What is Galvanic Isolation?
Galvanic isolation is a type of isolation between the two parts of an electrical system, in which the energy or signals flow between them, but there is no interconnection between them. It provides the physical partition between the two parts, the input, and output of the system. By adding galvanic isolation, it can remove all the grounding problems.
In this isolation, it allows the transfer of data but does not permit the electrical current between the isolated parts.
Purpose of Galvanic Isolation
When two devices are in communication, then DC current and AC signals flow freely between them. It is a safe way to work in low-voltage operating systems. But in high-voltage operating systems, this freely flowing DC current and AC signal will be dangerous. The presence of the high voltage will introduce a potential difference which causes the dangerous DC current and AC signals to flow into the other parts of the system. This will cause errors and dangerous conditions in the operating systems, so Galvanic isolation is needed in these circumstances.
Types of Galvanic Isolation
There are two major galvanic isolation that are:
Methods of Signal Isolation
This method includes:
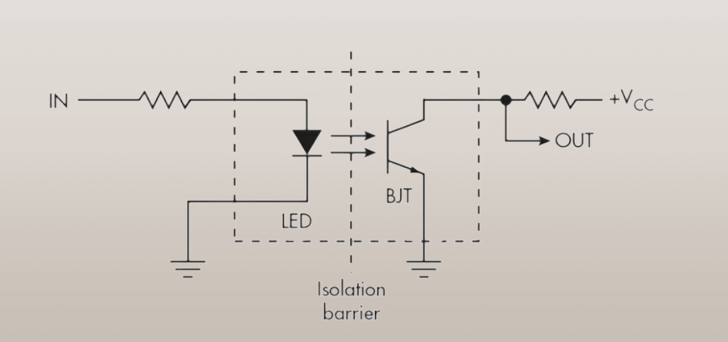
Opto-isolator
An opto-isolator is an electrical component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated systems through light. It prevents high voltage from affecting the electrical system in receiving the signals. It uses a photo-responsive transistor which is only activated whenever the internal light-emitting diode is activated. Usually, optoisolators transfer digital on/off signals and act as electronic switches.
The common types of opto-isolators available in the market are LED-Phototransistor, LED-Photodiode, LED-LASER, and lamp-photoresistor pairs.
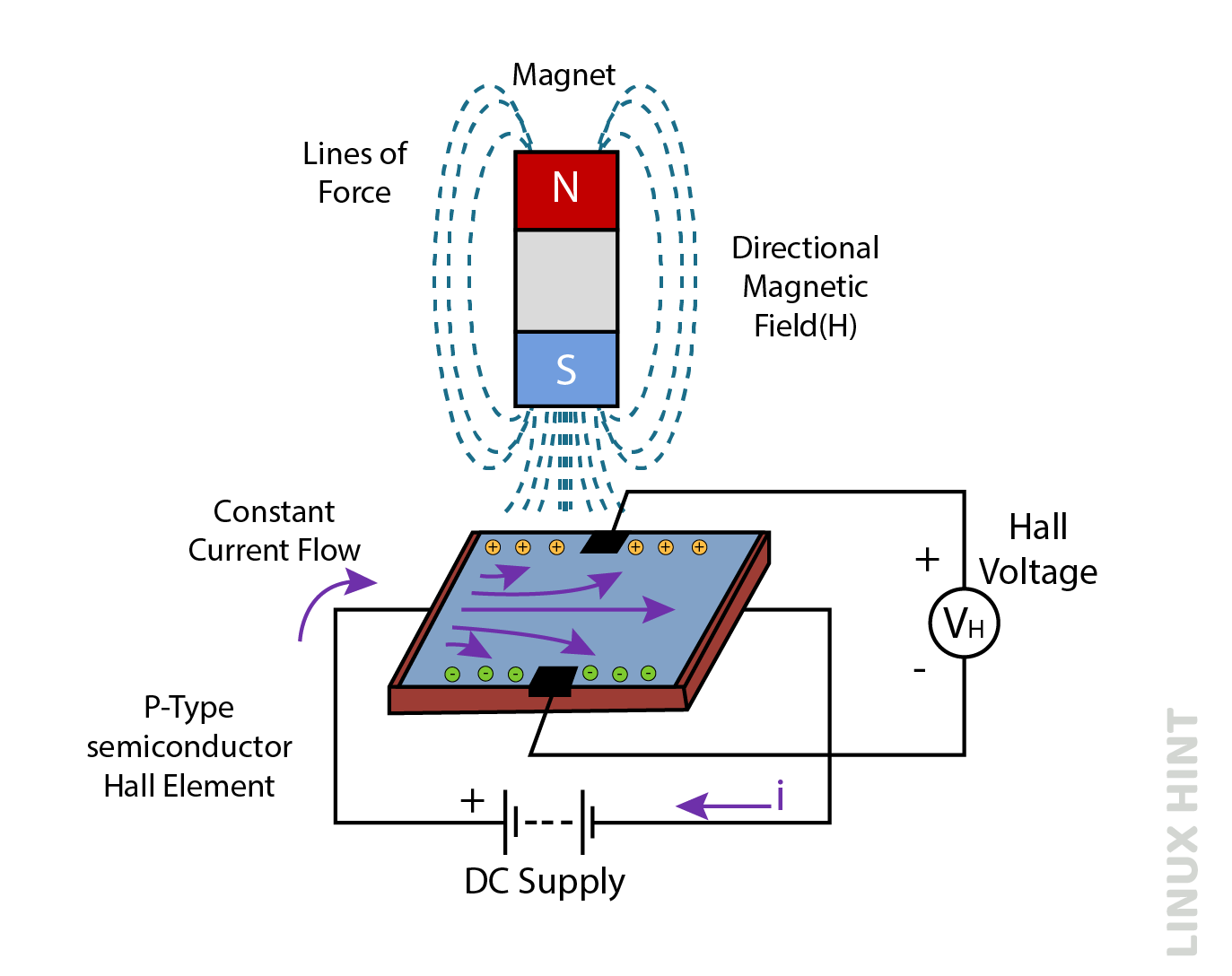
Hall Effect
Measuring current in different electrical circuits is a part of electrical engineering. Different sensing methods are used for measuring the current in an electrical circuit. It requires high voltage and current paths, and the measurement has to be sent on the low-voltage circuits to read them. Hall effect is a type of sensor used for measuring the current in a circuit. The electromagnetic field developed across the current-carrying conductor is used for measuring the value of current.
