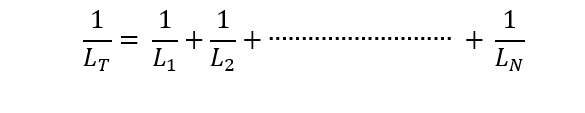Inductors play a crucial role in electrical circuits, and understanding how to connect them correctly can greatly impact circuit performance. Whether you’re designing a complex electronic system or working on a simple circuit, knowing how to connect inductors in series and parallel is essential. This article will provide a step-by-step guide on connecting inductors in series and parallel configurations.
Inductors
An inductor is an electrical component that is passive in nature and has the ability to store energy within a magnetic field as electric current passes through it. It is commonly composed of a coil made of insulated wire. The inductance of an inductor increases with the number of turns in the wire coil, meaning that a greater number of turns leads to a higher level of inductance.
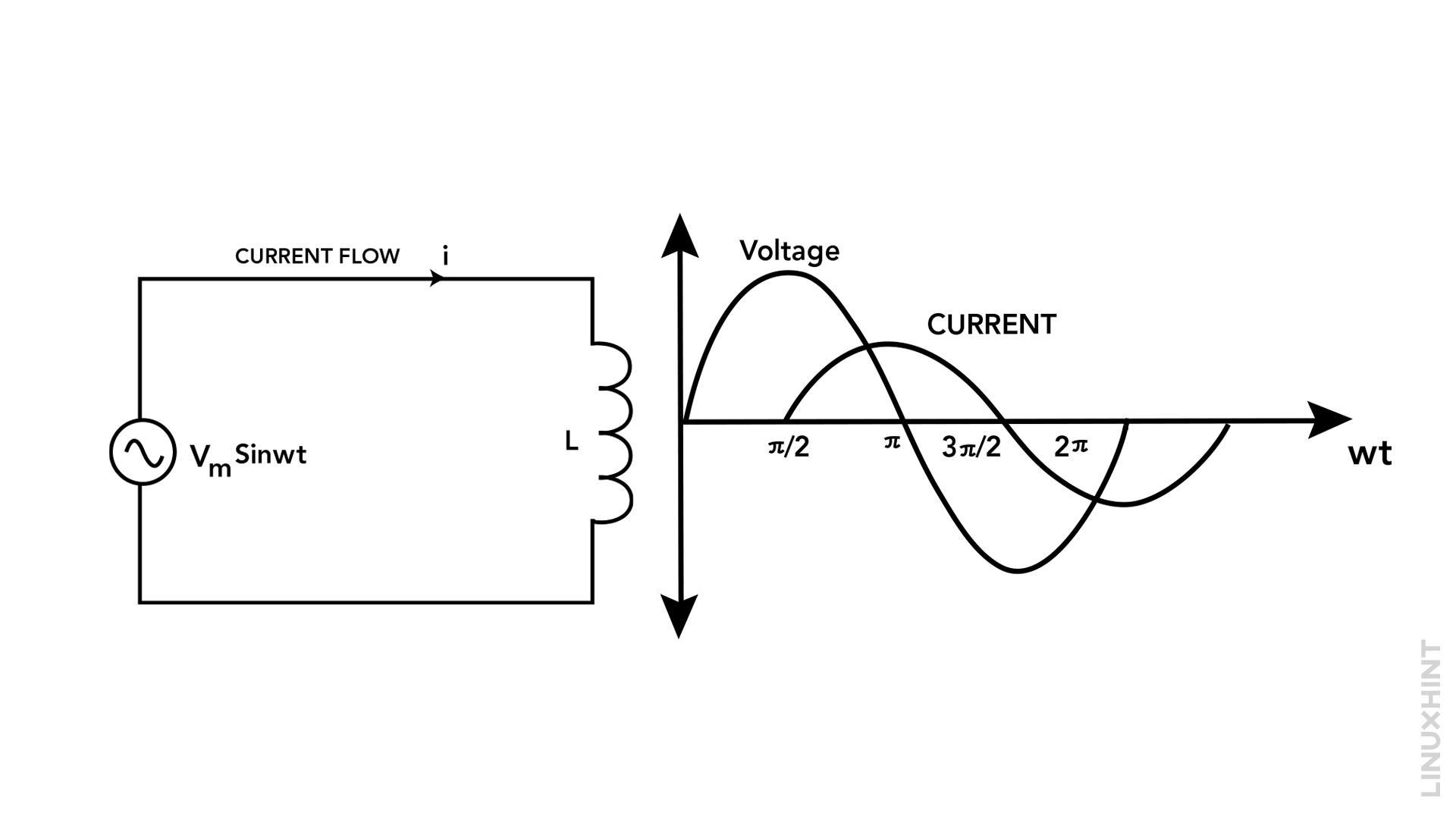
A magnetic field surrounds the coil of an inductor as an electric current passes through it. The magnitude of the current flowing through the coil exactly correlates to the strength of this magnetic field.
