A defibrillator is a machine that generates an electrical shock for a short period of time to regain a stable rhythm of the heart. Capacitors are normally used in defibrillators instead of batteries to provide such an instant shock. However, in portable defibrillators, batteries are used as a power source to charge up the capacitors.
Capacitors are storing devices that absorb any extra energy in the circuit or the transients in the system and then release the charge stored in them when needed. Moreover, they also act as short-term batteries that charge and discharge quite rapidly unlike conventional batteries, though they cannot hold the charge for a longer time.
Outline:
How Does a Defibrillator Work?
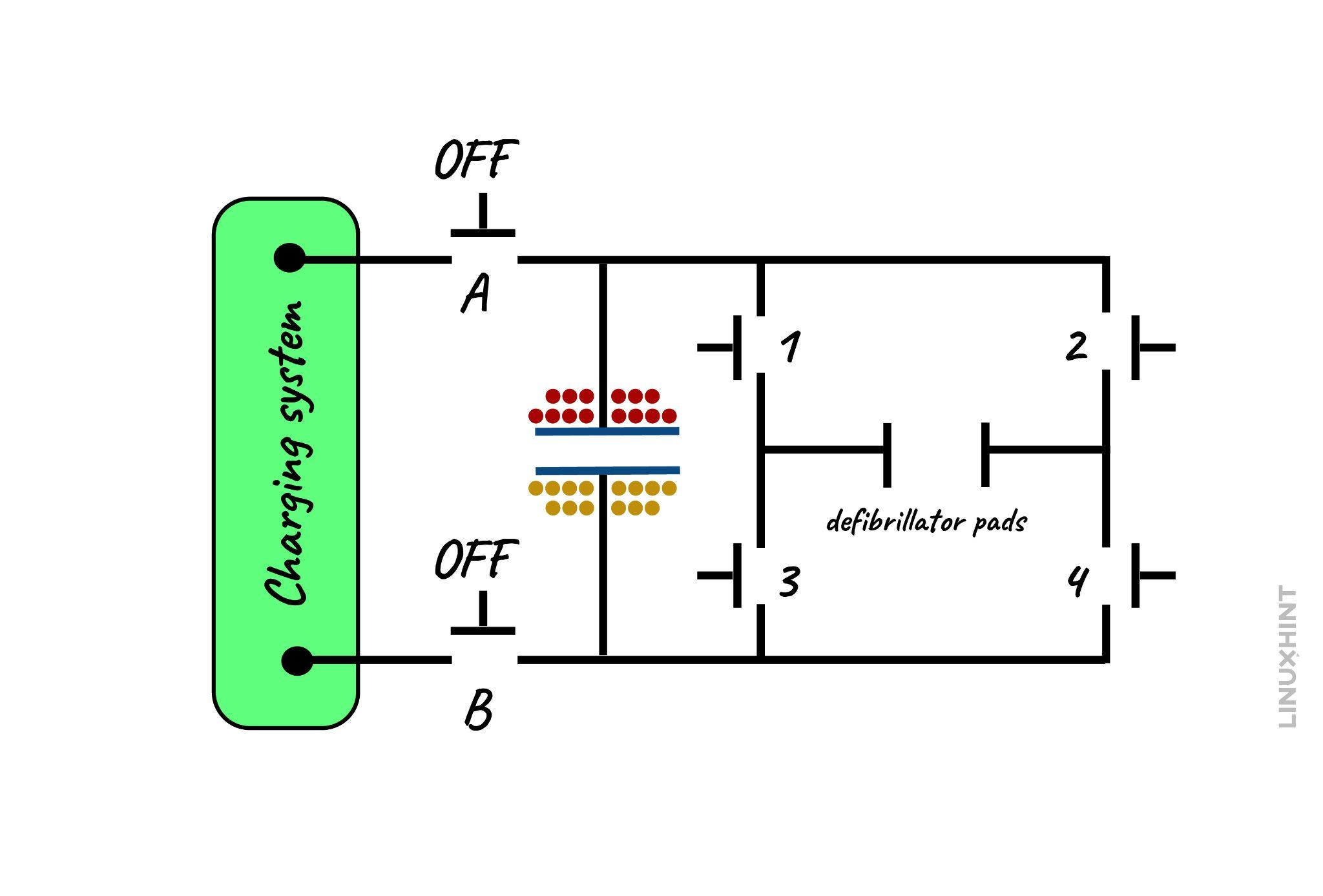
To understand the reason why capacitors are used in defibrillators it is necessary to know the working of the defibrillator. So, defibrillators have two circuits, one is responsible for charging the capacitor and the other is for discharging the capacitor. The process of charging and discharging is done by a small computer inside the defibrillator but to illustrate here is a simple circuit of a defibrillator:
In the above circuit switches, A and B are responsible for the charging of the capacitor whereas switches 1,2,3,4 are responsible for discharging the capacitor. When the power is turned on switches A and B are in on state, and the charging of the capacitor is started:
Once the capacitor and the charging system are on the same potential, the switches A and B go to OFF state which means that the capacitor is fully charged.