Methods of Power Isolation
Magnetic or electrical separation is used in power isolation to separate the two electrical circuits. Power isolation forms a barrier so that dangerous voltages cannot pass during a fault in the electrical system. There are two types of power isolation.
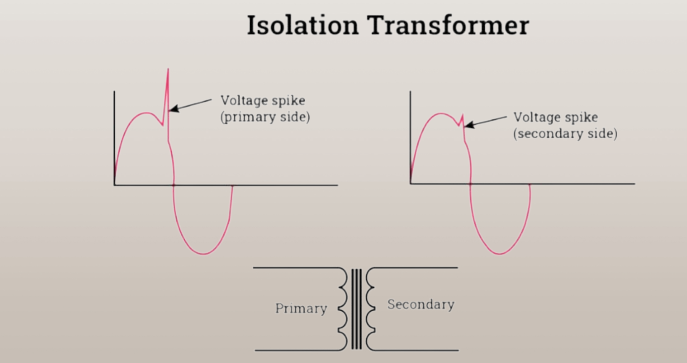
Transformer Isolation
An isolation transformer is used in this type of isolation, which isolates the two electrical systems. Two isolated windings without any direct electrical connection between them are used in the construction of an isolation transformer.
Galvanic isolation is the electrical and physical separation of the input from the output of the circuit. An isolation transformer achieves this type of electrical isolation. Output power is physically isolated from input in transformer isolation.
For the power supply in sensitive equipment such as computers and laboratory instruments, specially designed transformers with electrostatic shields are used.
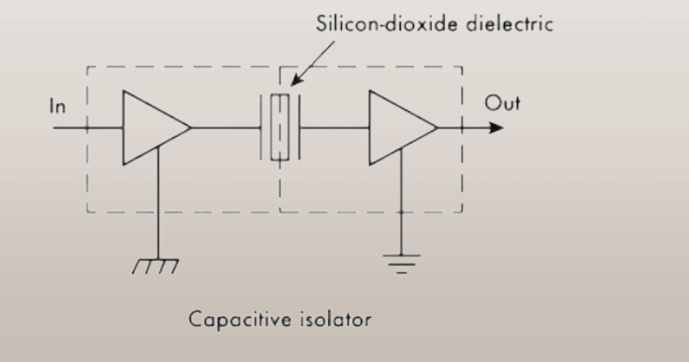
Capacitor Isolation
In capacitive isolation, electric fields are used for transferring power between two electrical systems. This is an effective method of isolating the electrical systems from AC mains. Capacitive isolation helps in simplifying the system designs. As compared to the optocouplers and other different isolation methods, this new design isolation has advantages in lower power loss, small and simplified boards, simplified system designs, and higher-speed operations.
A dielectric material separates two electrodes and is used in capacitive isolation as these form a capacitor and store electrical energy in the form of an electric field by applying the voltage supply across the electrode.
Conclusion
Galvanic isolation is a type of isolation between the two parts of an electrical system, in which the energy or signals flow between them, but there is no interconnection between them. It provides the physical partition between the two parts, the input, and output of the system. By adding galvanic isolation, it can remove all the grounding problems.