Potentiometers and rheostats are common electrical components used in various applications to control or measure resistance. Although there are similarities in their construction and functionality, notable differences exist between the two.
What is a Potentiometer?
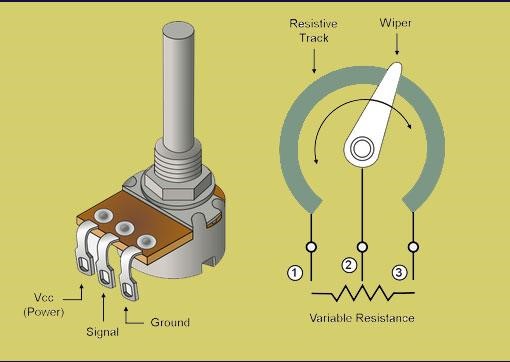
A potentiometer, often referred to as a pot, is a three-terminal variable resistor. The components of a rheostat include a resistive element, a movable contact (wiper), and two fixed contacts. By modifying the position of the wiper, the resistance between the wiper and a fixed contact can be adjusted accordingly. Potentiometers are commonly used as voltage dividers, position sensors, and volume controls in electronic circuits.
What is a Rheostat?
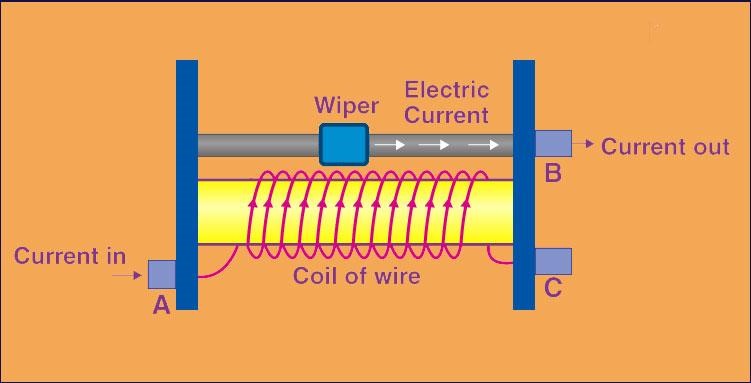
A rheostat is also a variable resistor, but it typically has only two terminals. A potentiometer comprises a resistive element and a movable contact (slider) that can be adjusted along its length, and the resistance can be altered by moving the slider. Potentiometers are primarily employed to measure and compare voltage or determine unknown resistance values, while rheostats are utilized to control current in a circuit by adjusting the resistance within the path.
Difference between Potentiometers and Rheostats
Despite having almost the same functionality, there are still some differences between potentiometers and rheostats, and the table below illustrates them:
| Characteristic | Potentiometers | Rheostats |
| Number of terminals | 3 terminals | 2 terminals |
| Function | Controls voltage | Controls current |
| Precision | Higher precision | Lower precision |
| Power consumption | Lower power consumption | Higher power consumption |
| Applications | Low-power applications, such as volume control in audio devices or position sensing in joysticks | High-power applications, such as dimming lights or controlling motor speed |
Conclusion
Potentiometers and rheostats are variable resistors that play crucial roles in electrical circuits. While both components enable the control of resistance, potentiometers excel in voltage control and position sensing applications, whereas rheostats are primarily used for current control purposes.