Using BETWEEN command with the date as the range in PostgreSQL:
The “ BETWEEN ” command is usually used as a subquery and is used by other commands such as “ SELECT ”, “ WHERE “ and “ FROM ”. The keyword “ AND ” is always used as a separator between the range that we provide from high to low values in the PostgreSQL syntax.
Since we have to implement this command in the PostgreSQL environment, we have to have a table and some values in it which we can use for the “ BETWEEN ” command. We will use several date types and arrangements to portray the use of this command in between those ranges. Take a look at the example provided below:
Example 1:
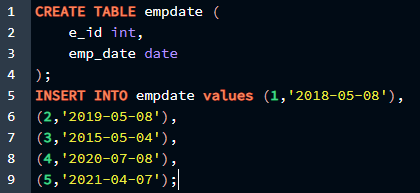
In this example, we will use the standard date format in PostgreSQL, “YYYY-MM-DD ”. We will create a table with 2 columns for an ID and a date to implement this example. Then we will insert several values in the table using the code below:
e_id int,
emp_date date
);
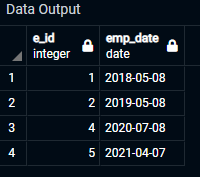
INSERT INTO empdate values (1,'2018-05-08'),
(2,'2019-05-08'),
(3,'2015-05-04'),
(4,'2020-07-08'),
(5,'2021-04-07');
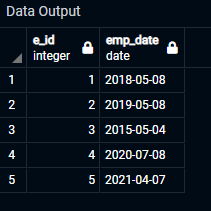
Attached is the output of the above query.
After successfully inserting entries into the table, we will utilize the ” BETWEEN ” command in
conjunction with other subqueries like as the ” SELECT “, ” FROM “, ” WHERE “, and ” AND ”
instructions to create a query. We will use the above table as an example and run the following
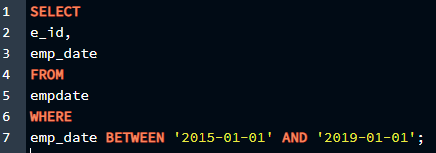
SELECT
e_id,
emp_date
FROM
empdate
WHERE
emp_date BETWEEN '2015-01-01' AND '2019-01-01';
In this query, we will be giving a range to the “ SELECT ” command from which we can filter out the output and narrow it down. We will retrieve the ” e_id ” and ” emp_date ” from the table we made before, but only the dates between ‘2015-01-01’ and ‘2019-01-01’ will be present in the output.
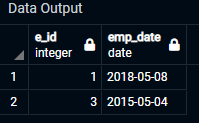
As the output suggests that only two “ e_id ” are present in the table with dates between the given range. This query helped us filter out the given values and give a more processed view of the table with which we can easily operate.
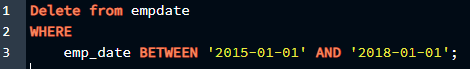
With ” DELETE “, ” FROM “, and ” WHERE “, we will apply the ” BETWEEN ” command as a subquery. The “ DELETE ” command will use the date range given by the “ BETWEEN ” command and delete the values present in between that range. For this method, we will use the query given below:
WHERE
emp_date BETWEEN '2015-01-01' AND '2018-01-01';
This query will delete the rows from the “ empdate ” table whose dates are between ‘2015-01-01’ and ‘2018-01-01’
As you can see in the output above, we have successfully removed a row from a table that was present in between the date range provided in the query.
Example 2:
Now we will use the date in the standard format with the time as well, but we will not be selecting the time zone. We will create a table with two columns, one for the id and the second for the date, and will also insert some rows in the table to alter them with our further queries.
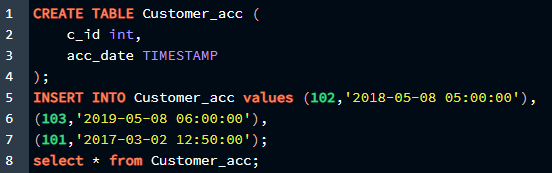
c_id int,
acc_date TIMESTAMP
);
INSERT INTO Customer_acc values (102,'2018-05-08 05:00:00'),
(103,'2019-05-08 06:00:00'),
(101,'2017-03-02 12:50:00');
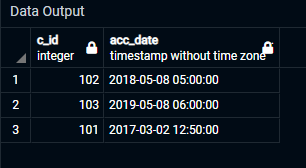
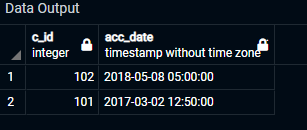
Select * from Customer_acc
Attached is the output of the above query.
