Check disk space and usage
Most commonly used commands for checking disk spaces or usage or free spaces are df, du and free. The use of these commands with various options are shown in this section.
df command:
df command is used to get the details disk spaces information of the file system. Here, df stands for disk filesystem. Many options can be used with this command to check the disk space related information in different ways. The function of some options are explained below using examples.
–help is the common option for any command to get all information for using the command. Before using df command you can run df command with –help option to get detail information about the use of this command.
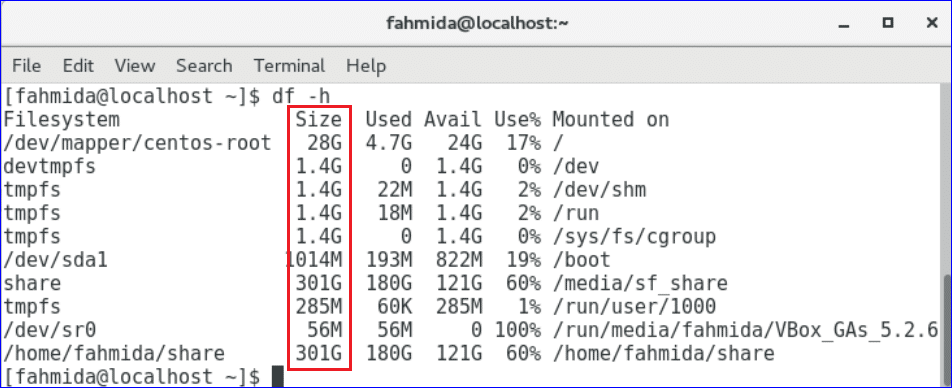
-h option is used with df command to display the disk space in human readable format. Disk space value will be shown in GB and MB.
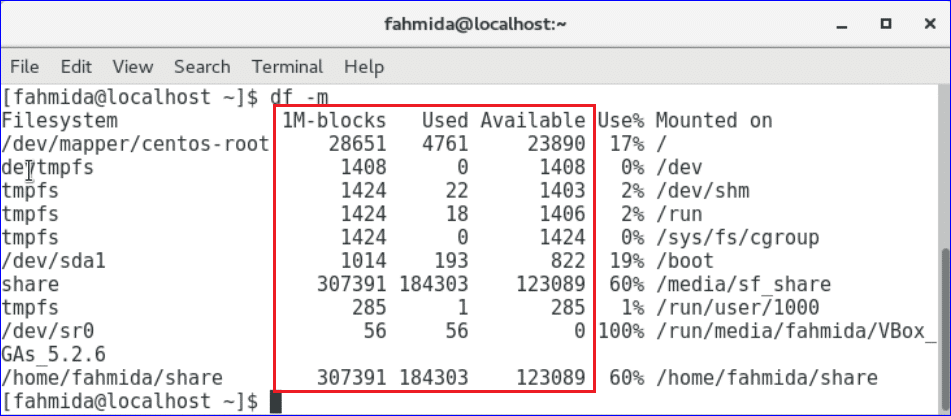
-m option is used with df command to show the disk space in MB.
