Htop is more like an immersive Centos 8 system process viewer and device monitor. It shows resource-usage measures in color and helps you to conveniently keep track of the performance of your system as an enhancement. With both an additional array of choices and a clear picture on the board, it is the same as the standard main command. It shows details about the usage of Processor & RAM, tasks being done, average load, and uptime. Besides, Htop shows a list of all operating processes and can even show it in a tree-like structure. If you are interested to interactively control your device, then one of your best choices ought to be the Htop command. It runs on all distributions of Linux, and in most situations, is enabled by default.
In this tutorial, you will learn to install Htop on Centos 8 using the command-line.
The installation process for HTOS Centos 8 is as follows:
Open the terminal window in CentOS 8. Connect to the remote Centos 8 server using the ssh command or login panel.
Switch on EPEL repository
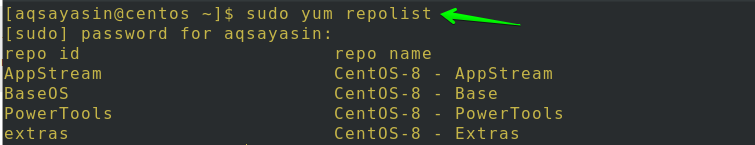
First, you’d have to make sure that your centos 8 has an epel repository installed and enabled. For this purpose, execute the following command:
You can see that no epel repository is installed in the system, as shown in the image below.
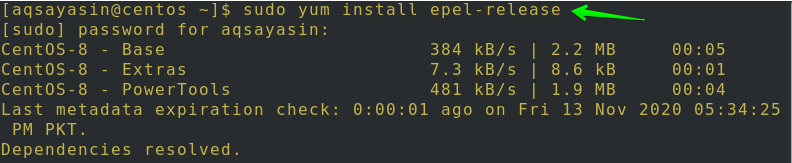
You have to execute the following command to install the Centos 8 epel repository:
Or
Or
After that, you will be questioned to affirm your action. Type ‘y’ and then tap Enter to continue, as shown in the image. You can see that the epel repository will be installed in your system.
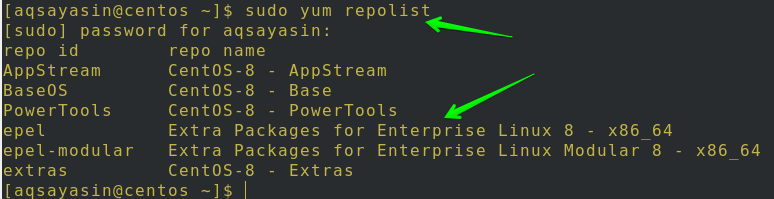
Using the repolist command, you can see that the epel repository is now installed in the system.
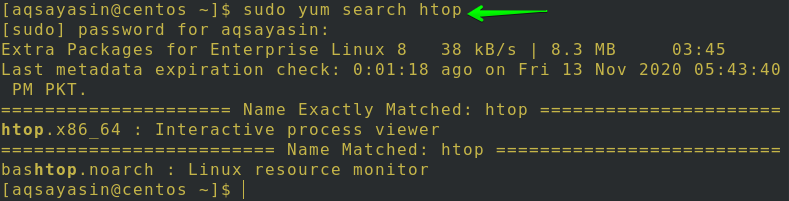
It’s important to understand how to check for packages of some sort. Consequently, enter the following yum command to check for the Htop packages in Centos 8:
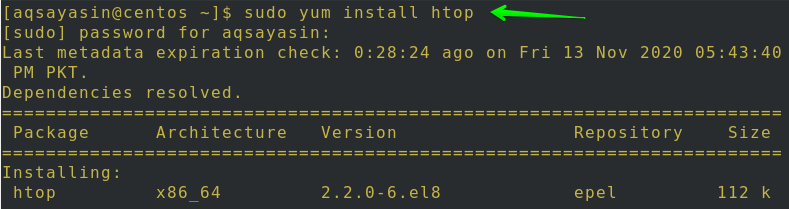
Install Htop Package
You can use any of the below-mentioned commands to install the HTOP package on your Centos 8:
Or
Or
You will be questioned more than once to affirm your action. Type ‘y’ and then tap Enter to continue as shown. You can see that in the image, the epel repository will be installed in your system.
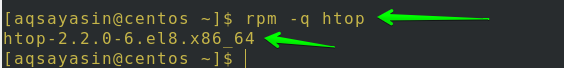
After the complete installation, to check whether the package is loaded or not, Open the terminal and then use the command below:
If your Htop package is successfully installed on your system, it will display its version and release information, as shown in the below image.
