The kubectl command is used by the Kubernetes managers to switch and accomplish the clusters of Kubernetes. The abundance of management done in a Kubernetes cluster is completed with kubectl. To construct the kubectl command-line tool, we utilize the kubeconfig file found in the directory. The kubectl command points to the cluster and further contextual data that we can use to accomplish the cluster. We utilize the Kubernetes to execute the instructions. We also utilize kubectl to organize applications, review and achieve resources, and observe logs. Kubernetes states the forms of structure that offer a mechanism for organizing, maintaining, and scaling applications or user-defined metrics.
Kubernetes are lightly joined and extensible to accommodate a variety of workloads. Much of this extensibility is delivered by the API. This API is utilized by interior constituents and containers running in Kubernetes. Platforms switch computing and storing sources by describing sources as items and allowing them to be achieved in that way. An application executing on the same physical or computer-generated machine in a non-cloud situation corresponds to a cloud application executing on the identical logical host. Storing multiple containers in a pod makes it easy to acquire and exchange data between containers. The Windows operating system allows us to observe and save different files, execute codes, run different software, and offer a method to associate to the internet. Kubernetes utilize a command-line efficacy called kubectl to communicate by the API server. The kubectl is accessible in numerous operating systems. This possibility is frequently easier than manually downloading and installing. This article will help us download and install the kubectl binaries provided by Windows operating system.
Download kubectl.exe:
First, we have to download the .exe file of kubectl. This file is kept in the folder, and that folder is identified. We make a folder that contains tools for usage with Kubernetes. These tools are self-sufficient executable files that we run from every directory. Instances are kubectl and helm.
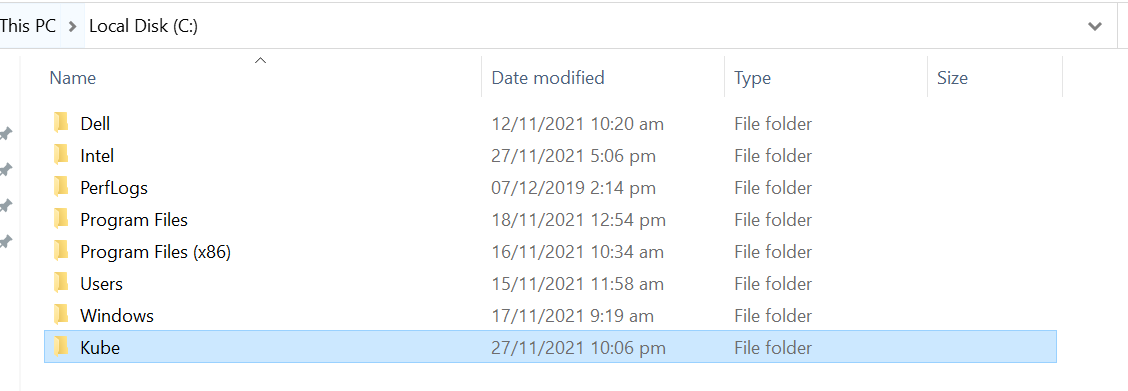
Create the Kube Directory:
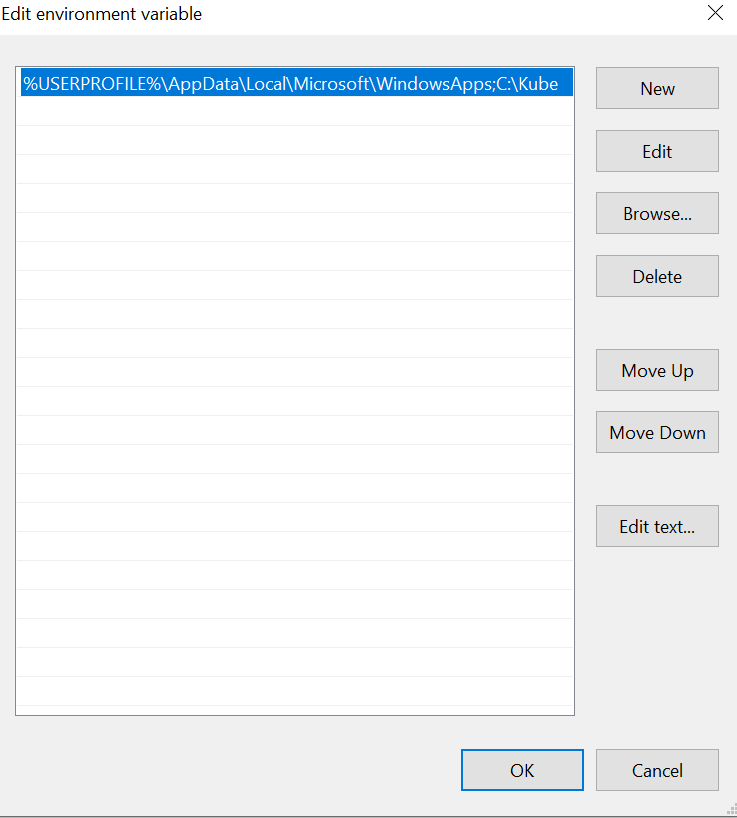
We have downloaded the kubectl efficiently and created a Windows PATH declaration to execute the command from the command line framework. We have to make a directory where the command forms for the configuration. This is the origin of the user’s directory, which is executing the commands on Windows. We just made a “Kube” directory. This directory contains all the tools that we utilize to interact with Kubernetes. Then, we use any Kubernetes tool we have placed in the folder by simply adding the file to the Windows PATH variable.
