For converting light energy into electrical energy without any mechanical movement, solar panels are used as they contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that produce electricity when subjected to light. An important point related to PV is that it works on light not on heat, so the cold PV cells are more efficient.
Role of Bypass Diodes in Solar Panels and Arrays
Solar panels are made up of solar cells and the solar cells are constructed by the layers of semiconductors. N-type and P-type layers are created, and excess electrons are created by how one layer is treated with the substance, and this results in an N-type layer. If the deficiency of electrons is created by the other layer, then this results in a P-type layer.
Use of Diode in Photovoltaic cell
The diode always acts like a one-way switch, meaning the current can only pass through it when it is connected in a forward bias direction. The main advantage of the diode is that it blocks the current coming from different parts which saves it from any kind of loss, and this diode is also known as a blocking diode. PN junction diode and Schottky barrier diodes are the most popular diodes and are used as the bypass diode due to their best performance:
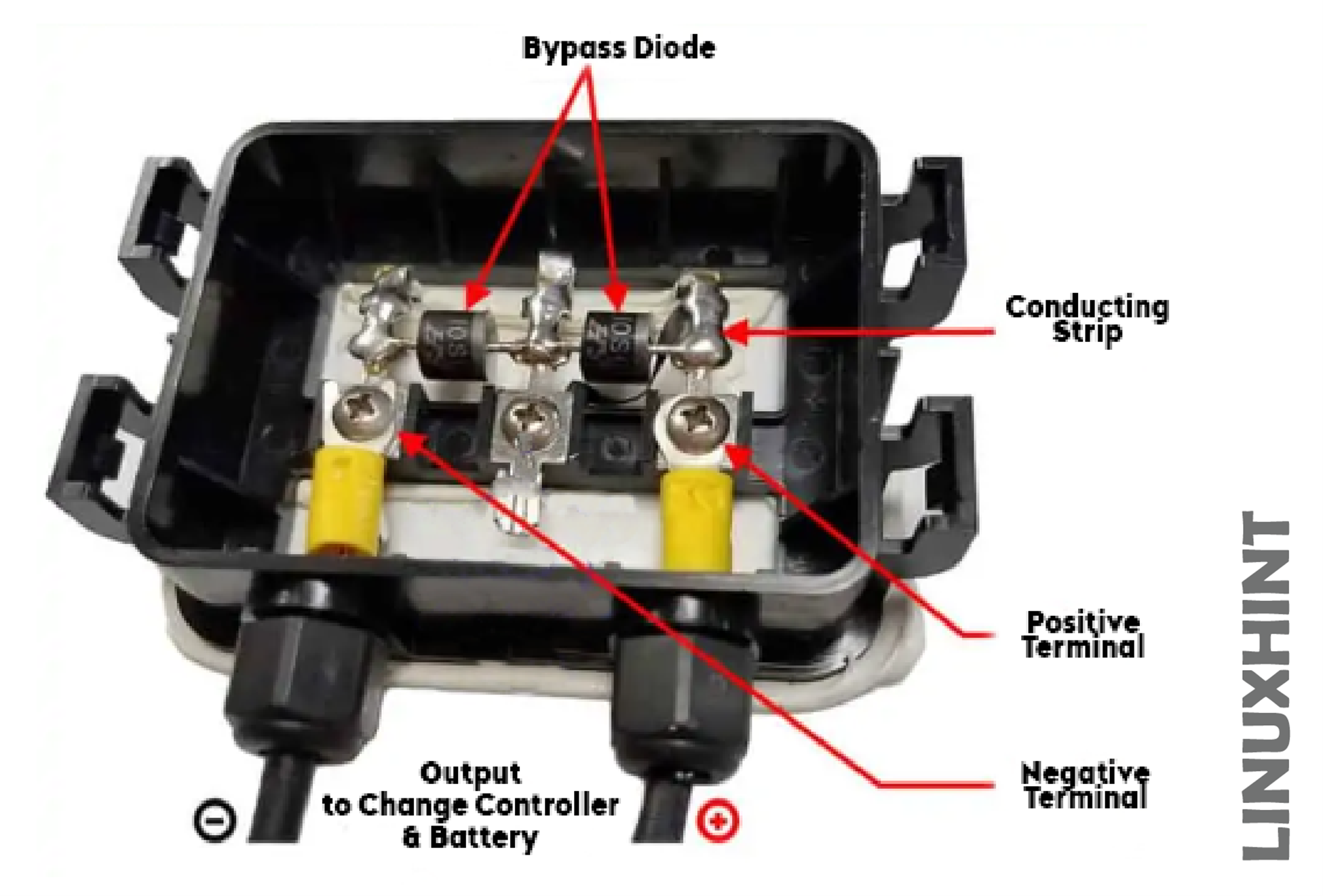
Solar Panel with Bypass Diode
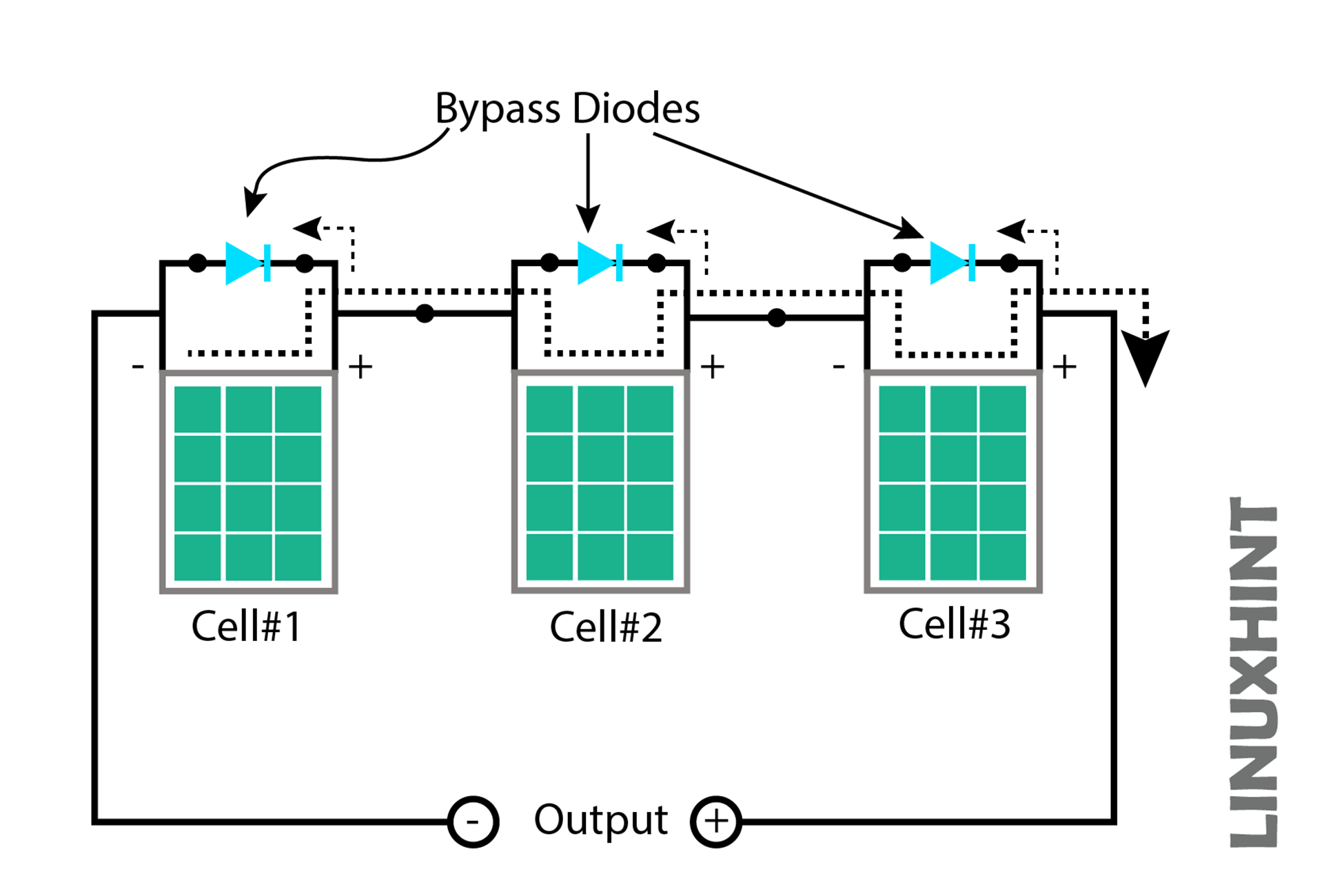
The bypass diodes primarily restrict the current flow to the cells that are receiving enough amount of light and pass it through the cell that is receiving quite less amount of light, which in turn prevents that cell from getting damaged:
The bypass diodes are connected in parallel with the PV cell, these diodes are used to block the current pass from well-exposed cells to prevent it from overheating, and burnout and provide the current to the partially shaded cell.
In this case, there is a cloud on cell 2, due to this shade it becomes a load instead of generating electricity. Here the bypass diode starts its role and diverts the direction of the electric current, and this maintains the string of the PV cell. The below figure shows the bypass diode action in the case of clouds.