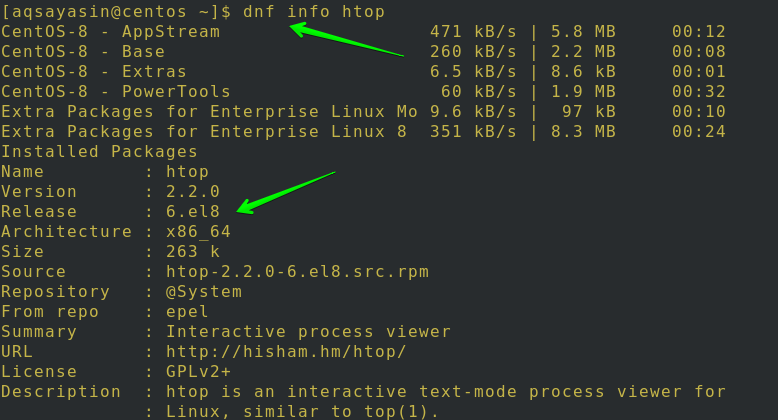
Enter the following command to get more details about the Htop package you just installed on your system:
Launch Htop in Centos 8
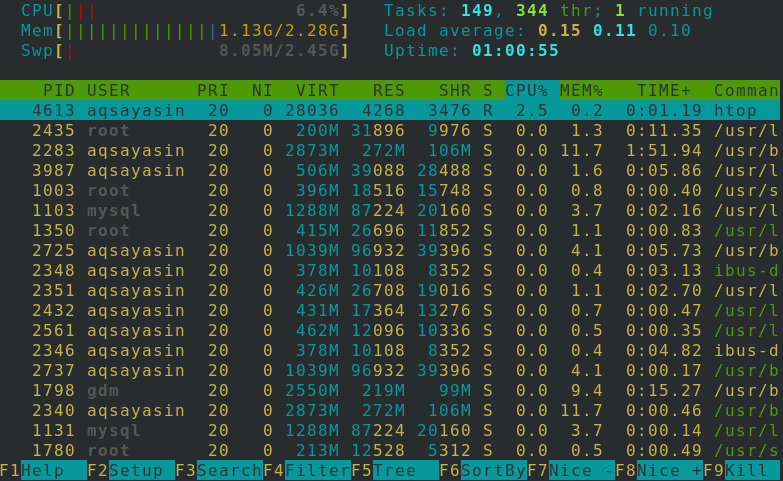
You have to simply execute the below-mentioned command to launch the Htop package:
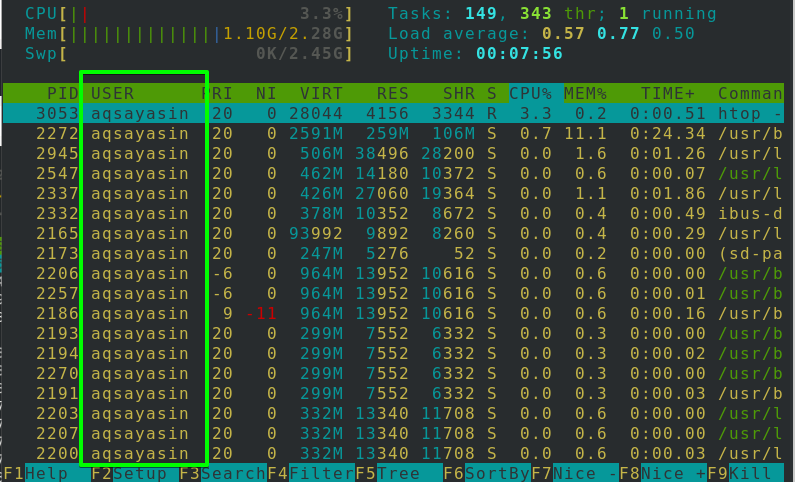
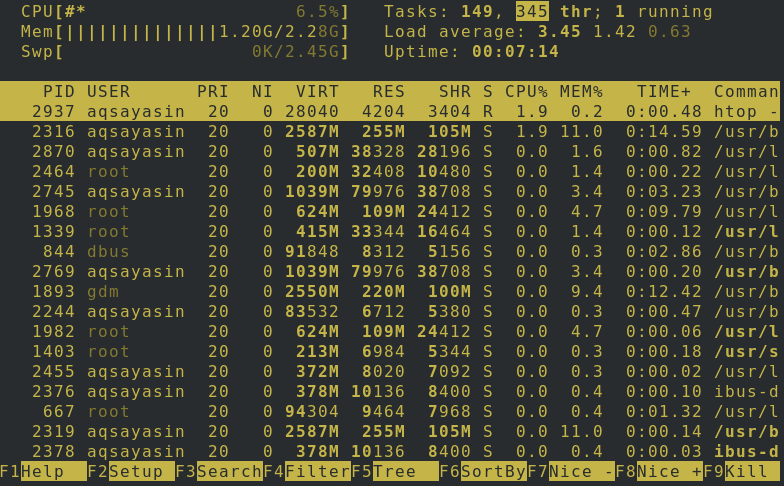
The below-mentioned image has the information where any single bit of details about the device can be seen. The storage and swapping use can be checked out at the top. To exit the HTOP session, tap F10 or q from your keyboard.
Usage of keys is the main advantage of Htop. You can use F2 to setup, F3 to search, F4 to filter, and F9 to kill any process.
