The array is used in any programming language to store multiple numeric values or string values. Sometimes, it requires calculating the sum of numeric array values. Array variables can be declared in Java by mentioning all values or by defining the value of each index separately. Since Java is a strongly typed language, you have to define the data type of array values at the time of array declaration. The methods of calculating the sum of array values using the “for” loop, custom function, and the built-in function are shown in this tutorial.
Example 1: Using the “For” Loop
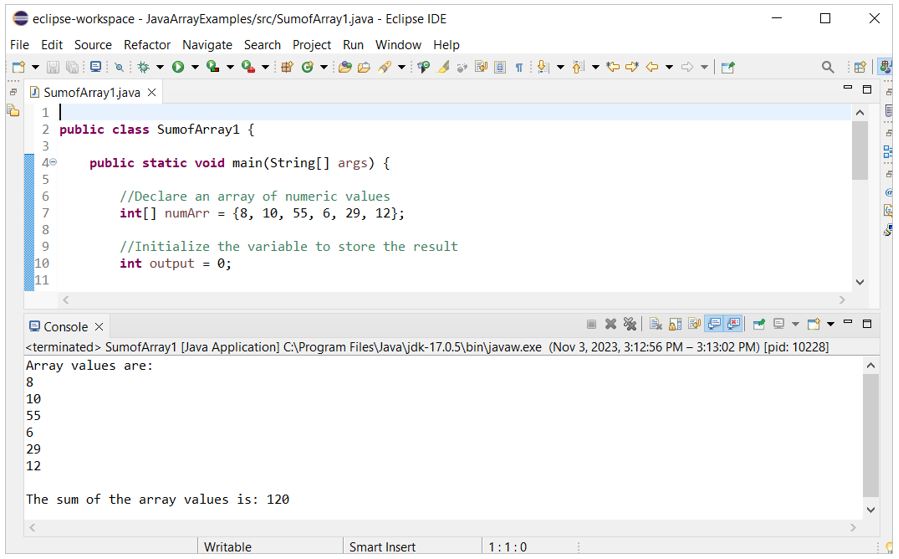
Create a Java file with the following code that calculates the sum of all array values using a “for” loop. An array of 6 numbers is defined in the code. A variable is initialized to store the sum value. Next, the length of the array is counted by the length property and the “for” loop is used to calculate the sum of the array values by accessing each value of the array.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare an array of numeric values
int[] numArr = {8, 10, 55, 6, 29, 12};
//Initialize the variable to store the result
int output = 0;
//Count the number of total array elements
int size = numArr.length;
System.out.println("Array values are: ");
//Calculate the sum of the array values and print the array values
for (int n = 0; n < size; n++) {
System.out.println(numArr[n]);
output = output + numArr[n];
}
//Print the sum of the array values
System.out.println("\nThe sum of the array values is: " + output);
}
}
Output:
The following output appears after executing the code. The values of the array and the sum of the array values are printed in the output:
Example 2: Using the User-Defined Function
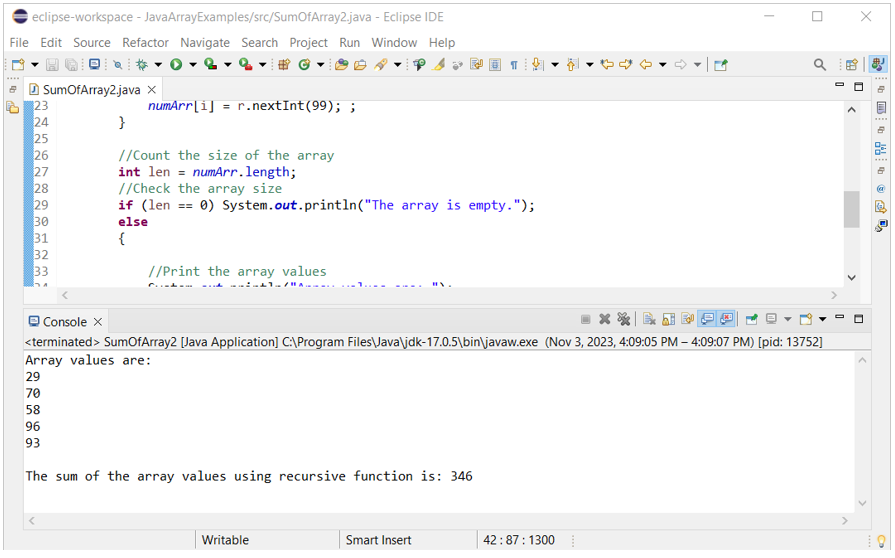
Another way of calculating the sum of array values is to use the user-defined function. Create a Java file with the following code that declares an array of five elements, initialize the array with random numbers, and calculate the sum of array values using a user-defined function. A recursive user-defined function is used in the code to calculate the sum value. Next, the sum value is printed.