The phenomenon known as self-inductance refers to the inherent tendency of an inductor’s magnetic field to resist any alterations in the current that passes through it. This means that the magnetic field generated by the inductor opposes changes in the current flow, leading to the concept of self-inductance.
If the current is increasing, the inductor’s magnetic field will increase, which will create a voltage across the inductor in the opposite direction of the current. This voltage will oppose the increase in current.
If the current decreases, the inductor’s magnetic field will decrease, creating a voltage across the inductor in the same direction as the current. This voltage will oppose the decrease in current.
Connecting Inductors in Series
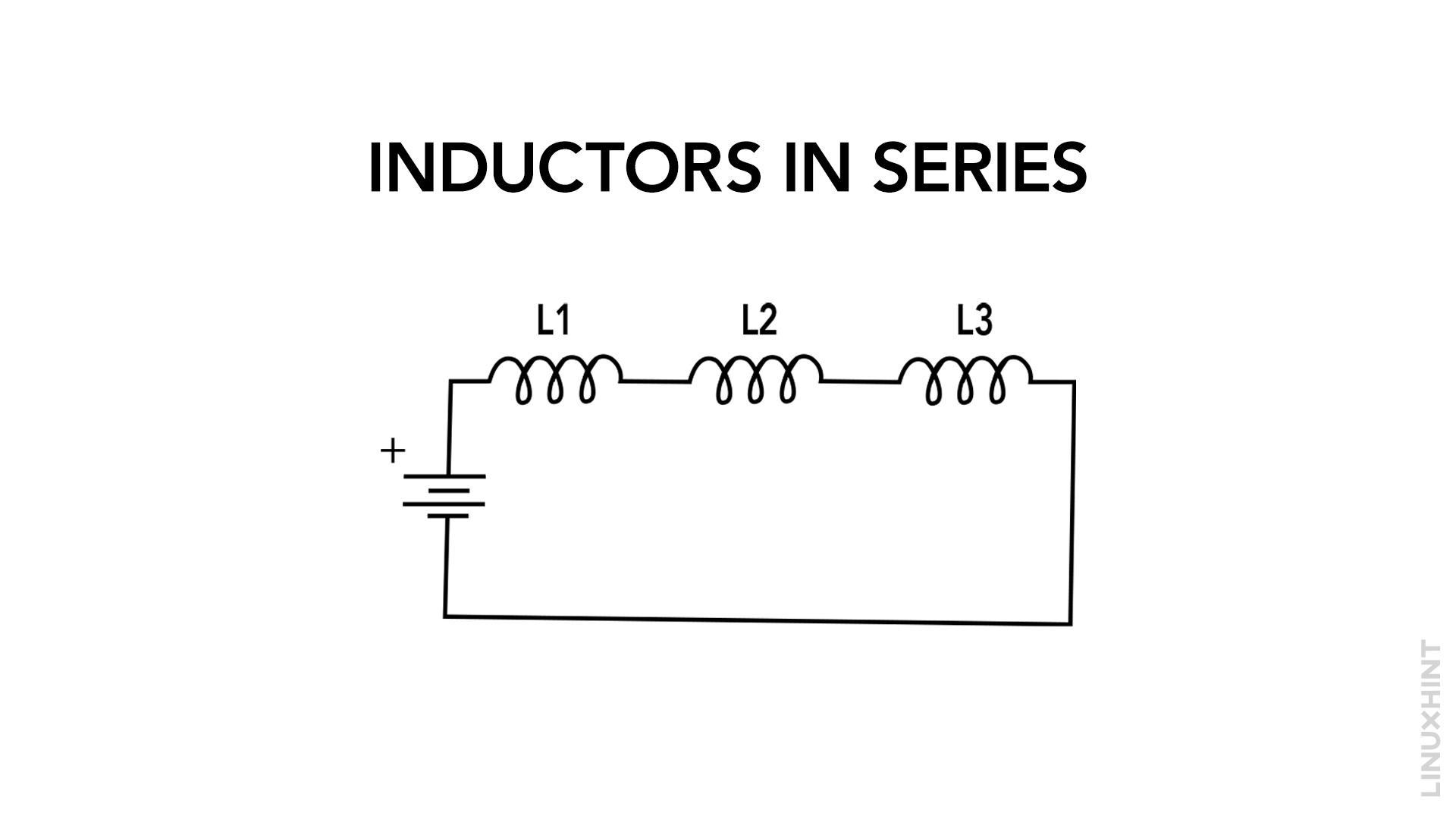
When multiple inductors are connected in series, their combined inductance is greater than that of individual inductors. Connecting inductors in series follows a straightforward process:
- Identify the inductors: Gather the inductors that you want to connect in series.
- Connect the terminals: Connect one terminal of the first inductor to the positive terminal of the battery or voltage source.
