Google Chrome is one of the most widely used browsers right now. Google Chrome serves as the go-to browser for both desktop and smartphone users with its wide variety of features, privacy protection, and a huge selection of add-ons to choose from.
Updates in the security features of Google Chrome have allowed it to mark connections to different websites as “Secure” or “Not secure”. You might have come across these warnings when you visit certain websites.
This guide will help you understand the error and what steps you should take to get around or fix it. By the end of this guide, you should be able to navigate yourself through a website safely even if it has a “Not secure” prompt for it.
HTTP vs HTTPS
It is necessary to understand the difference between HTTP and HTTPS to understand why you’re getting the “Not secure” prompt when you browse certain websites.
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. It is a protocol that establishes effective communication between a web server and a browser. It allows you to share media-based documents such as HTML.
Despite being the go-to protocol when it came to online communication, HTTP does not possess encryption methods, nor does it provide authentication methods. You’ll normally see the site is not secure warning when browsing a website using the HTTP protocol.
Most websites switched to HTTPS with the “S” in the name meaning secure. This version provides them with proper authentication methods along with encryption.
SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are another way your browser verifies the security of a website. These certificates serve as proof that the website you’re visiting is safe and probably uses HTTPS as the protocol.
SSL certificates can be obtained in different ways. Website owners can apply for SSL certificates online after verifying their site information and generating CSR (Certificate Signing Request) for their domain.
What Does It Mean If a Website Is “Not Secure”?
Browsing websites that is not secure can potentially be dangerous.
If a website does not have an SSL certificate or uses HTTP instead of HTTPS, it implies that the website doesn’t have any strong means of protecting your information. This means that any personal information that you give on these sites can be stolen pretty easily by hackers.