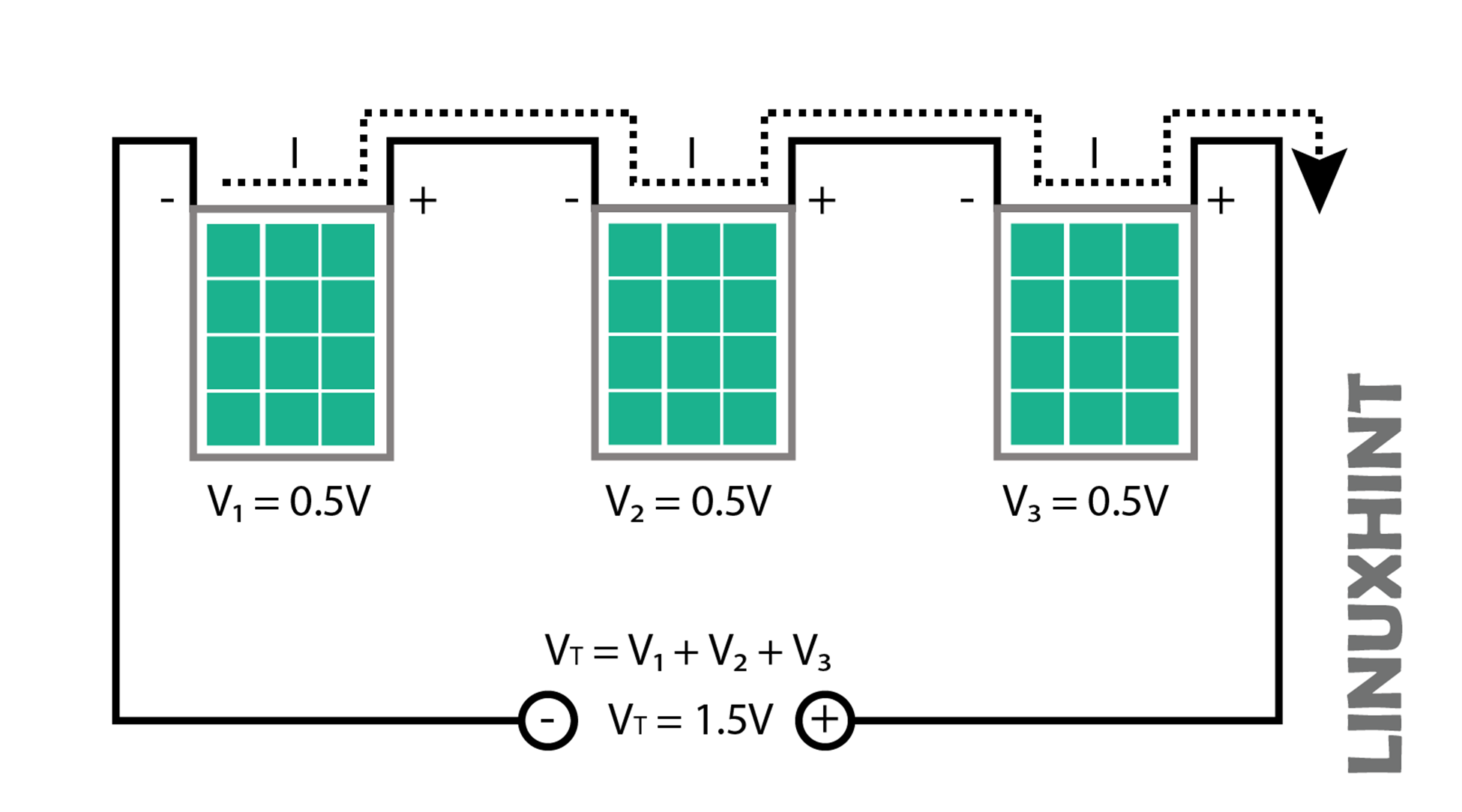
Solar Panel without Bypass Diode
The below figure shows the string of PV cells connected in series without the Bypass diode. Three cells are in series, so the output voltages of these are given as:
All three solar cells are producing the rated power in currents and volts under normal operating conditions, meaning that all the photovoltaic cells are operating flawlessly. Both in series and parallel connections, the power is additive. In amperes and volts, we arrive at the ideal maximum rated power.
When without the bypass diode, one cell is covered by the cloud the whole current starts flowing through the clouded cell, which results in too much heat dissipation and may cause it to burn out. Normal cells without shades attempt to counteract the voltage decrease at shaded cells by raising the open circuit voltage. As a result, the impacted shaded PV cells get reverse biased and experience negative voltage across their terminals.
Conclusion
PV panels are the source of electricity, they convert the sunlight into electricity without any mechanical movement. Blocking and bypass are the two main parts involved in the installation of PV panels, The blocking diode acts as a way switch, and the bypass diode protects the PV cell from overcurrent and provides the current to the partially shaded cell.