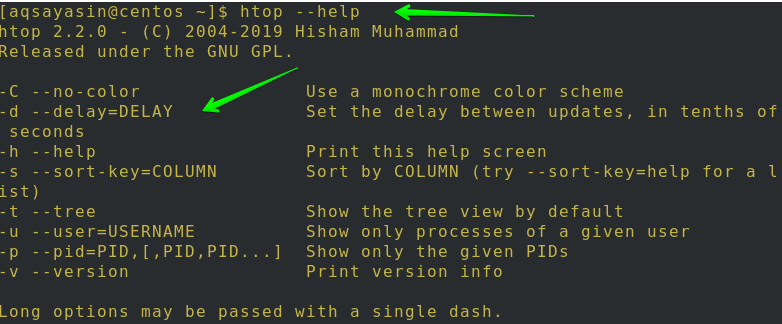
To get support with the used command, simply execute the following command:
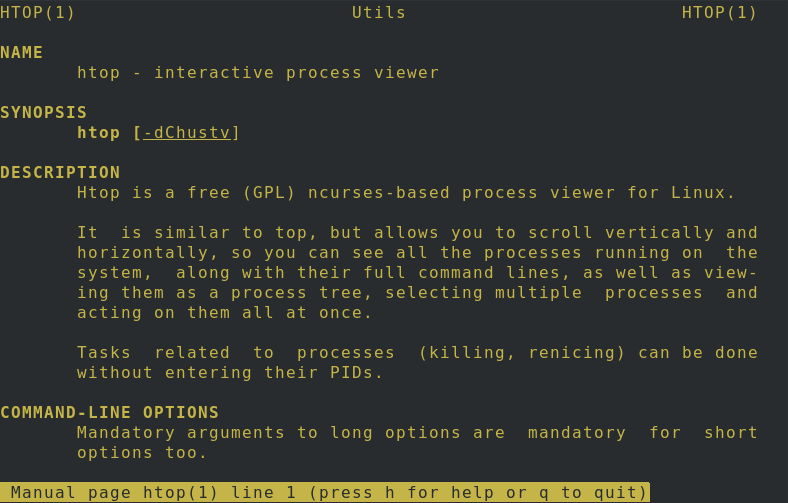
Conversely, you can access the man pages by running this simple command:
You will see the following output:
Show Processes of Specific User
Consequently, many arguments may be forwarded to the command. Let’s assume that aqsayasin is running a command. You have to use the following command to access aqsayasin processes:
Or
Here in the main pane, you can conveniently check what choices and details are available. It will display all the system statistics for user aqsayasin, as seen below.
Set the Monochrome Color Scheme
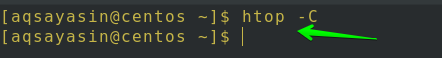
One can use a monochrome color scheme in Htop using a very easy command as follows:
Or
As you can see in the image below, all the output is monochromatic, and there is no, other than one color, on-screen output.
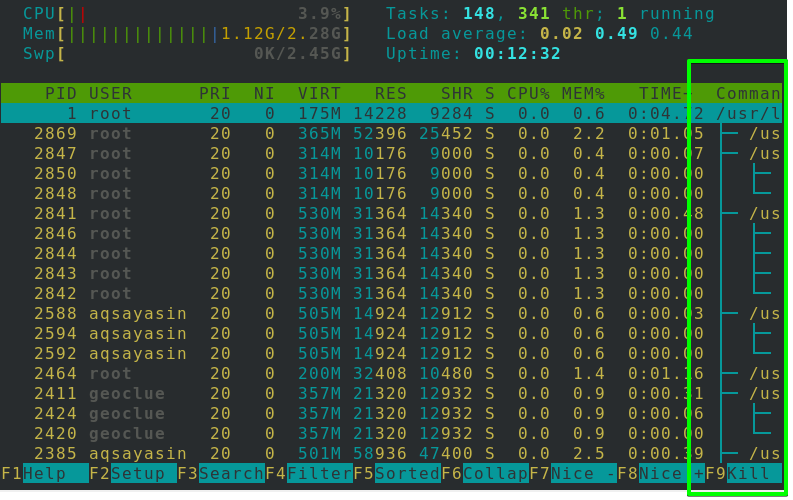
Tree Visualization
It’s everybody’s favorite viewpoint since it helps you to grasp the hierarchy of each operation. Would you like to see tree visualization by default while Htop is running? For this purpose, try the command listed below:
Or
To see tree visualization of a specific user, Click F5 or the “t” button while a specific user must have been selected. Here you will be able to see tree visualization of processes using system resources in the below image.
Limit Processes for Given PID’s
You can also show the processes of some specific PIDs using very simple commands. In this command, you just have to mention the PID of a particular user instead of its username as shown in the following:
Here, PID is the Person ID assigned by the system. For example:
You can also limit the processes for more than one PID’s as follows:
Conclusion:
In this guide, we have explored how to install the Htop and how to utilize it in Centos 8. We have seen how to switch on epel repository, install Htop package, launch Htop in Centos 8, display specific user operations, fix monochromatic color scheme, tree representation, and restrict processes for relevant PIDs.
I believe this guide will help you quickly understand the HTOP order in Centos 8.