Some Useful Java List Methods:
Java list contains many built-in methods to perform different types of operations on Java list data. Mostly used Java list methods are mentioned here.
| Method | Purpose |
| add(element) | It adds an element at the end of the list, and it returns a Boolean value. |
| add(index,element) | It adds an element at the specific position of the list, and it returns nothing. |
| addAll(list) | It adds all elements of one list at the end of another list, and it returns a Boolean value. |
| addAll(index, list) | It adds all elements of list2 at the particular position of the list1, and it returns a Boolean value. |
| equals(Object) | It compares a particular object with the list elements, and it returns a Boolean value. |
| get(index) | It retrieves the element from the particular position of the list. |
| subList(from_Index, to_Index) | It retrieves elements from a given range. |
| isEmpty() | It checks the list is empty or not. |
| remove(index) | It removes the element from a particular index. |
| remove(Object) | It removes the first occurrence of the object. |
| removeAll(list) or clear() | It removes all elements of a list. |
| set(index, element) | It replaces the element of a particular position. |
| size() | It returns the number of elements of a list. |
| sort(comparator) | It sorts the list elements based on the specific comparator. |
The uses of the above methods are shown in the next part of this tutorial by using different examples.
Example-1: Create a Java list and insert elements in the list
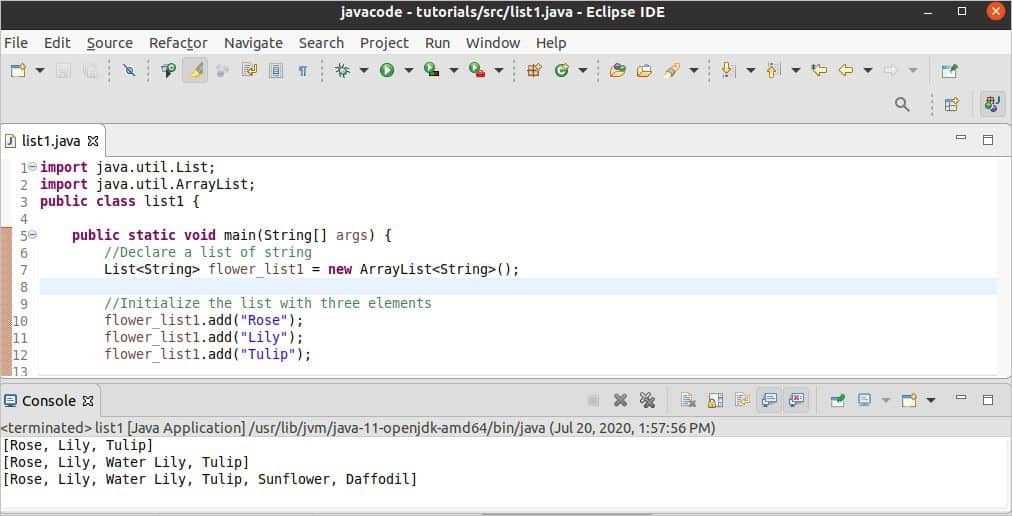
Two lists of string datatype are declared, and the different methods for inserting data to the list are used in the following example. An ArrayList named flower_list1 is declared, and three values are inserted serially using add() method. Next, another element is added by mentioning the insertion position. Another ArrayList named flower_list2 is declared, and two values are inserted like before. addAll() method is used to merge the values of flower_list2 at the end of the flower_list1.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class list1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a list of string
List flower_list1 = new ArrayList();
//Initialize the list with three elements
flower_list1.add("Rose");
flower_list1.add("Lily");
flower_list1.add("Tulip");
//Print the current list
System.out.println(flower_list1);
//Insert an element in the third position
flower_list1.add(2,"Water Lily");
//Print the current list
System.out.println(flower_list1);
//Declare another list of string
List flower_list2 = new ArrayList();
//Initialize the list with two elements
flower_list2.add("Sunflower");
flower_list2.add("Daffodil");
//Insert all elements of second list to the end of the first list
flower_list1.addAll(flower_list2);
//Print the current list
System.out.println(flower_list1);
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the code.
