In this article, we will provide a detailed guide to use $in and $nin operators in MongoDB:
It is recommended to complete the following items of the prerequisites list to proceed to the application of these operators.
Prerequisites
This section contains a set of components from MongoDB that are necessary to be adopted to follow this guide:
- MongoDB database
- A collection inside a database
- documents in a collection
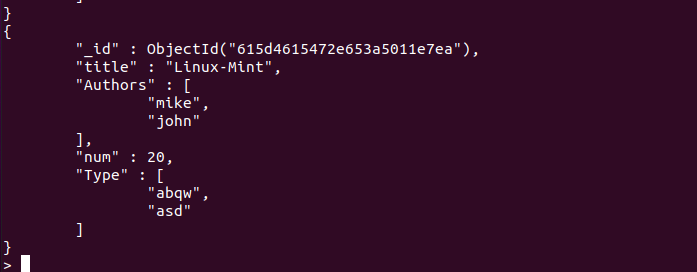
In this post, we will use the following database and a collection to apply $in and $nin operators:
Database Name: linuxhint
Collection Name: debian
You should also insert a few documents in a collection.
How to use $in and $nin operators in MongoDB
This article is divided into two parts; one refers to the $in operator and the other one demonstrates the use of the $nin operator.
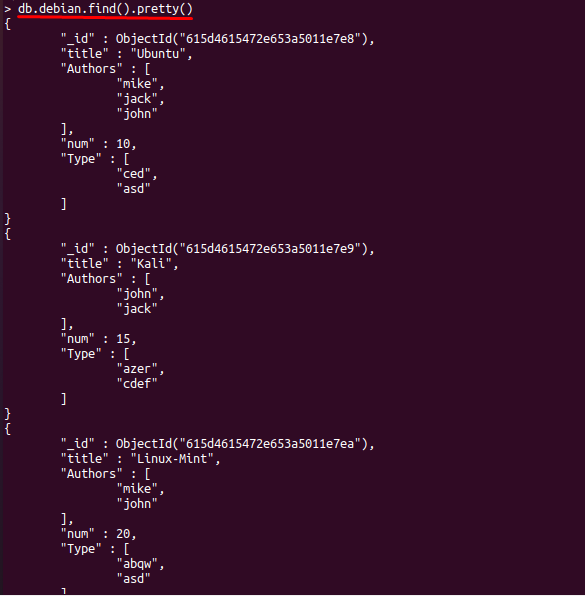
Firstly, we will check the documents available in our collection (so that we can perform actions accordingly).
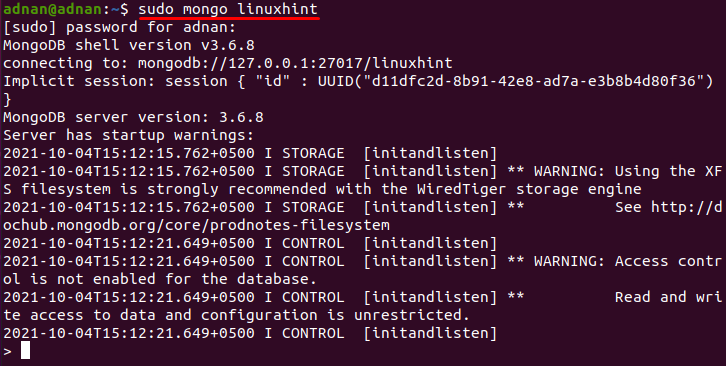
Connect to your MongoDB by issuing the following command in ubuntu terminal: It is noticed that this command will automatically connect you to mongo shell as well.
After that, you can get the display of all the documents available in your collection: For instance, the following command will help to retrieve documents available in the “debian” collection:
How to use $in operator in MongoDB
The $in operator will look for the array and shows the document that matches the value: The syntax of $in is written below:
You have to specify the field name and the values you want to search for:
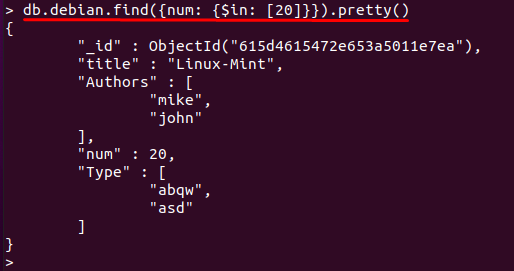
Example 1: Using $in to match a value
The $in operator can be used to match a value in a field and will print the documents that match that value. For instance, the following command will display all those documents that have “num“(field) equals to value “20“: As only one document contains value “20“; thus only that one is printed:
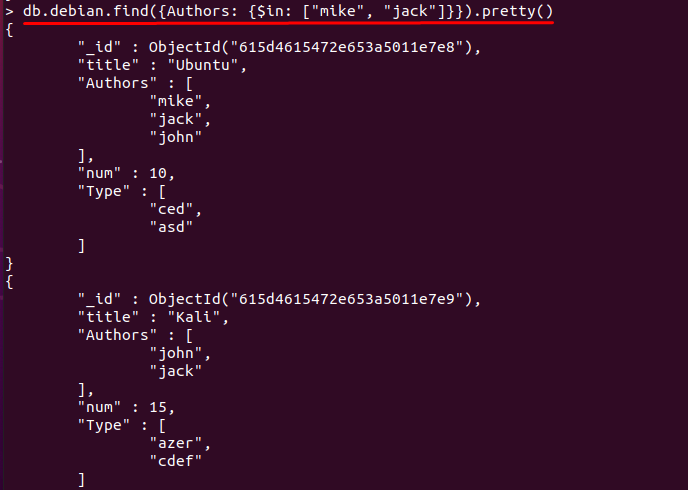
Example 2: Using $in to match an array value(s)
Moreover, you can also use the $in operator to look for array values in the MongoDB database. In our case, the command mentioned below will display the documents that have values “mike” and “jack” in “Authors” field:
