Syntax:
variable_names;
abstract method1();
public method2(){
statements 1..N
}
}
An abstract class can contain attribute or variables, abstract method, and normal method or anyone of them. But the subclass of the abstract class can only implement the abstract method of the abstract class.
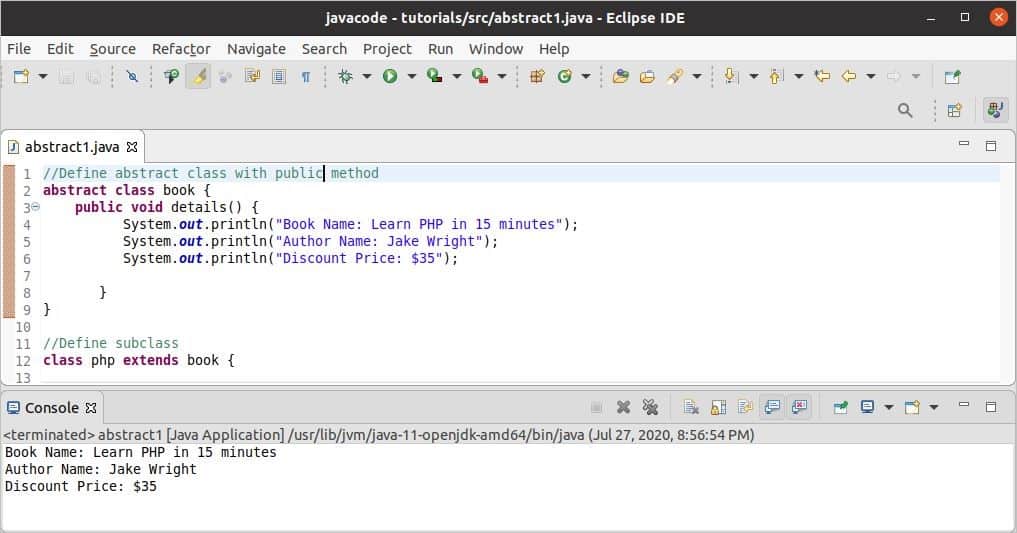
Example-1: Abstract class with a public method
The following example shows how you can declare an abstract class with a public method and the way of using an abstract class by creating a subclass. Here, the abstract class contains a public method named details() that is implemented inside the abstract class. The object of the subclass is created to access the public method of the abstract class.
abstract class book {
public void details() {
System.out.println("Book Name: Learn PHP in 15 minutes");
System.out.println("Author Name: Jake Wright");
System.out.println("Discount Price: $35");
}
}
//Define subclass
class php extends book {
}
//Main class
class abstract1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
php bk = new php();
bk.details();
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after running the code. Here, the details() method of abstract class is called, and the text is printed from the method.
Example-2: Abstract class with the abstract method and public method
The following example shows how an abstract class can be declared with variables, an abstract method, and a public method. The statements of the public method are defined inside the abstract class, but the body of the abstract method is empty that is implemented inside the subclass of the abstract class. Here, two subclasses are declared by extending the abstract class. The subclass named square will calculate and print the area of a square-based on the value of n variable. The subclass named rectangle will calculate and print the area of the rectangle based on the value of h and w variables. The public method, readData() is called by a parameter named type to identify which variable(s) of the abstract class will be initialized. The value of the type variable will be 1 for initializing the value of n and 2 for initializing the value of h and w.
abstract class area{
public int n, h, w;
abstract void result();
public void readData(int type) {
if (type == 1) {
n = 10;
}
else {
h = 20;
w = 30;
}
}
}
//Define square subclass
class square extends area {
public void result() {
//Calculate the area of the square
int areaVal = n*n;
System.out.println("The area of the square is " + areaVal);
}
}
//Define rectangle subclass
class rectangle extends area {
public void result() {
//Calculate the area of the rectangle
int areaVal = h*w;
System.out.println("The area of the rectangle is " + areaVal);
}
}
//Main class
class abstract2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create object of the square class
square sq = new square();
sq.readData(1);
sq.result();
//Create object of the rectangle class
rectangle rq = new rectangle();
rq.readData(2);
rq.result();
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after running the code. The output shows the area of a square where the value of n is 10 and the area of a rectangle where the value of h is 20, and the value of w is 30.
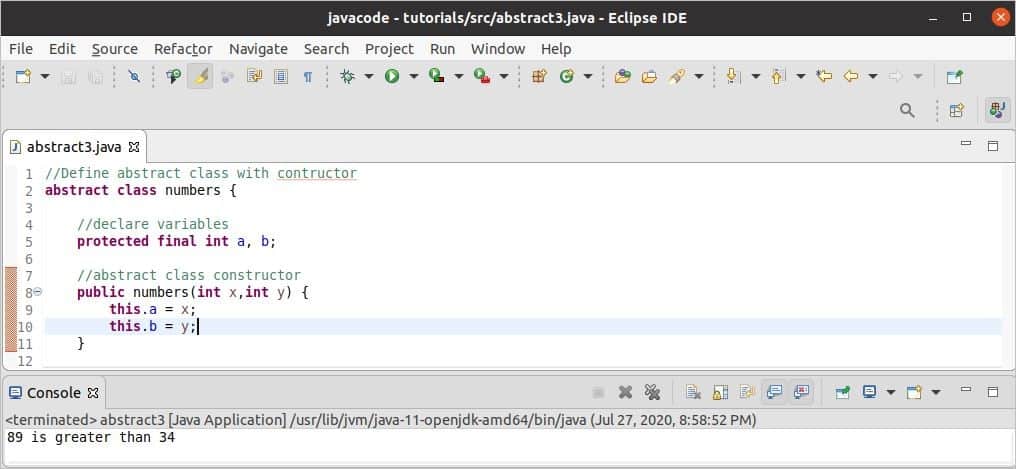
Example-3: Abstract class with the constructor
The following example shows how constructor can be declared and used within an abstract class. The constructor of the abstract class will initialize the values of a and b. The abstract method, maxval() is implemented in the subclass named findMax. super() method is used in the constructor of the subclass to call the constructor of an abstract class. The abstract method maxval() will find out the maximum value of two numbers that will be given to the parameters of the constructor of the subclass at the time of object creation.
abstract class numbers {
//declare variables
protected final int a, b;
//abstract class constructor
public numbers(int x,int y) {
this.a = x;
this.b = y;
}
//Public method
public abstract void maxval();
}
//Define subclass
class findMax extends numbers {
//Subclass constructor
public findMax(int x,int y){
//Call abstract class constructor
super(x,y);
}
//Implement abstract method
public void maxval() {
if(a > b) {
System.out.println(a + " is greater than " + b);
}
else {
System.out.println(b + " is greater than " + a);
}
}
}
//Main class
class abstract3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create object of the subclass
findMax fmax = new findMax(34,89);
//Find the maximum
fmax.maxval();
}
}
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script. Here, 34 and 89 are given as parameter values of the constructor. These values are compared in the abstract method that is implemented in the subclass and printed the following message.
Conclusion:
An abstract class is used to make the program more organized and understandable. Several related classes can be grouped by using abstract classes. The concept and the implementation of the abstract class with different parts are explained in this tutorial by using simple examples. I hope the readers will be able to understand the use of abstract class and apply it in their code properly after reading this tutorial.