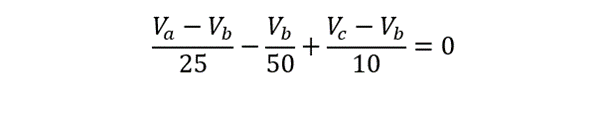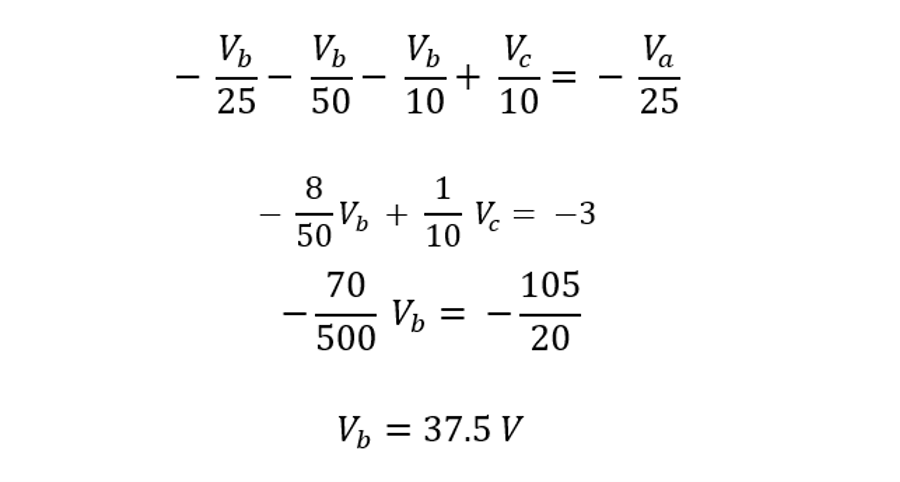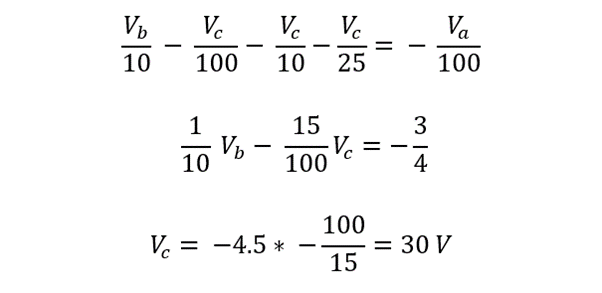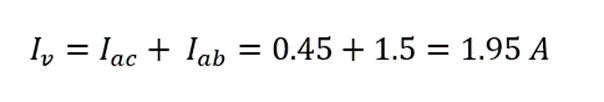What is Nodal Voltage Analysis?
Nodal voltage analysis, also known as the node-voltage method or the branch-current method, is a systematic approach used to solve electrical circuits by focusing on the fundamental principle that the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving that node. By assigning node voltages as variables, nodal voltage analysis simplifies complex circuit equations and enables efficient analysis of electrical networks.
Procedure for Nodal Voltage Analysis
1. Identify Essential Nodes: Begin by identifying the essential nodes within the circuit. These nodes typically include points where two or more circuit elements (such as resistors, capacitors, or voltage sources) connect.
2. Assign a Reference Node: Select one node as the reference node or ground node, as assigning a node as the reference simplifies the analysis and allows for the determination of absolute voltage values at other nodes.
3. Apply Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): For each non-reference node, apply Kirchhoff’s Current Law, which states that the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node. Express the equations in terms of the node voltages and the circuit elements connected to each node.