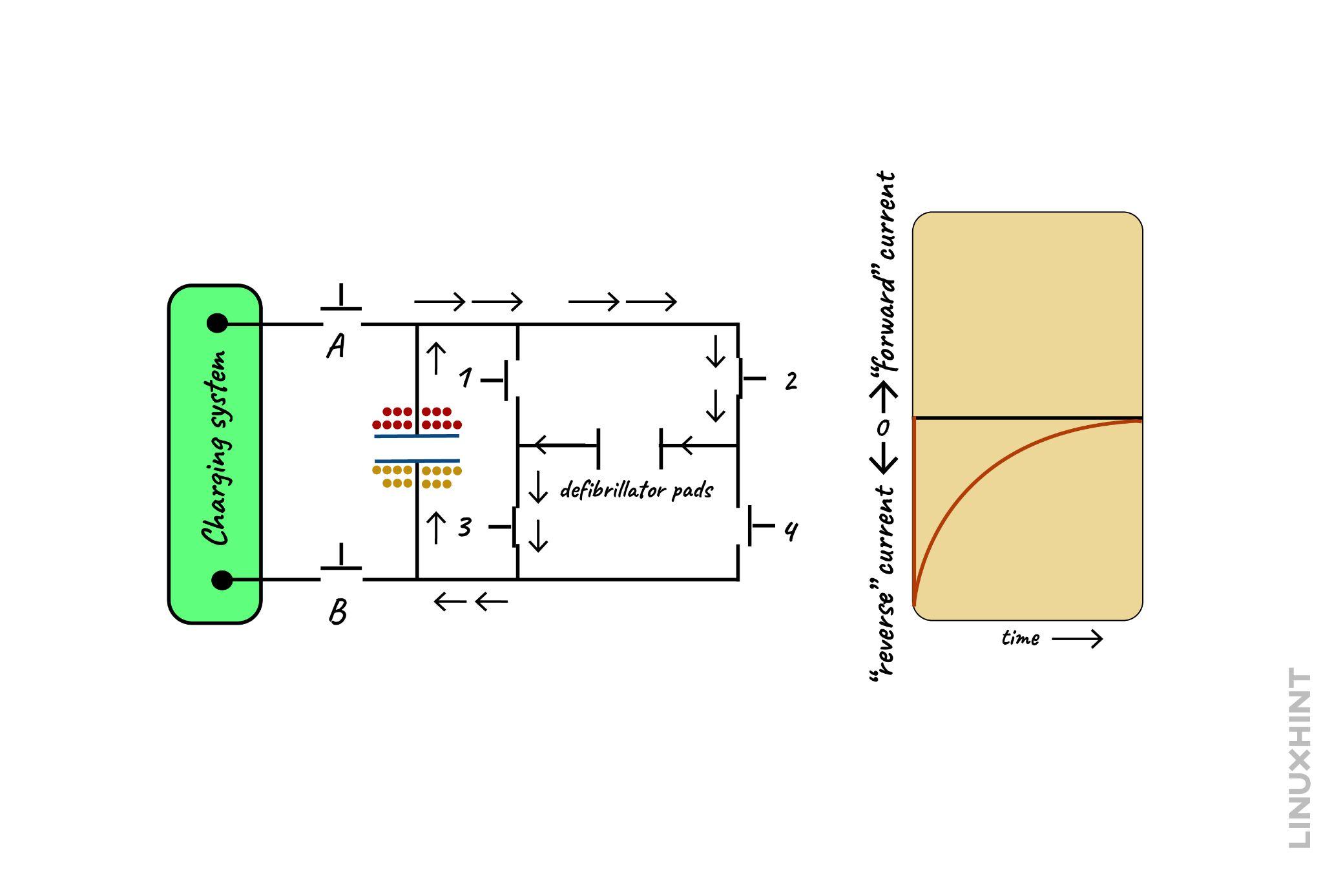
Now when the probes of the defibrillator are attached to the designated area of the body the capacitors start to discharge resulting in an instant shock to the heart. First switches 1 and 4 are closed and the current starts to flow, and this direction of current is known as the forward direction.