import java.util.Random;
public class SumOfArray2 {
//Declare an array of 5 elements
public static int numArr[] = new int [5];
//Define the function to calculate the sum of array values
public static int SumArrayValues(int l, int[] arrval) {
//Check the current index values
if (l == 0) return arrval[l];
//Call the function itself until the value of l becomes 0
return arrval[l] + SumArrayValues(l-1, arrval);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Insert 5 random values into the array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
Random r = new Random();
numArr[i] = r.nextInt(99); ;
}
//Count the size of the array
int len = numArr.length;
//Check the array size
if (len == 0)
System.out.println("The array is empty.");
else
{
//Print the array values
System.out.println("Array values are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(numArr[i]);
}
//Call the function to calculate the sum of array values
int output = SumArrayValues(len-1, numArr);
//Print the sum of the array values
System.out.println("\nThe sum of the array values using recursive function is: " + output);
}
}
}
Output:
The following output appears after executing the code. The random values of the array and the sum of the array values are printed in the output:
Example 3: Using the Sum() Method
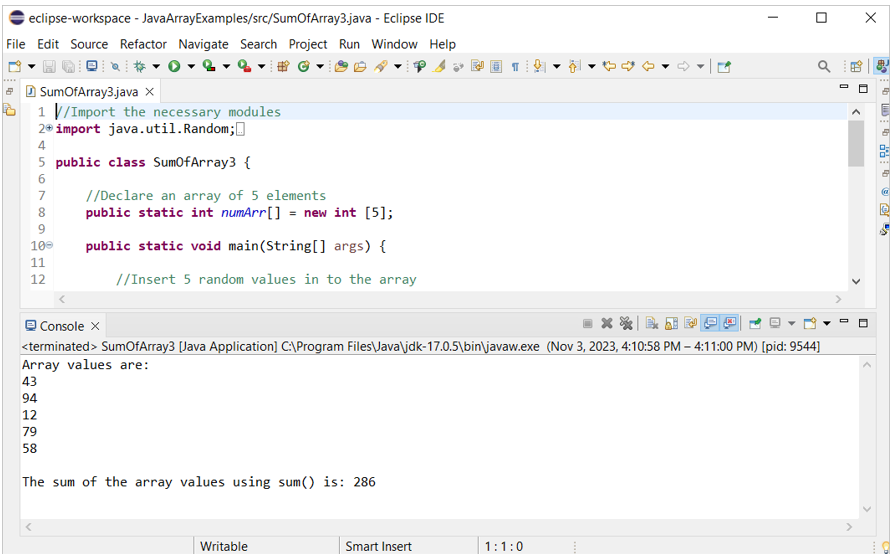
Create a Java file with the following code that uses the sum() method of Java Steam API to calculate the sum of array values. An array of five numbers is defined at the beginning of the code. Next, the sum() method is used to calculate the sum of array values.
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SumOfArray3 {
//Declare an array of 5 elements
public static int numArr[] = new int [5];
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Insert 5 random values into the array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
Random r = new Random();
numArr[i] = r.nextInt(99); ;
}
//Count the size of the array
int len = numArr.length;
//Check the array size
if (len == 0)
System.out.println("The array is empty.");
else
{
//Print the array values
System.out.println("Array values are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(numArr[i]);
}
//Call the function to calculate the sum of array values
int output = Arrays.stream(numArr).sum();
//Print the sum of the array values
System.out.println("\nThe sum of the array values using sum() is: " + output);
}
}
}
Output:
The following output appears after executing the code. The random values of the array and the sum of the array values are printed in the output:
Conclusion
Different ways of calculating the sum of array values in Java are shown in this tutorial using multiple examples.