Pre-requisites
To use kubectl to run the exec command on Kubernetes pods as root, you must have the minikube cluster installed on your system. You will also need sudo rights to get into your system. We utilized Ubuntu 20.04 LTS to make this article ready for our users. You can choose your selected or desired operating system for execution. Our system already has kubectl installed. Before you can use this guide, you must first install it.
Method to use Exec commands on Kubernetes pods as root
You should first deploy a minikube cluster before using the exec command on Kubernetes pods as root. In Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, we will need to use the command prompt shell. The terminal window can be launched using one of two basic methods. One option is to use the application bar in your operating system to get to it. Another option is to use the “Ctrl+Alt+T” shortcut key combination, which is the most basic. When you utilize either of these approaches, the command-line terminal will appear.
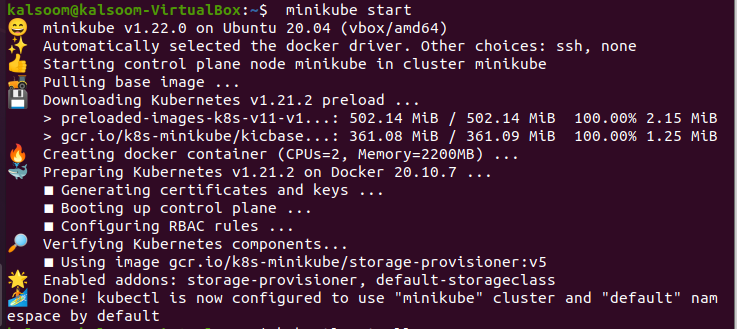
To begin, launch the minikube cluster, which is already built on your Ubuntu 20.04 LTS operating system. To start minikube, type the associated instruction in the command prompt:
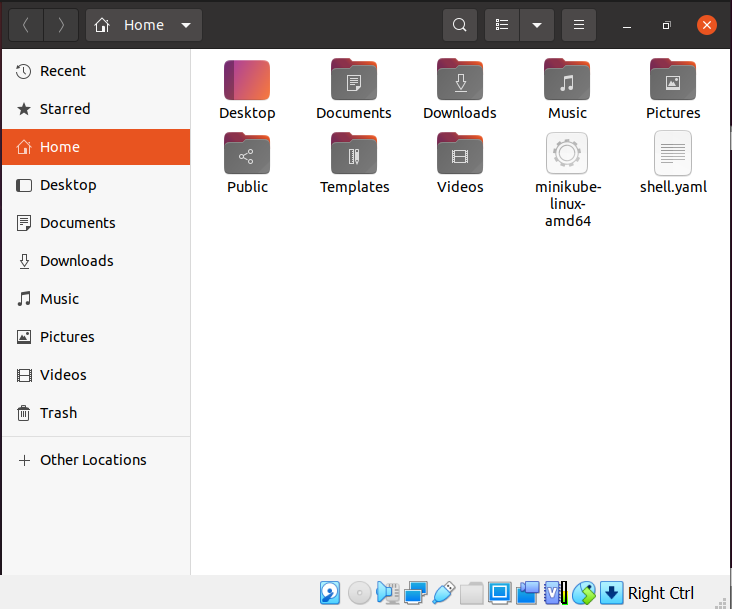
After executing this command, you have to wait a few moments before using minikube. After the command has been completed successfully, you may also check the minikube version presented. We are creating a file with a touch command named “shell. yaml”. Touch is a Linux Based command which can be utilized for a range of tasks other than simply creating a blank file.
After the execution, the created file can be seen in the home directory of the Ubuntu 20.04 system.
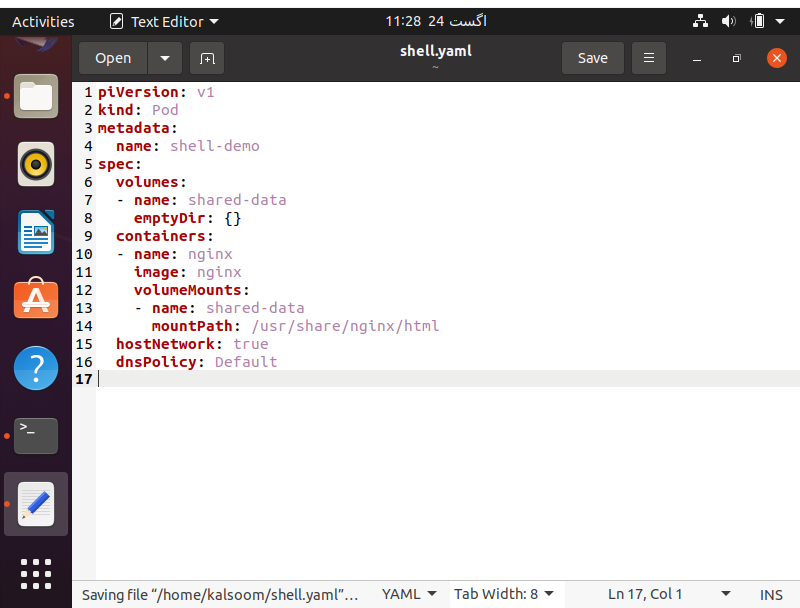
Now it’s time to generate a configuration file for pod formation. In the attached image, we have included an example of a pod formation configuration file. We are going to make a pod with only one container. The container runs the Nginx image.
Using the same configuration file we prepared previously, we can now build a pod in the terminal window. So, in the terminal, enter the following listed command in Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
You can see that it was effectively formed in the command’s output. Now we can verify whether the container is running or not, run the following listed command in the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
By performing the following command in the console of the Ubuntu 20.04 operating system, you can get a shell towards the running container. To verify this, execute the listed command in Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
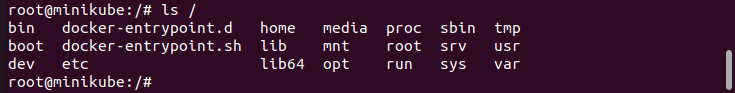
You can check out that the exec keyword has been used in the above-shown command. Also, “root@minikube” can be seen in the output, which depicts that we have successfully used the exec command on Kubernetes pods as a root.
To display the root directory in the shell, execute the listed command in Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
You can further use this shell as per the work assigned to you.
Conclusion
Although Kubernetes is a complex system, executing commands directly on an operating pod is often the fastest and most obvious way to identify a problem. Luckily, the Kubernetes command-line interface, kubectl, includes an exec function built-in, which is perfect for this. We went over how to use the exec command in great detail. The article listed the method to create pod using configuration file and usage of exec command on Kubernetes pods as root. I assure you that after reading this post, you will have no concerns about using kubectl exec on Kubernetes pods as root.