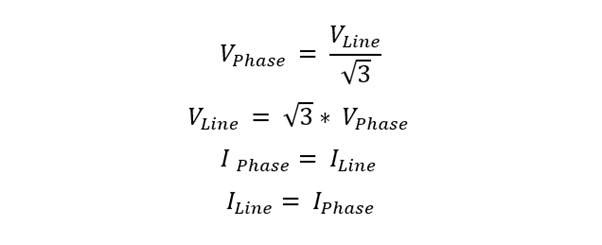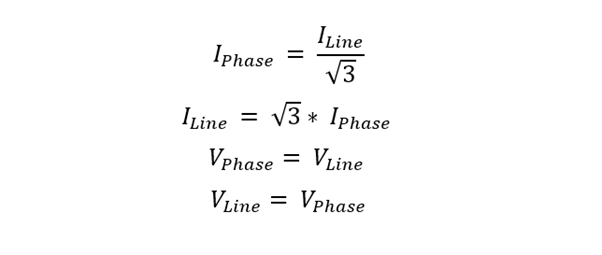What are Three-Phase Transformers?
Three-phase transformers are specialized electrical devices created specifically for the purpose of transferring electrical energy between three-phase systems. Their design and functionality are tailored to facilitate efficient and reliable power transmission in three-phase electrical networks.
They consist of three separate but interconnected single-phase transformers, each with primary and secondary windings. These transformers are widely used due to their ability to handle higher power loads more efficiently compared to single-phase transformers.
Working Principle of Three-Phase Transformers
Three-phase transformers operate on the electromagnetic induction theory. A spinning magnetic field is created when a transformer’s primary windings are supplied with a three-phase AC voltage. This rotating magnetic field then induces a corresponding voltage in the secondary windings of the transformer, enabling the efficient transfer of electrical energy between the primary and secondary circuits.
The primary windings of the transformer are linked to the three-phase power source, establishing the connection between the transformer and the electrical grid. On the other hand, the secondary windings are interconnected with the load, enabling the transfer of power from the transformer to the intended electrical devices or equipment. The primary and secondary windings are wound on separate limbs of the transformer’s core to prevent electrical coupling between them.
The Star-Delta Combination Connections
The star-delta combination connection is a common configuration used in three-phase transformers. It provides flexibility in transforming voltage and current levels to meet specific power distribution requirements.
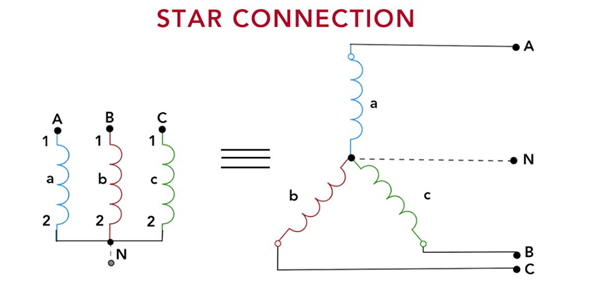
1. Star (Y) Connection
In a star connection, one terminal of each transformer winding is interconnected to create a shared neutral point, typically grounded. The electrical connection is then completed by connecting the remaining winding terminals to the relevant phases of the three-phase power source.
The star connection is primarily used when the load requires a neutral point for grounding or to provide a balanced three-phase output. It provides a line-to-line voltage equal to the phase voltage, making it suitable for low-voltage distribution systems.
Here are the line and phase formulas for current and voltage:
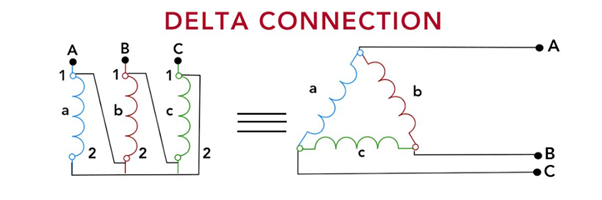
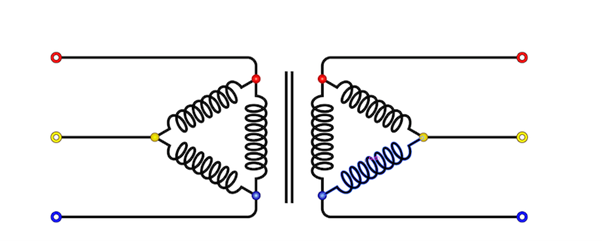
2. Delta (Δ) Connection
In a delta connection, the start of each winding is connected to the end of the next winding in a cyclic manner, creating a closed-loop configuration. The three-phase power supply is then connected to the junctions between these windings, establishing the electrical connection.
The delta connection is employed when a three-phase load does not require a neutral point. It is commonly used in high-voltage transmission systems, where the line-to-line voltage is higher than the phase voltage.
Here are the line and phase formulas for current and voltage:
Conclusion
In order to ensure effective power distribution and voltage transformation, three-phase transformers are essential parts of electrical power systems. Knowing their working principle and the star-delta combination connections, you can effectively design and implement three-phase power networks. The star connection provides a neutral point and balanced outputs, while the delta connection enables high-voltage transmission.