It should be noted, however, that “Not secure” doesn’t imply that the destination is affected by malicious malware. So, visiting the website won’t necessarily give you malware or virus on your computer.
Visiting these sites, however, means that you’re leaving your information prone to attacks, as any information you enter can be compromised easily.
How to Identify if a Website Is Secure on Chrome?
Thanks to Google Chrome, identifying these websites has never been easier. Chrome’s advanced security features allow it to automatically detect whether the websites or servers have a valid SSL certificate.
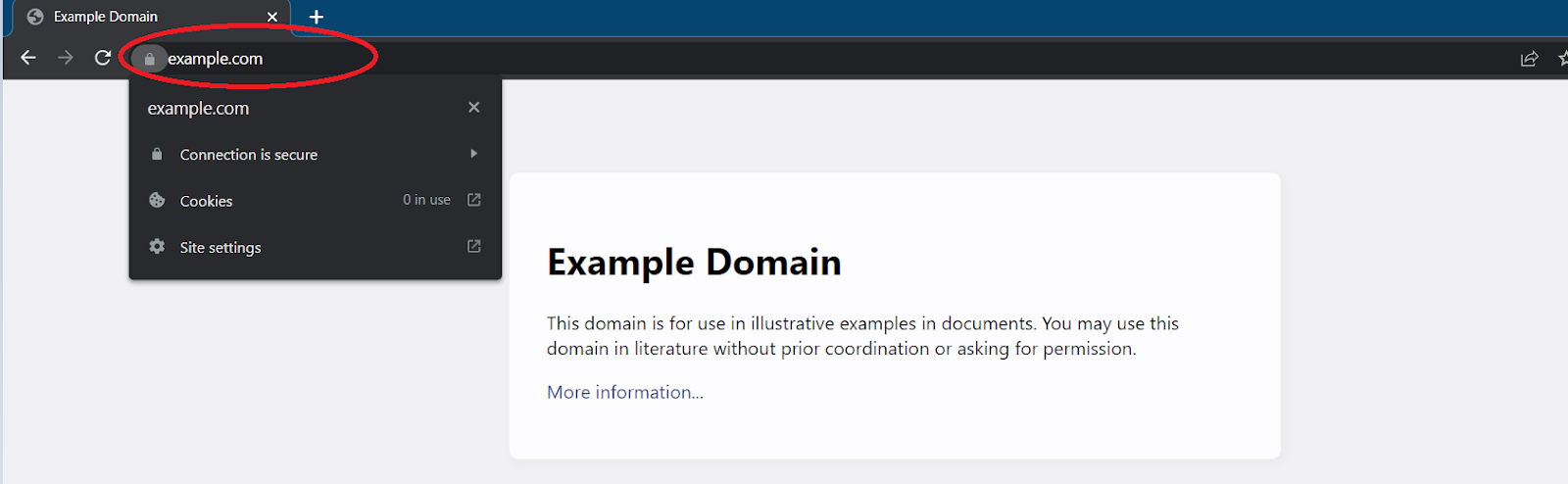
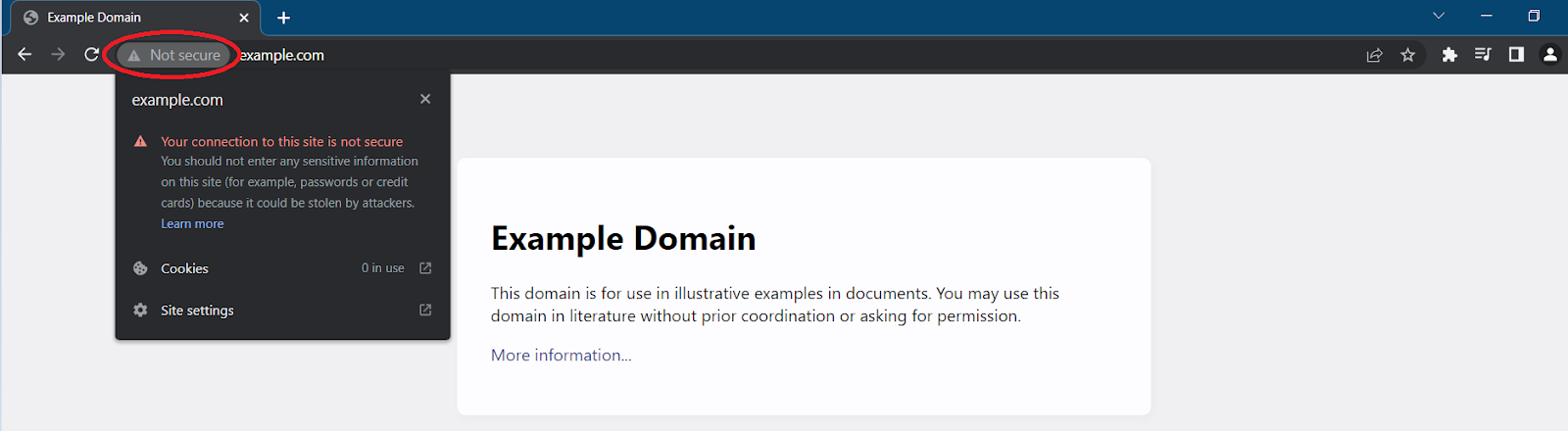
When you open a website in Chrome, it marks it as secure or not secure. This is represented by a “lock” icon in the search bar.
When a website is secure, you should see a closed lock icon as shown in the image below. Clicking on the lock will show you that the connection is secure.
When a website is not secure, you should see a quarantine icon with the text Not secure as shown in the image below. Clicking on the icon will present you with more details.
It is advised that you keep an eye out for these prompts as they’ll prevent you from providing personal information to potentially harmful websites.
What to Do if a Site Is Not Secure?
In case the website you’re visiting is not secure, here’s a list of things you should remember in case you have to use it.
- Don’t conduct any personal transactions on these websites. Since these websites are not secure, providing your information to them will most likely result in your information being compromised.
- Try using these websites as less as you can. Remember that even if you’re just viewing site information, you’re still very prone to attacks since your activity can easily be monitored.
- In case you have to use these websites regularly, try contacting the site owners and asking them to switch over to HTTPS rather than HTTP.
Conclusion
We hope this guide helped you understand what to do when you’re prompted with a not secure option on Google Chrome. We covered some basics of HTTP and HTTPS, along with how to identify your connection as “Secure” or “Not secure” on Chrome and what you can do when browsing insecure sites. With this, we hope you have a safe browsing experience.