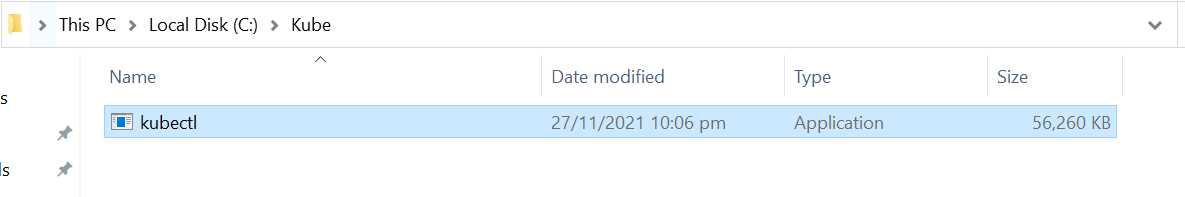
Create the Windows Kubectl File:
After creating the Kube directory, we have to make the kubectl file required for the kubectl command. This folder is located on a local disk (C). And it is termed as “Kube”. The file consists of the configuration required to state kubectl as the method of connecting with the cluster:
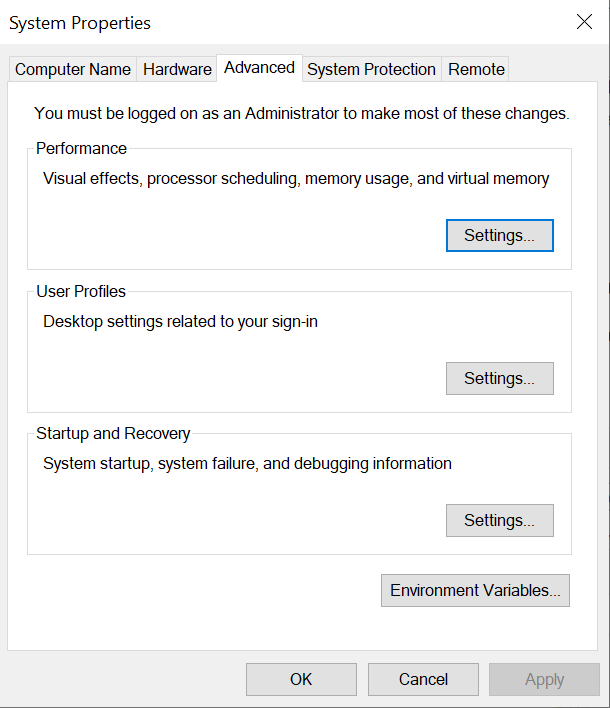
Setting the Path:
Now, we open system properties. There are different options shown there. We choose the option Advanced. We modify the settings according to the need. Here, we change the performance settings, user profile, startup, and recovery:
Enter the Folder Location:
After creating the folder, we add it to the Windows PATH variable. This eradicates the need to go to the kubectl path to execute the commands. We simply enter different commands. The Docker Desktop enhances its specific form of kubectl to Windows PATH. When we have Docker Desktop installed, we have to mention a PATH record formerly entered by the Installer or eliminate kubectl from Docker Desktop.