After creating a table and inserting values in it, we will use the “ SELECT “ and “ BETWEEN ” commands to filter some rows in the table that we created. For this method, we will use the query given below:
c_id,
acc_date
FROM
Customer_acc
WHERE
acc_date BETWEEN '2015-03-01' AND '2019-02-15';
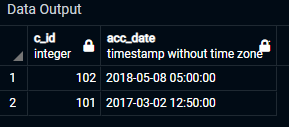
The rows between ‘2015-03-01’ and ‘2019-02-15’ will be filtered in this query.
In this output, we can see the filtered view of the table because of the “ BETWEEN ” command. Now we will use the “ Delete ” and “ BETWEEN ” command together on the “ Customer_acc ” table to see the effect of these commands on the modified date range.
WHERE
acc_date BETWEEN '2015-03-01' AND '2018-05-08';
With the help of this query, we will be deleting the rows between the ‘2015-03-01’ and ‘2018-05-08’ date range. The below output suggests that we have successfully deleted the value that was present between the range given in the query.
Example 3:
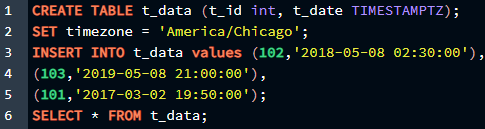
We will now utilize the data in standard format with the time and the time zone. We will make a table with two columns, one for the id and the other for the date, and then we will add some rows to it so we can change it with our other queries.
SET timezone = 'America/Chicago';
INSERT INTO t_data values (102,'2018-05-08 02:30:00'),
(103,'2019-05-08 21:00:00'),
(101,'2017-03-02 19:50:00');
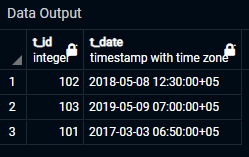
SELECT * FROM t_data;
Attached is the output of the above query.
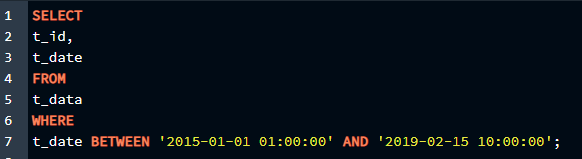
Now to filter particular rows in the table we created, we will use the ” SELECT ” and ” BETWEEN” commands. After we have created the table and added rows to it. We will use the following query for this method:
t_id,
t_date
FROM
t_data
WHERE
t_date BETWEEN '2015-01-01 01:00:00' AND '2019-02-15 10:00:00';
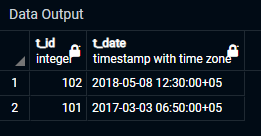
Attached is the output of the above query.
Because of the ” BETWEEN ” command, we can see the filtered view of the table in this output. On the ” t_data ” table, we will use the ” Delete ” and ” BETWEEN ” commands together to observe how they affect the changed date range.
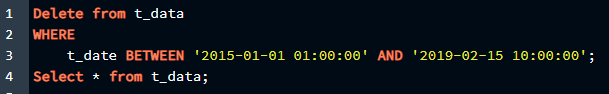
WHERE
t_date BETWEEN '2015-01-01 01:00:00' AND '2019-02-15 10:00:00';
Select * from t_data;
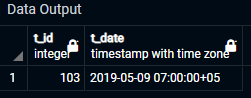
We will delete the rows between the dates ‘2015-01-01 01:00:00’ and ‘2019-02-15 10:00:00’ using this query. As shown in the result below, we were successful in deleting the value that was present between the ranges specified in the query.
Conclusion:
This article provided a guide on using the “ BETWEEN ” with several other queries in PostgreSQL. We implemented this command with different types of dates. First, we used a standard date format in PostgreSQL with the “ BETWEEN ” command. Then, we modified the data range by using timestamps with and without setting the timezone to better understand this command. We have concluded that the “ BETWEEN ” command can be used with almost every variation of the date range and provide us with a simplified and filtered view of the table.