4. Solve Simultaneous Equations: With KCL equations established, solve the simultaneous equations.
Example for Nodal Voltage Analysis
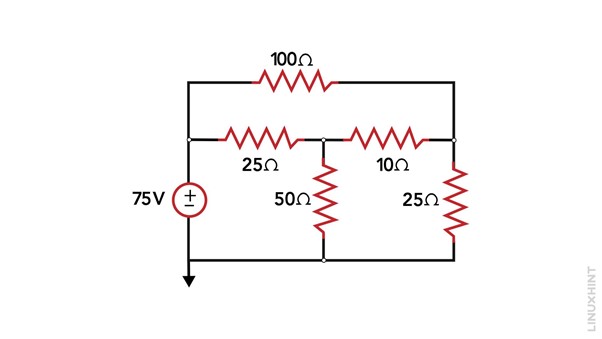
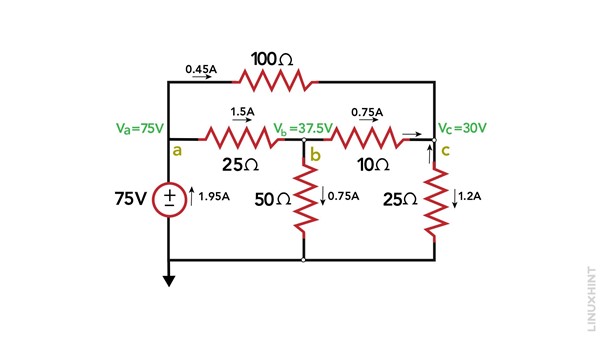
Consider the below-given circuit that has five resistances and one voltage source:
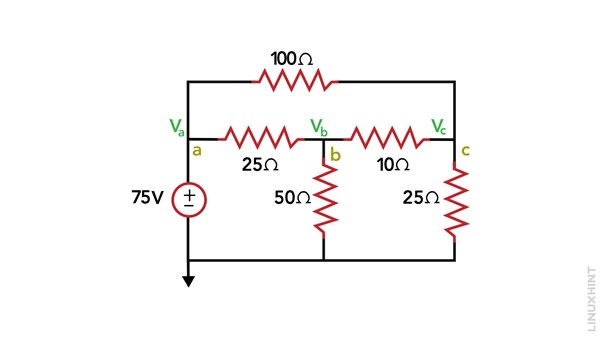
1: Identify Essential Nodes: There are four nodes in the circuit Va, Vb, and Vc:
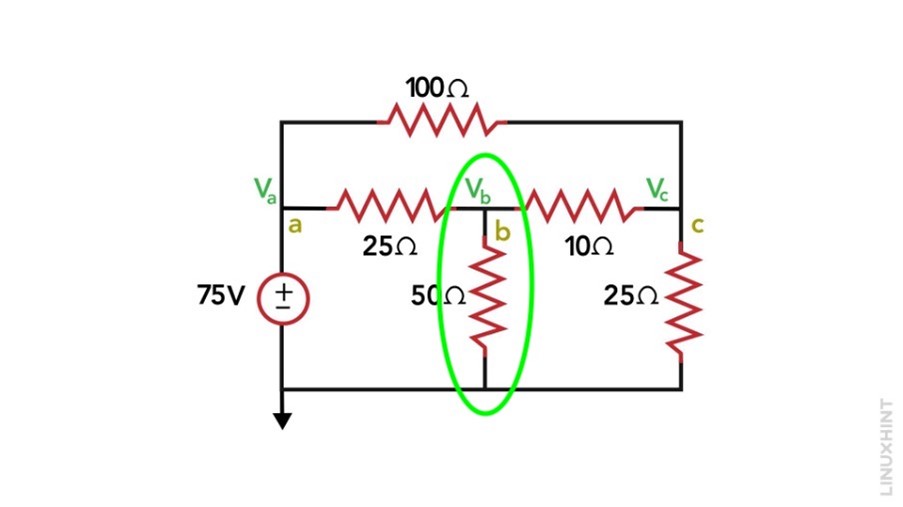
2. Assign a Reference Node: Here I have set the Vb as the reference node. The selection of the node located at the bottom of the schematic as the reference node is advantageous due to its multiple connections (3) and is connected to the negative terminal of the circuit.
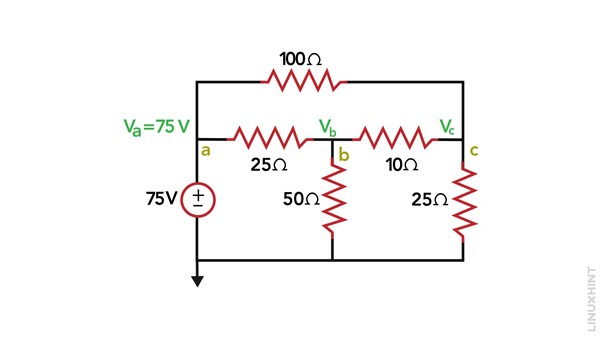
3: Apply KCL and Solve the Equations: Node A is considered a straightforward node as it is directly connected to a voltage source with its other terminal connected to the ground.
By inspection, we determine the voltage at node a to be Va = 75 and find the voltage of node b using:
Now for finding the voltage for node c:
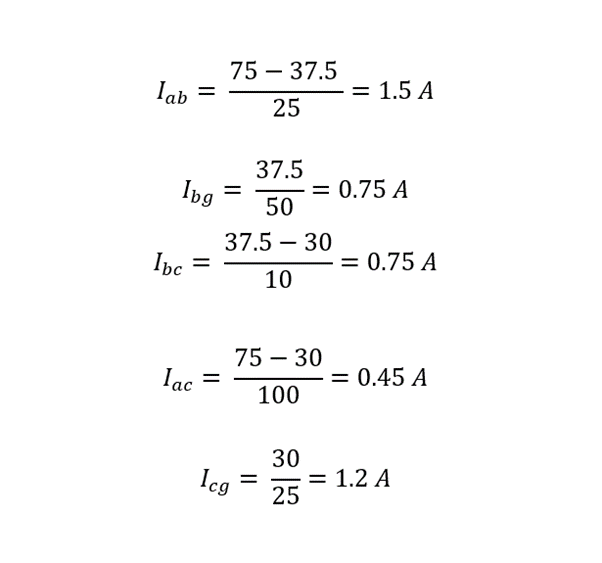
Now finding the currents:
Now calculate the total current provided by the voltage source, using the formula:
Conclusion
Nodal voltage analysis is a powerful technique for analyzing electrical circuits. By applying Kirchhoff’s Current Law and assigning node voltages as variables, engineers can simplify complex circuit equations and efficiently solve for voltage, current, and power flow.