- Complete the circuit connection by linking the remaining terminals: Join the negative terminal of the first inductor to the other terminal of the second inductor.
- Calculate total inductance: The total inductance (LT) of the series-connected inductors is the sum of individual inductance values
Connecting Inductors in Parallel
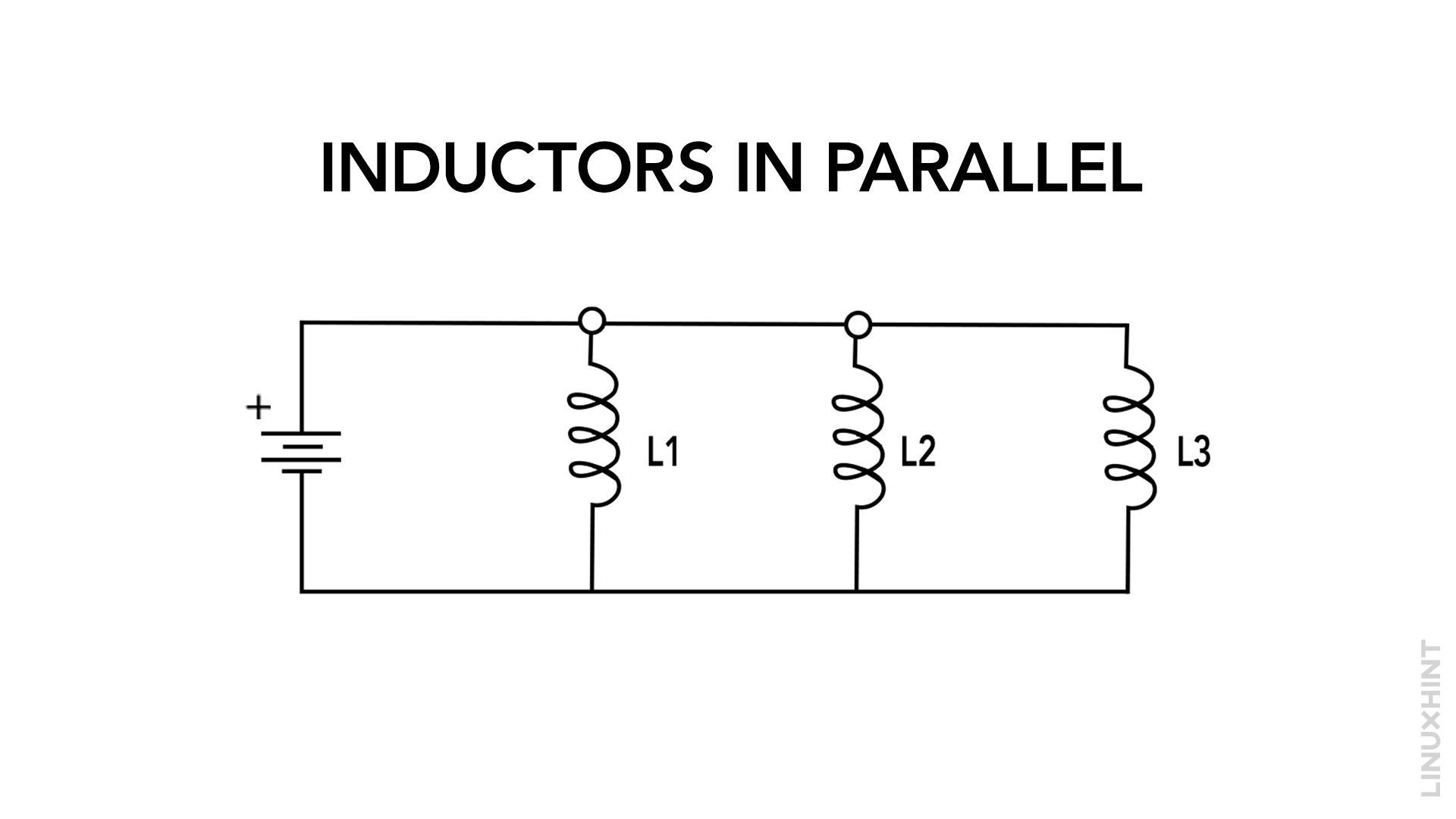
When multiple inductors are connected in parallel, their combined inductance is lower than that of individual inductors. Connecting inductors in parallel involves following a step-by-step process:
- Begin by identifying the specific inductors that you intend to connect in parallel.
- Establish the connection between the terminals by linking the positive terminals of all the inductors together.
- Connect the remaining terminals: Connect the negative terminals of all the inductors together.
- Calculate total inductance: The total inductance (LT) of the parallel-connected inductors is calculated using the formula:
Conclusion
Properly connecting inductors in series or parallel is crucial for achieving desired circuit characteristics. By adhering to the step-by-step instructions provided within this article, you will be able to successfully connect inductors in your preferred configuration. Remember to consider the benefits and considerations of each connection method based on your specific circuit requirements.