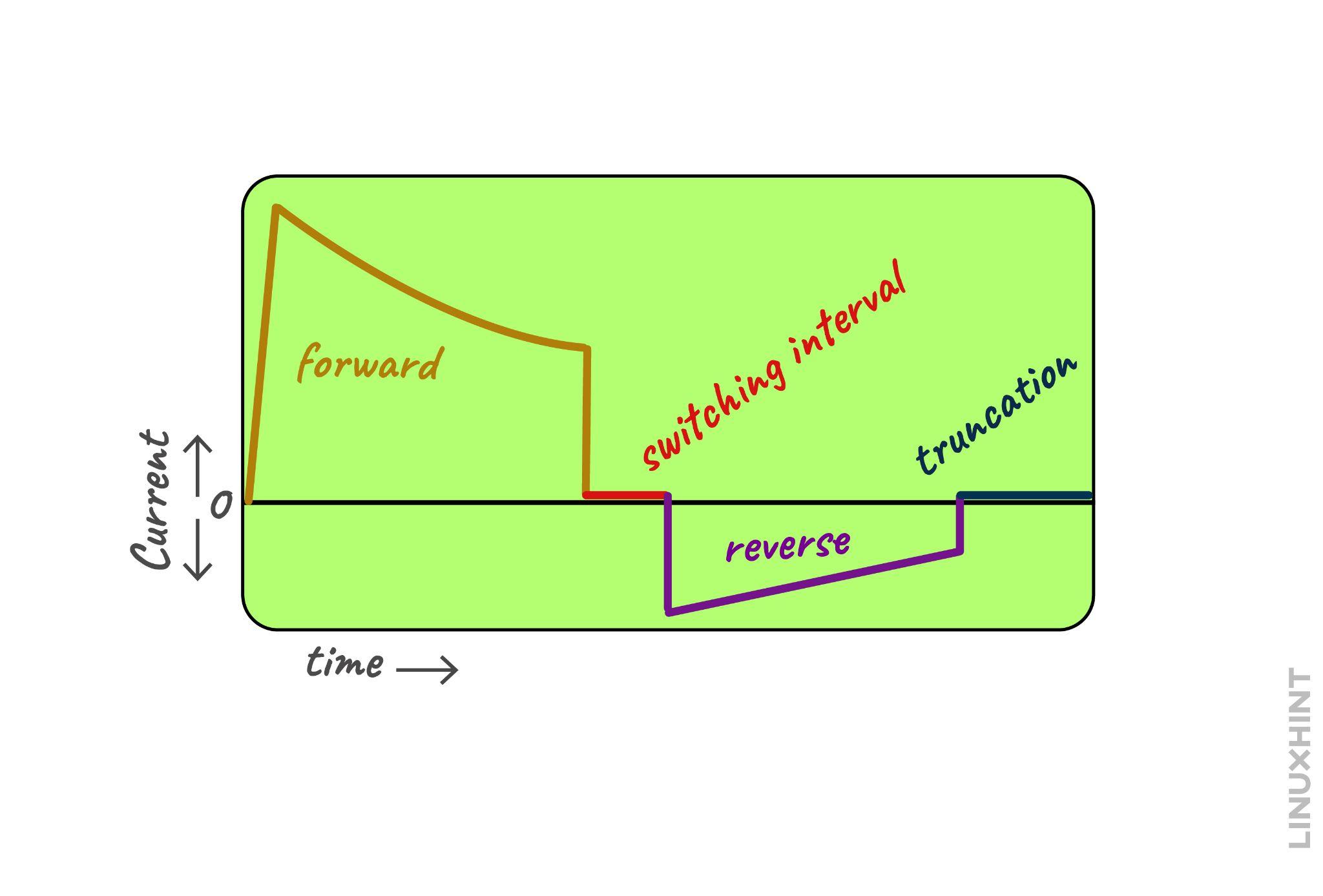
After some time, the direction of the current will change and it will start to flow in the opposite direction, the waveform it shows is named as biphasic waveform.
Now once the graph reaches zero permanently this means that the capacitor is fully discharged and here is the waveform of the defibrillator:
The switching interval here is the time when the current changes its direction and all four switches of the discharge circuit go into the OFF state to avoid a short circuit.
Why is a Capacitor used in a Defibrillator?
The capacitor, as compared to the batteries, can store charge rapidly because of their smaller size and advanced technology. Moreover, the defibrillator requires a significant amount of voltage at the output, which a battery cannot provide due to the size constraint.
Batteries usually use chemical reactions to store and release the energy and this puts a limit on how fast it can be charged, and the same is the case for its discharge. Moreover, the batteries start to degrade faster as compared to the capacitors, and thus their charging capacity also decreases. This draws the conclusion that batteries cannot hold high voltage levels for extended periods of time.
On the other hand, the capacitors due to their composition can store high voltages quite easily in less amount of time. Moreover, the life span of the capacitor regarding its capacity for storing the charge is quite high especially when it comes to supercapacitors. With a capacitor, instant shock can be delivered easily due to the rapid discharge with a constant flow of current without any sparks.
Conclusion
A defibrillator is an electrical device that produces a shock that helps the heart regain a stable rhythm or provides treatment for ventricular fibrillation. Usually, to provide a high voltage shock to the heart there is a capacitor used which is charged by either a power supply or a battery. The use of capacitors is preferred because of their rapid charging and discharging, their ability to store high voltages and their stable output.