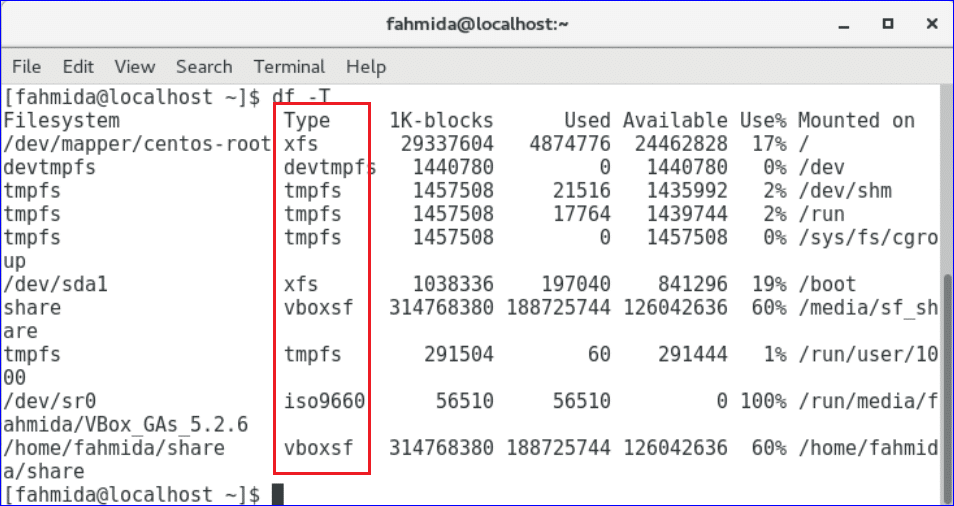
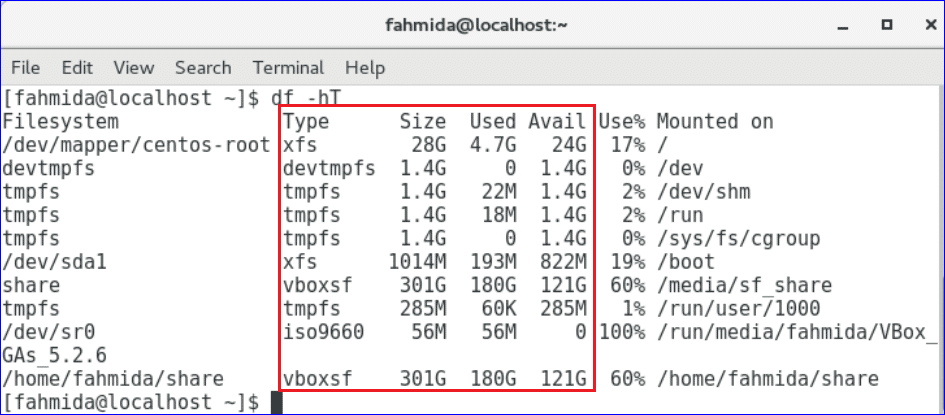
-T option is used with df command to show the file type.
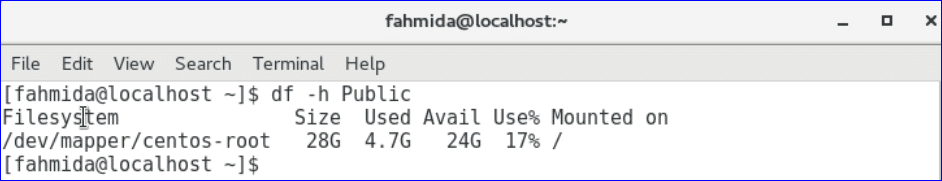
You can show the disk space information of any particular folder in human readable format by using above command. The output will show the disk space information of Public folder.
You can use two options -hT together to get the file types in human readable format.
du command:
Another useful command to find out the usage information is all files and folders. Here, du stands for disk usage. This command retrieves information of folders and sub-folders and files recursively. So, this command can be used to get more detail information of disk usage. The options mentioned for df command is also applicable for du command, but the output will be different.
The output will show all options to use du command.
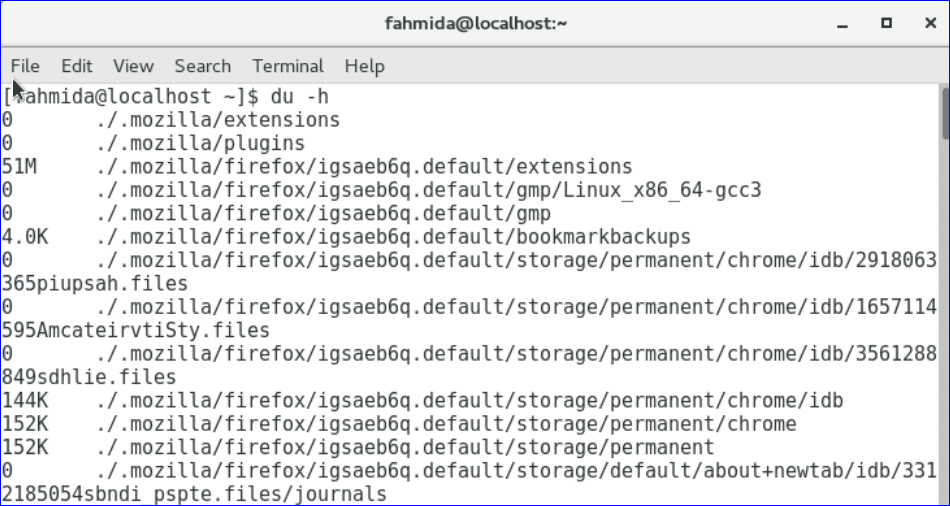
The output will show the size information of files and folders in more human readable format.
