Declaration and Assigning
This array has [2, 2] size. This shows that an array has two rows and two columns. We have implemented 2d array programs in different ways. Let us start elaborating on the functionality of 2d arrays.
Example # 1
Multidimensional array in C sharp is just like those in C++ and other programming languages. This array contains more rows and columns than a single array; hence the initialization of a 2d array is somehow different; we need to assign values in both dimensions by following the order of rows and columns. So the first example deals with declaring a 2d array. We will implement it in the program as we have seen the sample syntax. Declare the system library and the class to use the main program inside it.
Now, initialize the integer type 2d array named as “numbers”.
In this way, the integers to both the rows are initialized, having two columns each. This is the manual initialization of the elements of the 2d array. To access the items of an array, we will use a simple console statement to display the elements. First, we will display the first item of the 2d array of the first row so both the row and column values will be of zero indexes, as the array’s index starts from 0.
Similarly, for the first item from the second row, we will use the same statement; only the index number for the row will be changed. And, in the case of the second element from the second row, both the indexes of row and column will be incremented. [ 1, 1].
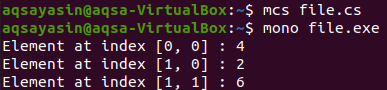
We will execute the previous code at the Ubuntu terminal. For this purpose, a compiler will be needed to assist the execution process. MCS is used to compile C sharp source codes. Furthermore, MONO will execute the compiled file with the “.exe” extension.
$ mono file.exe
You can see that the first two rows display the resultant value at index 0 in both rows. While the last one shows the second value in the second row.
Example # 2
After adding the items and initializing the array manually, we can alter the array by adding or removing items from it. This can be done easily by providing the details of items by specifying the indexes in rows and columns. As we declare and assign the values manually to arrays, it is easy to access and alter the items. Whereas for the loops, it becomes tough to search the item iterating through each element and then alter it. First, we have declared an array of [2, 2] sizes.
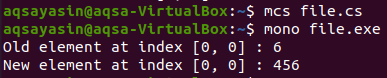
Display the items at the [0, 0] index before exchanging them with the new number. After that, assign the new number by using the following method:
By doing this, the first number will be replaced with the previous one. A directly assigned value removes the previous one automatically.
We will now display the value at the same index to confirm the replacement.
Example # 3
Till now, the methodology of accessing array elements was manually done. However, this approach can be changed by using loops in accessing multidimensional arrays. Loops can reduce the time complexity as compared to manual methods. Now, we will see the use of loops in C sharp 2d declaration and accessing.
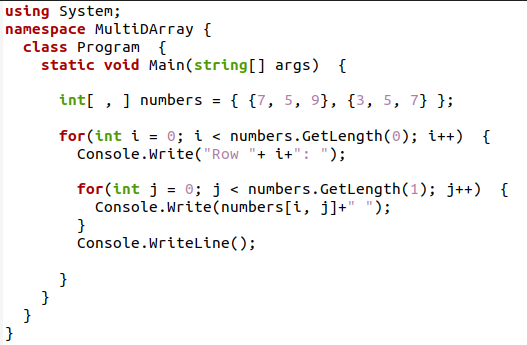
First, declare an array. We have not fixed the size of the array while the declaration; only the values are directly assigned. But the apparent size for a 2d array here is [2, 3], as it contains 2 rows and 3 columns.
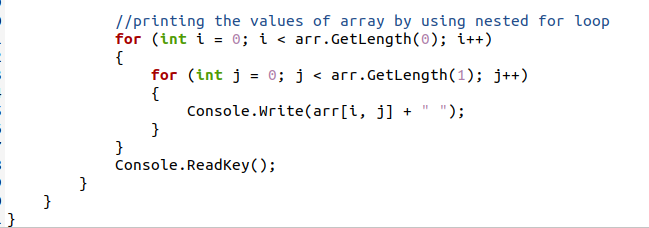
After the declaration of the 2d array, we will access the value through loops. In a simple one-dimensional array, a single for loop is used to iterate through an array. But in the case of a 2d array, we need two for loops; one is the outer for loop and the inner for loop. The outer loop is for the rows, whereas the inner loop represents the columns in a 2d array. As we have not mentioned the size of an array, so we will use GetLength(0); a built-in function to have the size of an array.
By using the size, the loop can iterate up to this extent. The outer loop will iterate only twice as the number of rows is 2. First, the outer loop starts and the inner loop iterates for each column in a single row. Then the outer loop is incremented, and the inner loop iterates for the second row until all the items are accessed and displayed. Two indexes are used for the inner loop, starting from the 0 indexes.
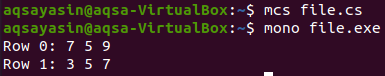
Now, compile and execute it in the console.
Each item of the respective row is displayed.
Example # 4
This example now deals with the looping mechanism in the C sharp 2d declaration and assigning values. The previous one was only displaying the items through a loop. We will dynamically declare the 2d array in the main program through the new operator.
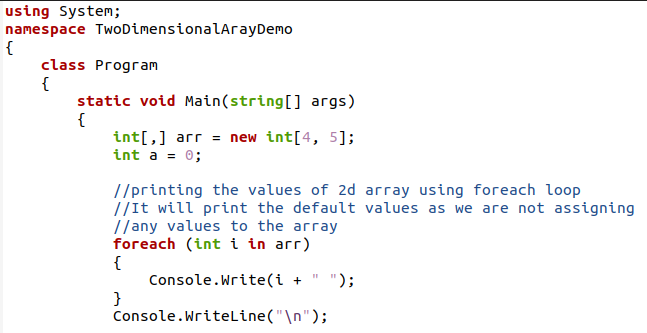
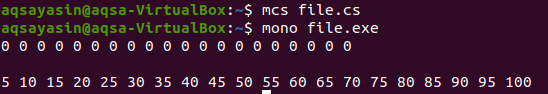
We will print the present value of an array. We have not assigned any value to the array yet, so by default; the value is 0 for each row and column.
Now, we will assign the values to the array by the nested loop.
arr[ I, j] = a;
We have used 5 numbers from the start, and each next index will take the new number obtained by adding 5 to the previous number.
Again, we will use the nested for loop to display the array’s items. This will follow the same technique as described above in the following example:
Now, execute the code. You will see that first, before declaring values, each index contains 0. Then each index of the array will have the number multiple of 5 up to the 20 number.
Conclusion
A multidimensional array is easy to declare by following the row and columns order in the array. A C sharp programming language is used to implement 2d arrays in Linux operating system. A 2d array is declared and accessed manually and through the loop. A multidimensional array is a collection of the one-dimensional array by increasing the area of items to be added in a single container in the form of a table. We have explained the implementation of a 3d array by simple declaration and assigning the values, replacing the value, and using loops in a 2d array.