Electrical units of measurement define the terms used for measuring and gauging electrical quantities. Every electrical circuit has four basic parameters which include current, voltage, frequency, and resistance. The units required to gauge these electrical characteristics are amperes, volts, hertz, and ohms. The standard body governing the selection and implementation of these units is called the international system, abbreviated as SI.
There are many other ac and dc electrical circuit parameters whose units can be derived from multiplying or dividing the basic SI units.
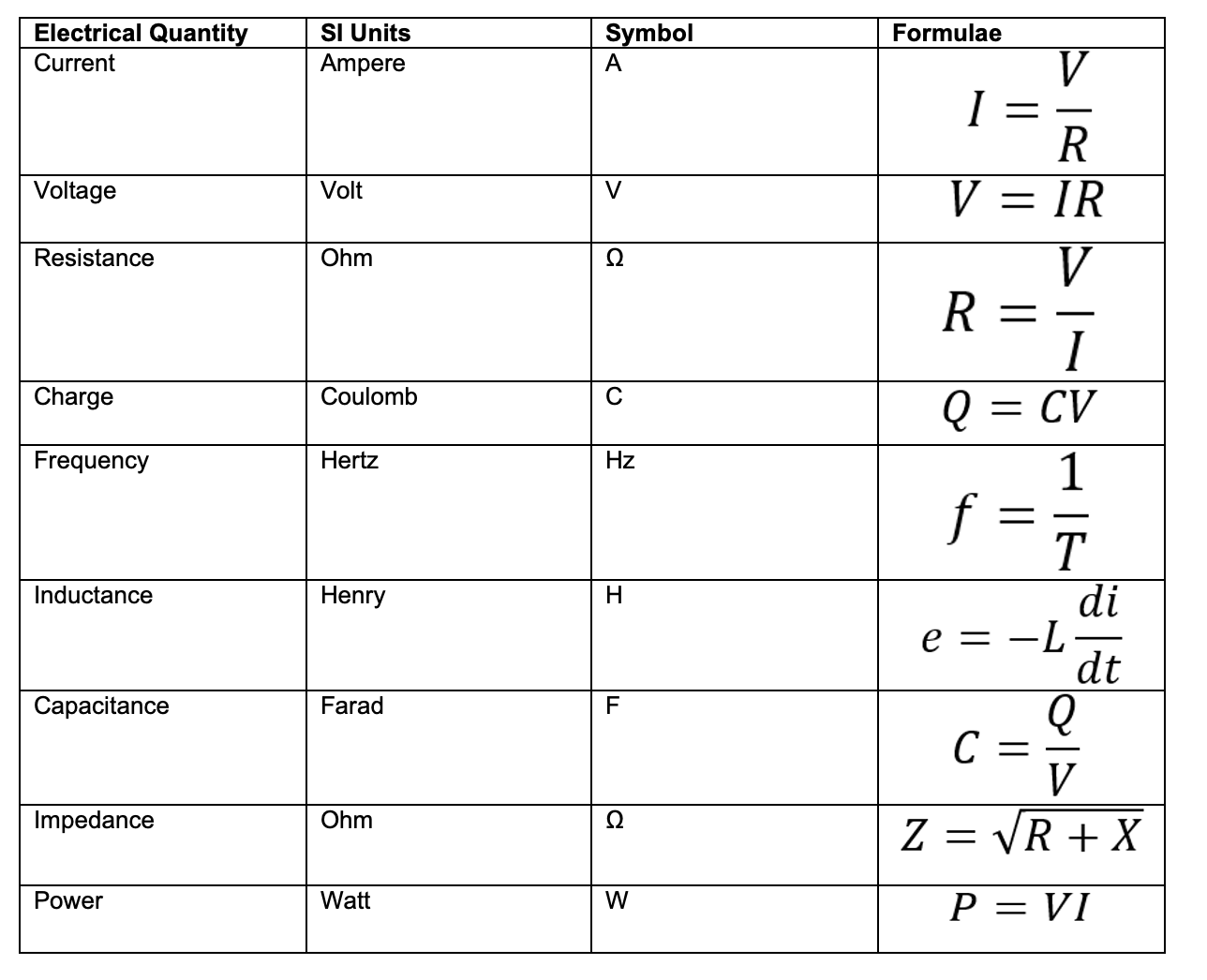
Standard Electrical Units
A table describing the most standard electrical parameter units and symbols with their formulae is shown below:
Multiples & Sub-Multiples of Units
Multiples are prefixes to standard units. Multiples help to reduce an excessive number of zeros in measurements. If the measured value is a multiple of thousands like 25,000,000, the multiples can reduce the whole figure into two numbers only. The table for multipliers along with prefix names is given below:
| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplier | Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pico | p | 1/1,000,000,000,000 | |
| Nano | n | 1/1,000,000,000 | |
| Micro | µ | 1/1,000,000 | |
| Milli | M | 1/1,000 | |
| Centi | C | 1/100 | |
| Kilo | k | 1,000 | |
| Mega | M | 1,000,000 | |
| Giga | G | 1,000,000,000 | |
| Tera | T | 1,000,000,000,000 |
Example
For 100,000V = 100kV
For 0.000,001F= 1µF
Important Electrical Units
Many other important electrical units are not included in standard electrical units. They are called non-standard units as they may not be used more often. The important non-standard electrical units are tabulated below:
| Electrical Quantity | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | WH | Amount of electrical energy consumed over a period of time. |
| Decibel | dB | Loudness is measured in decibel. However, due to low values, one tenth of decibel known as decibel is normally used. |
| Phase Angle | Deg/rads | Angular Difference between current waveform and voltage waveform. |
| Angular Frequency | Rads/s | Rotational units for frequency used in AC circuits. |
| Time Constant | S | Time taken to reach highest or lowest output values for a step input. |
Conclusion
Electrical units of measurement are essential to gauge and measure electrical quantities. These are developed by an international body known as the international system (SI). Therefore, the units of electrical quantities are mostly known as SI units.
