The entire process of updating containerized apps manually can be overwhelming and boring. Advancing a service to the next variant needs initiating the filtered version of the pod, terminating the out grade version of a pod, waiting and validating that the new variant has successfully been released, and occasionally moving back to the earlier version in the case of a botch.
If you perform all these tasks manually then there might be a chance of human errors, and properly scripting needs full potential and a substantial amount of effort. At last, they turn the launch process into a tailback.
To fix this issue, Kubernetes deployment makes the entire process repeatable and mechanized. However, the deployment confirms that the preferred number of pods is executing and vacant at all times. The entire update process is recorded and versioned with choices to continue, pause, and roll back to earlier variants. Here is the complete overview of Kubernetes deployment. Now, let’s proceed further to explain how to create or delete deployment in Kubernetes.
A Kubernetes Deployment executes many copies of your application and automatically substitutes any requests that fail or become impassive. When you are working with Kubernetes, you’ll frequently need to remove Kubernetes deployments. Creating or deleting deployments in Kubernetes is quite handy with the help of kubectl delete deployments commands. We’ll elaborate on the whole process of creating and deleting deployment in a bit more detail.
Pre-requisites
You will need to know your operating system version to remove a deployment in Kubernetes. In our situation, we use Ubuntu 20.04 operating system to implement kubectl commands. Once done with the OS your next step is to install the Minikube cluster on your system to smoothly run Kubernetes in Linux. Minikube provides a handy experience and a foster learning environment.
Methods to Delete Deployment in Kubernetes
Come, let’s check how to delete deployment in Kubernetes with the help of appended commands or steps.
Start Minikube
Once you successfully install the Minikube cluster, now it’s time to launch it with the help of two methods. The first method is to write “Terminal” from the Ubuntu 20.04 system application search bar or hit “Ctrl+Alt+T” simultaneously. Using these two methods, you can efficiently launch the terminal. Now, write the “start minikube” command in the terminal and wait a while until it gets successfully started.
Create Deployment
To delete deployment in Kubernetes we first need to create it as there is no built-in deployment. For this purpose, we first launch the Minikube and then use the given command to create a file in Ubuntu 20.04. The touch keyword in the below instruction creates the file.
Once you run the above-cited ‘touch deployment.YAML’ command the file is successfully created in Ubuntu 20.04. You can look it in the below screenshot.
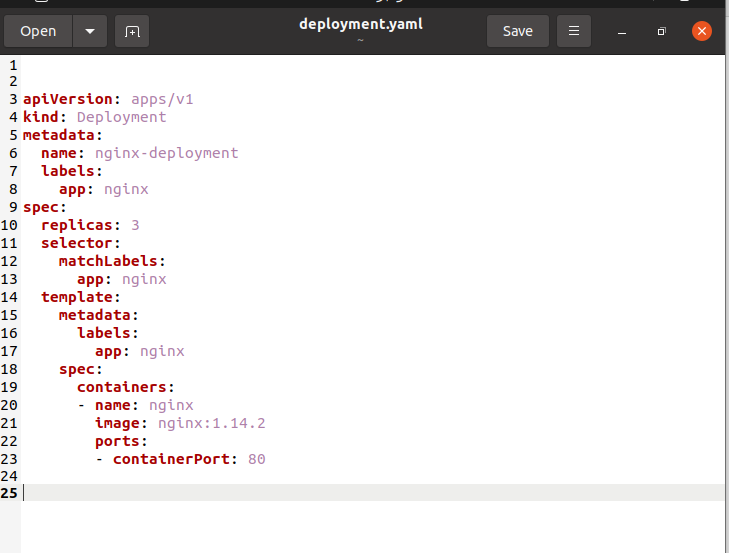
Now, save and open the file .yaml file. The appended screenshot is an illustration of a Deployment. It creates a DuplicationSet to carry 3 Nginx Pods.
The below screenshot states that:
- An nginx-deployment is formed, specified by the “.metadata.name” field.
- The nginx-deployment creates 3 identical Pods, specified by the “.spec.replicas” field.
- The Pod template contains the listed sub-fields:
- The Pods are categorized app: nginx using the .metadata.labels field.
- The “.template.spec” field, specifies that the Pods executes one container, nginx, which executes the nginx Docker Hub copy at 1.14.2 version.
- Form one container and specify its name using “.spec.template.spec.containers[0].name field.”
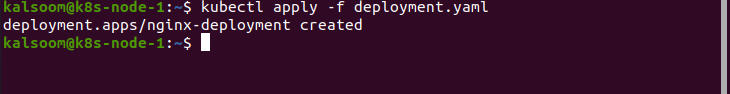
Our next step is to create the deployment. So, run the below-mentioned command:
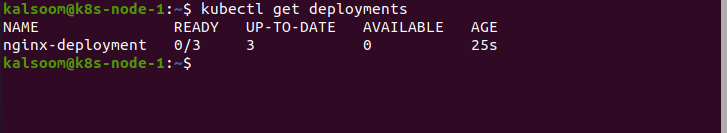
If you want to display the deployment to check whether it is created or not, then run the below command.
To check Deployments in your cluster, the appended fields are shown:
- NAME specifies the deployment names in the namespace.
- READY shows the availability of application replicas to your users.
- UP-TO-DATE prints the total of amount replicas that have been updated to get the chosen state.
- AVAILABLE specifies how many application replicas are offered to your users.
Delete Deployment
When we talk about delete deployment, we have two choices to remove them.
- Kubectl command
- Configuration file
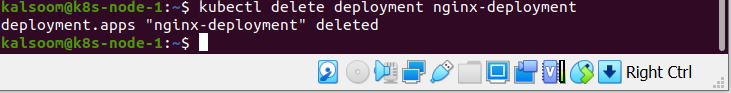
Here, we use the deployment name with the given command to delete the deployment.
The output shows that the deployment named “nginx” was deleted successfully.
Conclusion
So here in this guide, we have discussed the way through which you can create or delete deployment in Kubernetes. You may create any deployment depending on your work need. I hope you can now easily delete the deployment in Kubernetes.