Example-2: Update and remove elements from a Java list
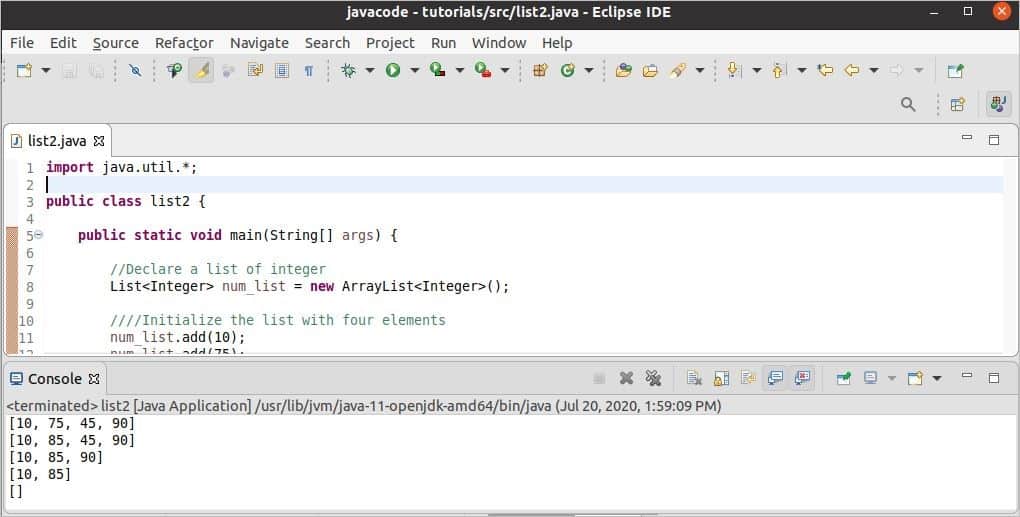
How the values of the list can be updated and removed are shown in the following example. A list of Integer datatype is declared here. Four numbers are added to the list using add() method. The set() method is used to replace the second value of the list. Next, two ways of deletion are shown here. Remove () method is used to remove the third element from the list, and the iterator object is used to remove the third value from the current list. The clear() method is used to make a list empty.
public class list2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a list of integer
List num_list = new ArrayList();
////Initialize the list with four elements
num_list.add(10);
num_list.add(75);
num_list.add(45);
num_list.add(90);
//Print the current list
System.out.println(num_list);
//Replace the second element and print the list
num_list.set(1,85);
System.out.println(num_list);
//Remove the third element and print the list
num_list.remove(2);
System.out.println(num_list);
//Declare an iterator
Iterator list_itr = num_list.iterator();
//Remove the third element using object
int counter=0;
while(list_itr.hasNext())
{
list_itr.next();
if(counter == 2)
{
list_itr.remove();
break;
}
counter++;
}
System.out.println(num_list);
//Remove all elements from the list
num_list.clear();
System.out.println(num_list);
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the code.
Example-3: Retrieve each element from a list using the loop
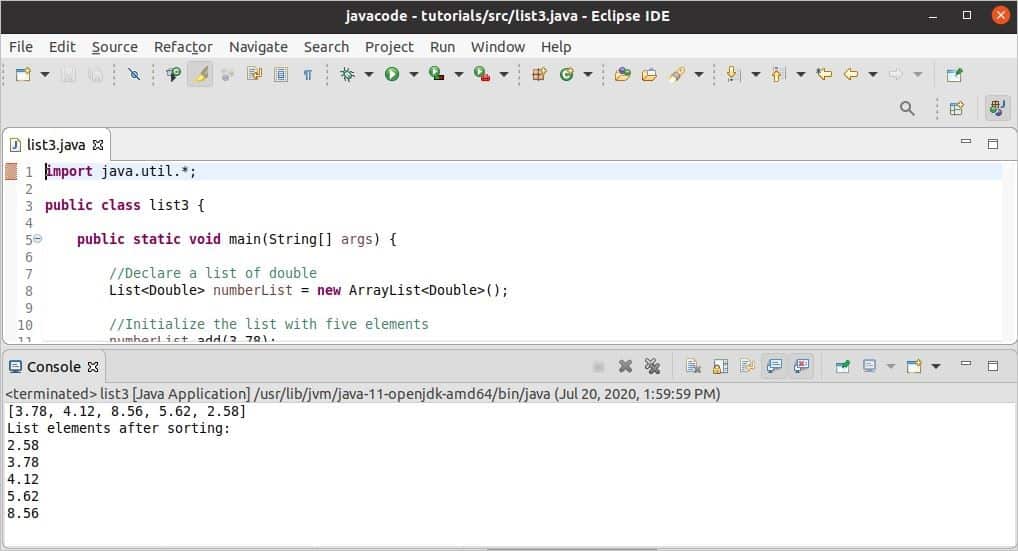
The list values are printed as the list in the previous two examples. This example shows the use of the loop to iterate each value from the list and print the value in each line. Here, an ArrayList of a double datatype is declared, and five values are inserted using add() method. Sort() method is used to sort the list before printing.
public class list3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a list of double
List numberList = new ArrayList();
//Initialize the list with five elements
numberList.add(3.78);
numberList.add(4.12);
numberList.add(8.56);
numberList.add(5.62);
numberList.add(2.58);
//Print the current list
System.out.println(numberList);
//Sort the list
Collections.sort(numberList);
System.out.println("List elements after sorting: ");
//Print the sorted list using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < numberList.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(numberList.get(i) + "\n");
}
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the code.
Conclusion:
Mostly used list methods are explained in this tutorial by using different ArrayList class. I hope the data insert, update, and delete tasks in the list are cleared after reading this tutorial, and the readers will be able to use the list in their code properly.