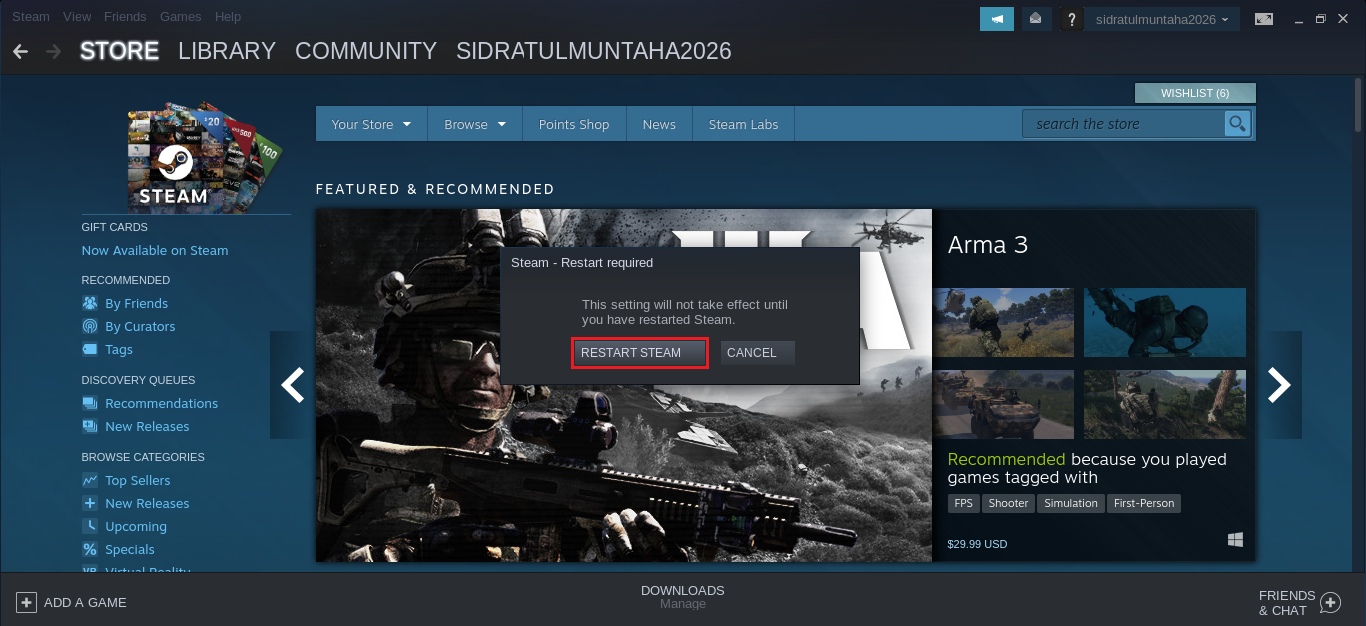
Check the options marked in the screenshot. As for the Proton version, ensure that it’s the latest version.
Steam will prompt for restarting the client. Select “RESTART STEAM” to take the changes into effect.
Uninstalling Steam
If for some reason, Steam is no longer required, you may want to uninstall it. Depending on the installation method, the uninstallation procedure will vary.
If Steam was installed from the RPM Fusion repo, then DNF can do the job.
If Steam was installed as flatpak, then use the following command instead.
To further clean up the Steam residue files and directories, run the following commands.
Final thoughts
Installing Steam is not a difficult task at all. Enjoy all your favorite games from Steam.
If you’re into gaming, there are some dedicated Linux distros out there. Check out some of the best Linux distros for gaming.
Happy computing!