In this step, we check the environment variables. We edit the “one drive” variable for HP. After this, we also change system variables:
Now, we edit the environment variable in this step:
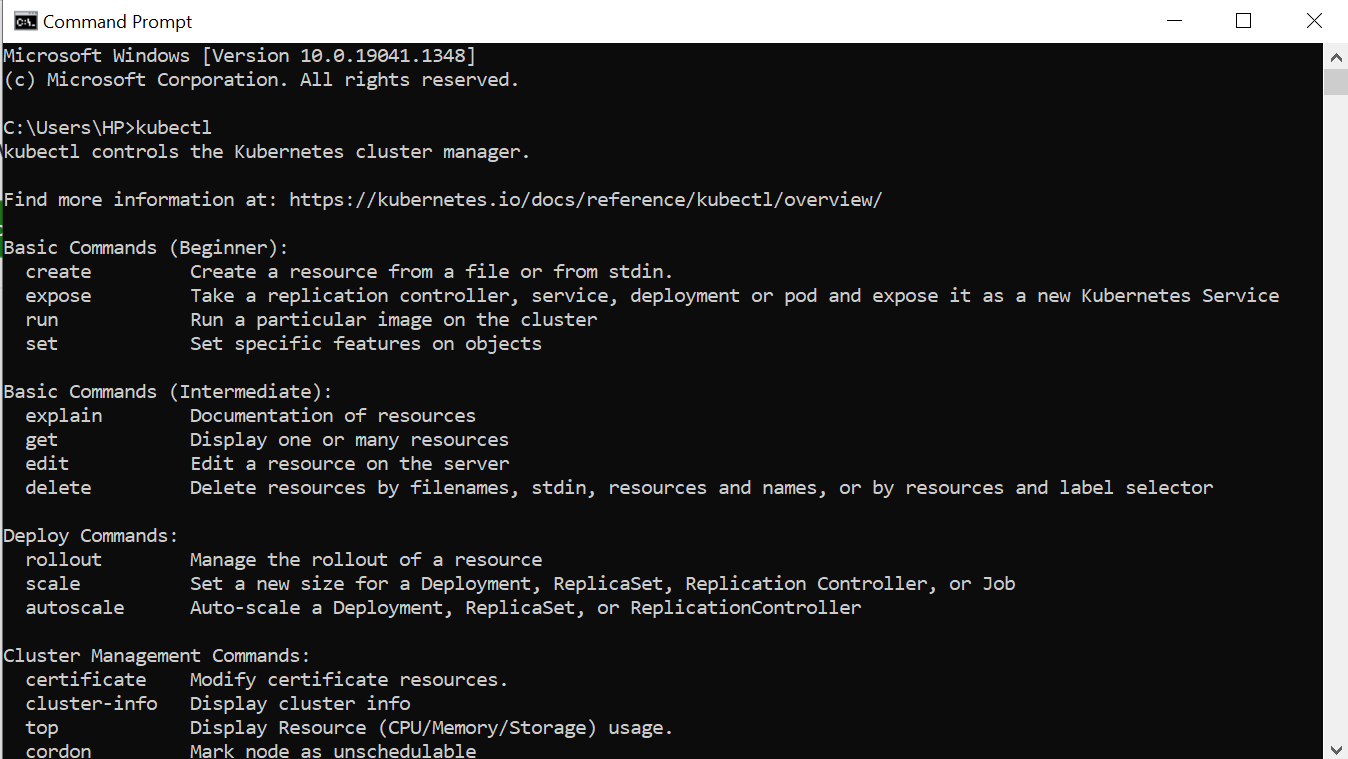
Command Prompt:
After configuring the declaration of PATH and downloading the kubectl command, we execute the kubectl command to confirm that the command is reverted by the offered constraints. This ensures that the declaration of Path is functioning as estimated. In the last step, we have to open a shell prompt. We run kubectl here to observe the commands that are maintained by kubectl:
Conclusion:
There are numerous techniques to configure kubectl on different operating systems. Here, we are discussing the method of installing kubectl on Windows. Installing kubectl on Windows and creating a Kube file support users who want to work with a Kubernetes cluster on Windows. After copying the required files to the correct location and configuring the Windows PATH variable, the procedure is very simple. All we observed was the version of the Kube file. We download kubectl.exe and store that file in some folder on the Windows file system. Then, we add the save location of that folder to the variable. We made several changes to the settings. Then, the command prompt is opened, and we can execute different commands here. We hope you found this article helpful. Check out Linux Hint for more tips and information.