In this descriptive post, we will guide you to create a database using MongoDB in Ubuntu. For this you must have following list of Prerequisites before creating a database:
Prerequisites
The list of prerequisites is quite simple, and it contains the packages required to create database in MongoDB:
- MongoDB must be installed on your system to perform any operation associated with MongoDB.
- The MongoDB shell provides a powerful command line support to perform database operations, specifically most used CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) operations.
How to create a Database in MongoDB
This section comprises several steps that must be followed for the creation of a database in MongoDB. Follow the steps carefully:
Step 1: Access the MongoDB Shell
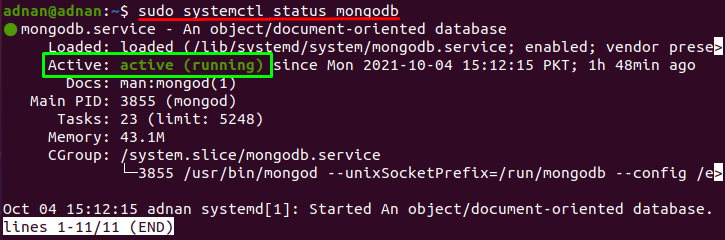
Open the terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and first check the MongoDB service status by using the following command:
The output of above command shows that MongoDB service is active and running:
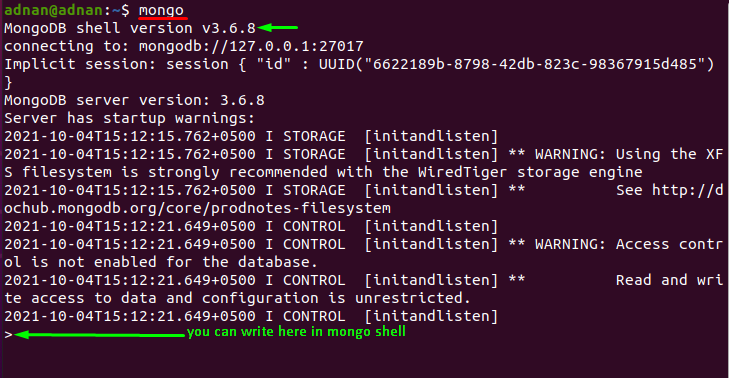
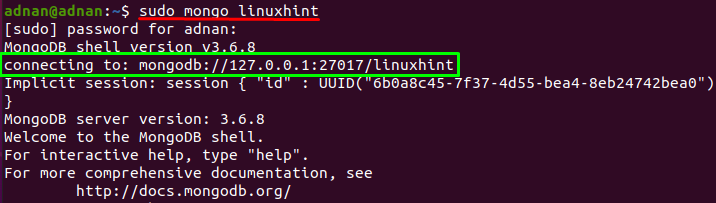
After that, access the mongo shell by using the below mentioned command in your Ubuntu terminal:
Step 2: Look for existing Databases
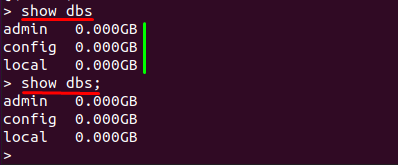
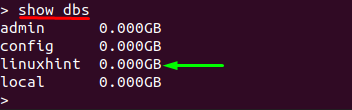
Once you have accessed the mongo shell, you can now check the databases currently listed on your MongoDB server. Use one of the following commands to check the available databases:
Or:
As the output shows, there are three databases currently on board: it is noticed that these are built-in databases.
Step 3: Create a new database
To create a new database using mongo shell; you must follow the proper syntax as mentioned below:
Following the above syntax; we have created a new database, “linuxhint,” with the help of following mongo shell command:
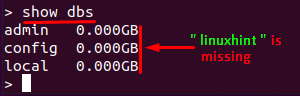
As we have only created an empty database; so, the system will not show it until we insert data into it:
Step 4: Activate the database.the
To activate the “linuxhint” database; we will use the following syntax to do so:
The “db” here refers to the selected database; “collection” is the name of the document you are inserting;
“({ })” contains the data to be inserted.
Before executing the command, you must ensure that you have selected the correct database; for this, use the following command in the mongo shell:
Or you can connect to the MongoDB database directly from the Ubuntu terminal; use the following command in terminal to connect to the “linuxhint” database:
Following the syntax, we have used the below-mentioned command to create a new user named as “jack”, its designation, and age.
Note: Once the command is executed successfully; it will show the output “WriteResult({“nInserted” : 1})”:
After inserting the document in “linuxhint”, verify that “linuxhint” is added to the databases list or not: to do so, execute the following command in the mongo shell:
How to drop a database in MongoDB using Ubuntu
Before executing the drop command, you must ensure that you are in the same database which you want to delete. You can check by using the “db” command in the mongo shell:
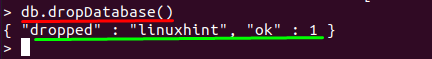
Now, if you will run the following command in your Mongo Shell; the “linuxhint” database will be dropped from MongoDB:
Conclusion
In this technologically rich era, automated management of data is the primary need of every organization. MongoDB is widely used as a DBMS (Database Management System) in IoT (Internet of Things), real-time applications, mobile applications, and content management. MongoDB provides extensive support for famous operating systems like windows, mac, and Linux-based distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, etc. This article aims at creating a database in MongoDB using Ubuntu as an operating system. The terminal support of Ubuntu is used to access MongoDB shells that are further utilized to create databases. With the help of mongo shell, we have created a database and inserted documents into it. The mongo shell support can also be used to perform other operations on databases like Update, Retrieve and Delete.