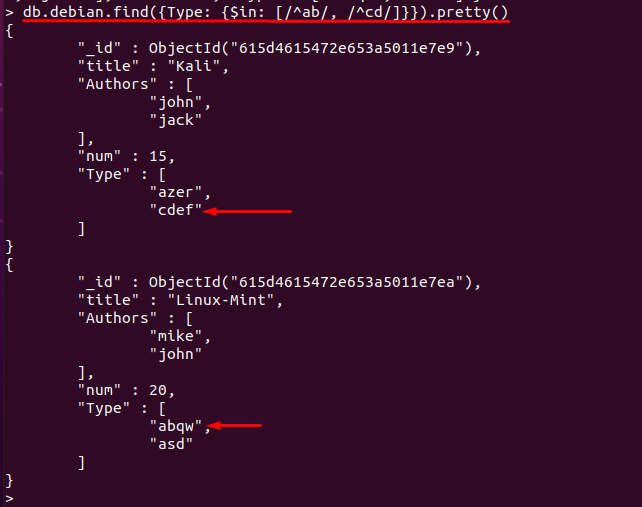
Example 3: Using $in to match Regular Expressions
The $in operator can also be used to match the values specified by a regular expression: the command mentioned below will display documents that contains a field “Type” and the strings in the field starts with either “ab” or “cd“:
How to use $nin operator in MongoDB
The $nin operator in MongoDB acts oppositely to $in; like $nin will display the document that does not contain the specified value. The syntax is alike of $in and is shown below:
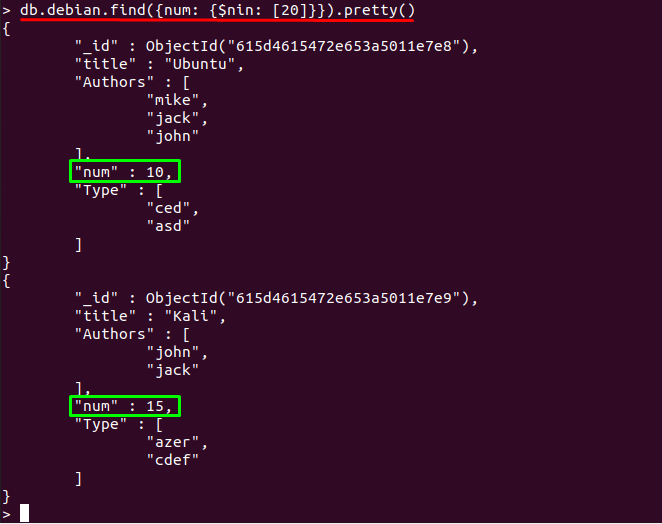
Example 1: Using $nin to match a value
As already mentioned, that $nin operator does not display the document that matches a value. The command below will display the documents that do not contain “20” in “num” field:
The output below shows that printed documents do not contain value “20“:
Example 2: Using $nin to match an array value
The following command will display the documents that do not contain “mike” and “john” in the “Authors” field. As none of the document is left behind because all documents have either “mike” or “john” as an author, there will be an empty output:
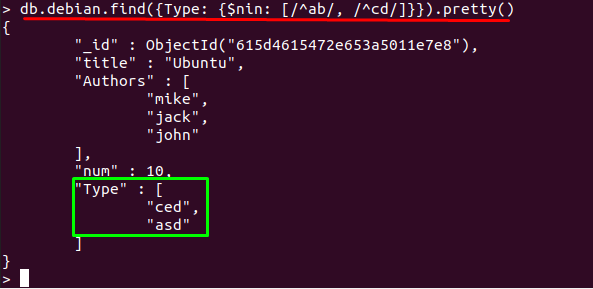
Example 3: Using $nin to match a Regular Expression
The $nin operator is also used to get the documents on basis of Regular Expressions; For example, in the below mentioned command, “Type” field is selected and $nin will print those documents in which “Type” value does not start with “ab” or “cd“:
Note: The “pretty()” method used in this article is just to get the output in a structured form; you can use only “find()” to get the same result but in an unstructured way.
Conclusion
Proper data management is the primary concern of any organization. They have to store data and rapid retrieval of data is preferred whenever needed. Several database management systems provide such functionality and MongoDB is one of them. In this post, we have described the use of two operators “$in” and “$nin” that help in retrieving array values in a MongoDB database. These operators help to get the required documents based on values matched by these operators. The $in operator prints the document that contains the match; whereas $nin prints those documents that do not match the value.