In this article, we are going to explore how to add a vector in the matrix in MATLAB using multiple examples.
How to Add a Vector in MATLAB?
A vector can be added to an existing matrix using square brackets []. We can add the vector vertically or horizontally in the matrix. This method can create a new matrix from the existing one by putting the newly added vector at the end of the matrix. If we add a vector in the matrix vertically, the vector and matrix must have an equal number of rows. If we add a vector in the matrix horizontally, the vector and matrix must have an equal number of columns.
Examples
Let’s consider some examples for understanding how to add a vector in the matrix in MATLAB.
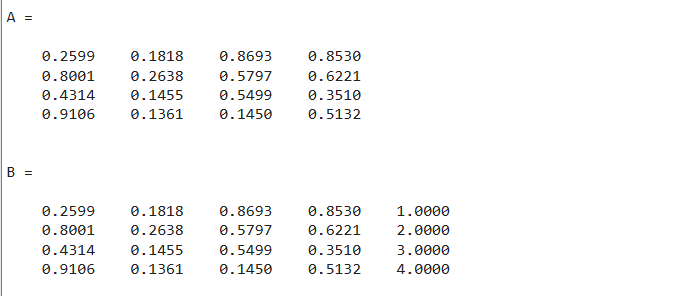
Example1
In this example, we will create a 4-by-4 matrix using the rand() function. After that, we will create a column vector of size 1-by-4. Then we use the square brackets to add the vector v vertically in the matrix A.
The resultant matrix B which is a combination of the matrix A and the vector v is displayed on the screen.
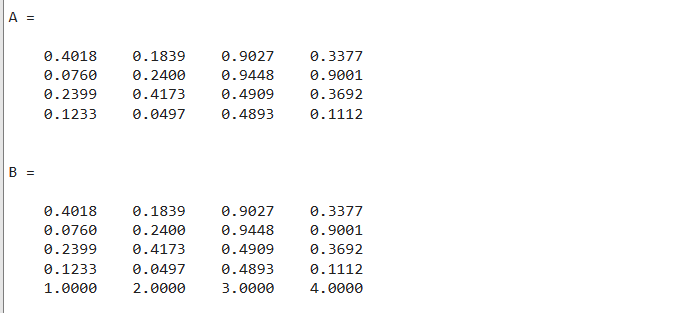
Example2
This MATLAB code creates a 4-by-4 matrix using the rand() function. After that, it creates a row vector of size 4-by-1. Then it uses the square brackets to add the vector v horizontally in the matrix A.
Conclusion
Adding a vector to a matrix in MATLAB is a versatile operation that allows for combining and modifying data efficiently. In this article, we have explored how to add a vector to a matrix, both vertically and horizontally, using square brackets []. This method enables the creation of a new matrix by appending the vector to the existing one. We provided examples demonstrating the process, showcasing vertical and horizontal vector additions.