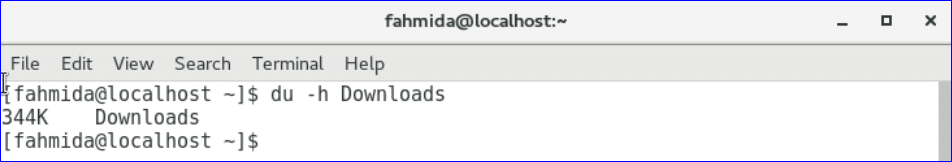
The output will show the size of Downloads folder.
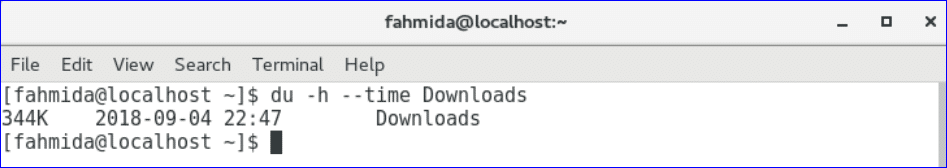
The output will show the size of Downloads folder with last modification time.
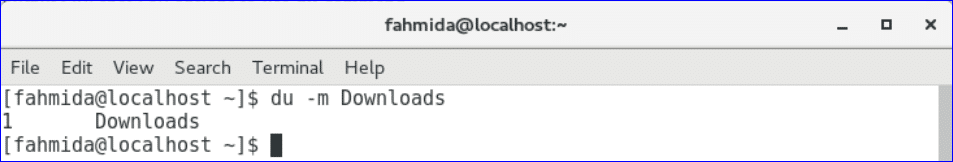
The output will show the size of Downloads folder in MB.
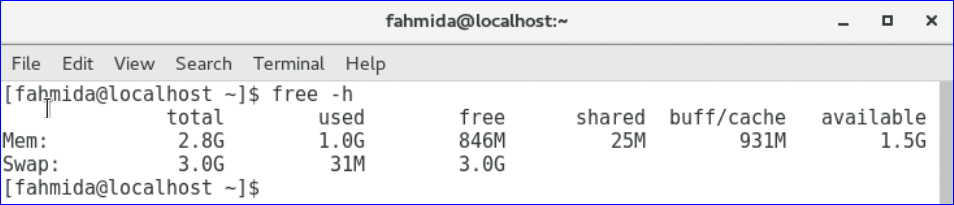
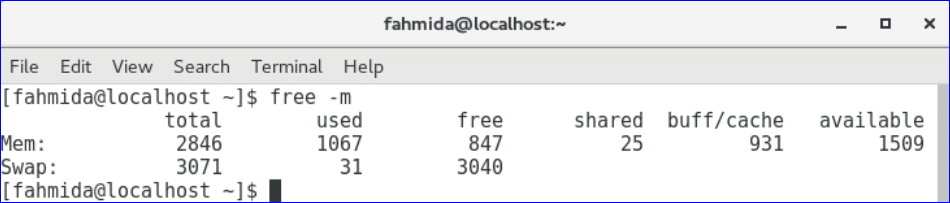
free command:
free command is used to get the detail used and unused information of the computer memory and swap. You can also apply –help, -h and -m option with free command like previous commands.
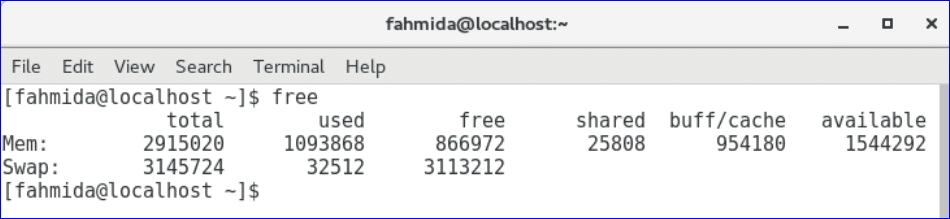
The output shows the memory and swap usage information in byes.
The output shows the memory and swap usage information in GB and MB.
The output shows the memory and swap usage information in MB.
Monitoring disks:
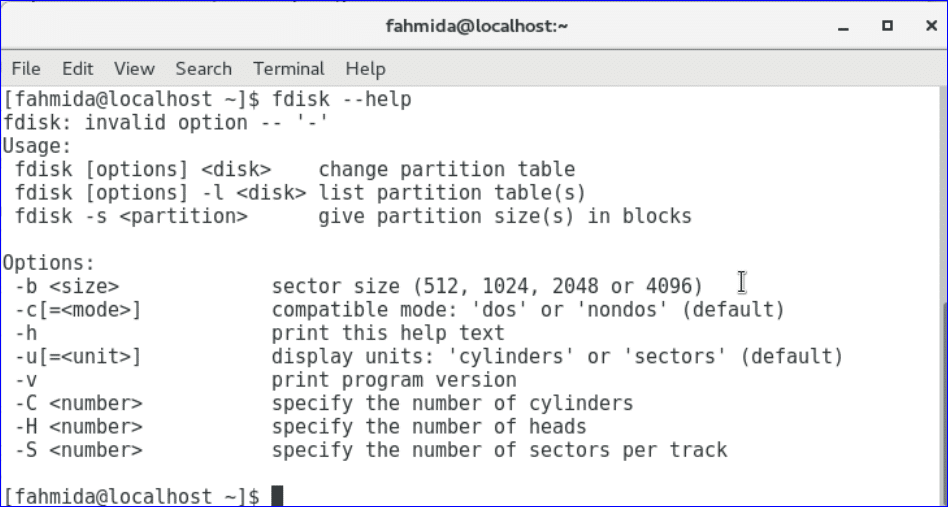
Many tools are available in Linux operating system to monitor the disk. Some of them are built-in and some tool you will need to download and install before use. One of the mostly used built-in tool to monitor the partition of the disk is fdisk. Using this tool you can not only monitor the disk partition but also create, move, copy and delete disk partitions. You must have root privilege to run this command. How you can use this command on CentOS operating system are shown using various examples in this section.
Run the above command to know the detail information of fdisk command for using it.
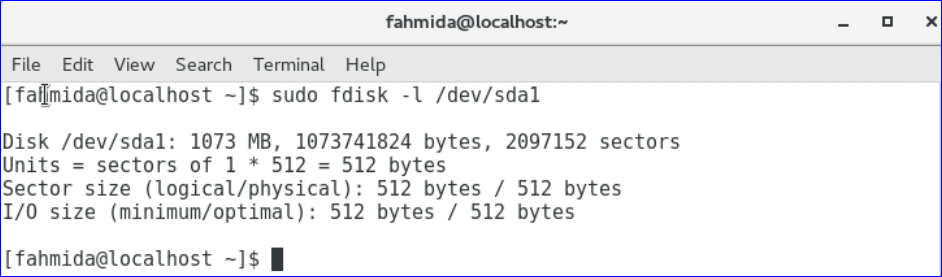
-l option is used to get information about all available partitions on your operating system. You have to provide root password to run this command.
You have to mention the device name with –l and fdisk command for getting the information of specific partition or device.
You can print the output of any device by executing fdisk command with device name. When you will run the command, a prompt will appear to take the next command if the device name exists. Type ‘p’ to print the output.
Conclusion:
The basic uses of df, du, free and fdisk command are shown in this tutorial. Many other fdisk commands are available to modify the disk partitions like creating new partition, deleting existing partition etc. For a video on this topic see below: