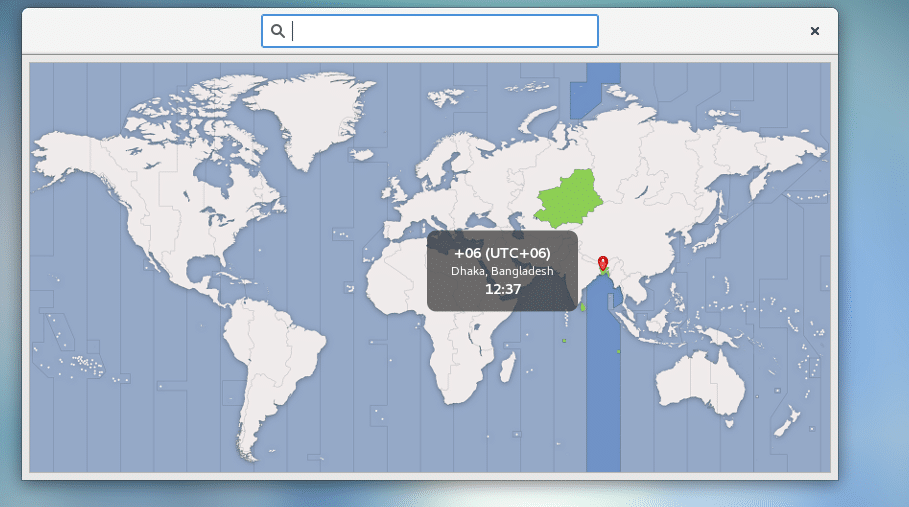
In this article, I will show you how to set timezone on CentOS. I am using CentOS 7 for the demonstration. Let’s get started.
Checking Currently Set Timezone Using timedatectl:
There are many ways you can print the current timezone set on your CentOS machine.
You can run the following command to check your currently set timezone:
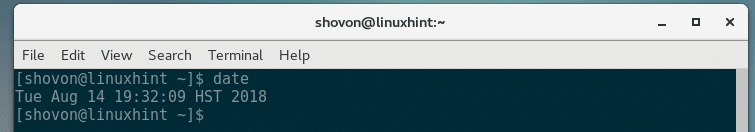
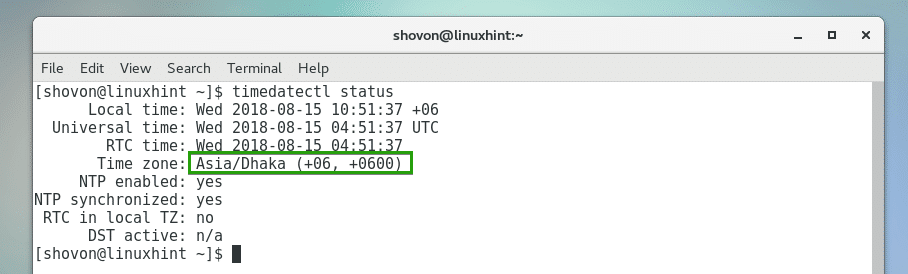
As you can see, my currently set timezone is Asia/Dhaka.
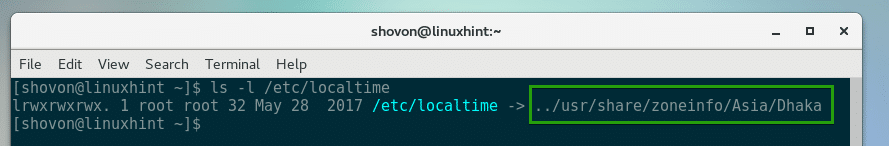
Checking Currently Set Timezone Using /etc/localtime:
You can also check which file /etc/localtime file is linked to, to determine the currently set timezone on CentOS.
To check which timezone is set that way, run the following command:
As you can see, the /etc/localtime file on my CentOS machine is linked to /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Dhaka file. So my currently set timezone is Asia/Dhaka.
Listing Available Timezones using timedatectl:
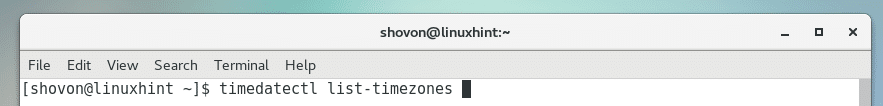
You can list all the available timezones of your CentOS machine with the following command:
A list of all the available timezones should be printed.
The terminal screen can’t show them all, but you can press <Enter> or <Space> to navigate through the list.
List and Set Timezone using tzselect:
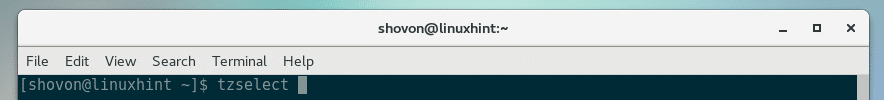
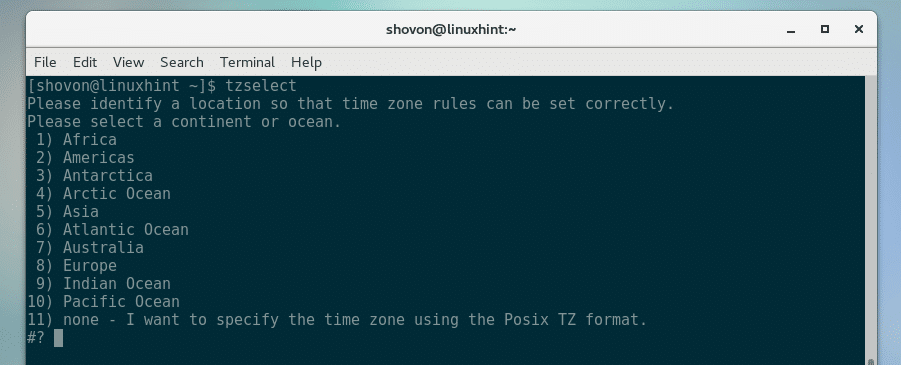
You can find your timezone easily using a ncurses based command line utility tzselect.
Start tzselect with the following command:
Now type in any number between 1 and 11 and press <Enter> to select your continent or ocean. I am going for Americas for this demonstration. So I am pressing 2.
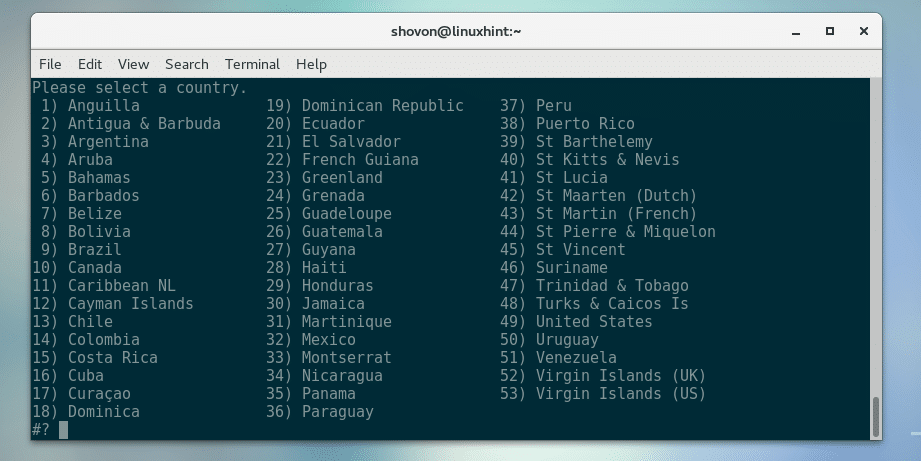
Now type in any of the numbers and press <Enter> select your country. I am going for United States for this demonstration. So I typed 49.
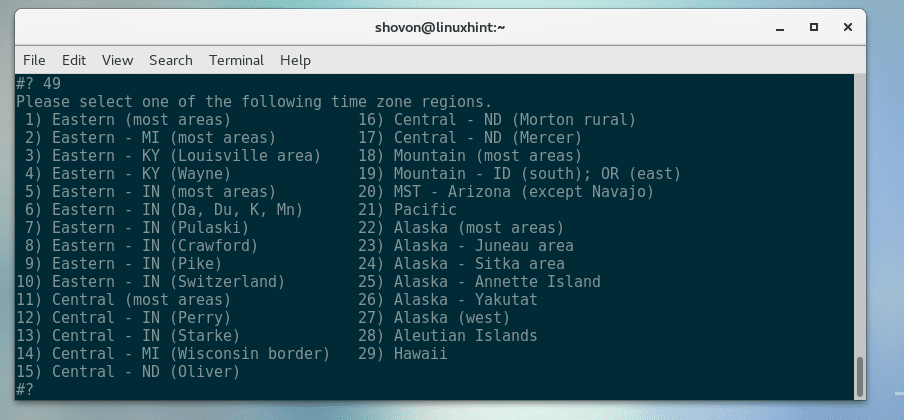
Now type in any of the numbers from the list and press <Enter> to select any of the timezone regions from the list. I am typing in 29 which is Hawaii’s timezone for the demonstration.
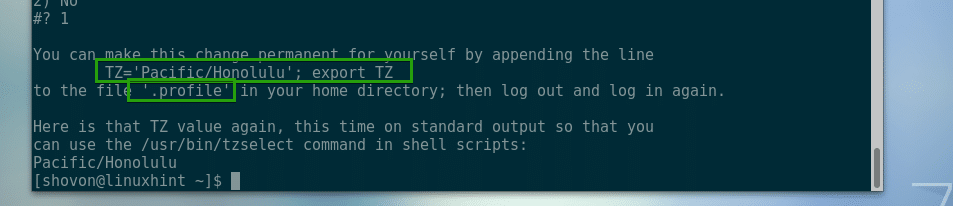
The timezone information should be displayed. As you can see, the timezone is Pacific/Honolulu. If you think everything is alright, the press 1 and then press <Enter>.
Now tzselect should tell you how to set the timezone. All you have to do is copy the marked line and append it in the ~/.profile file. Then restart your computer. Your timezone should be set. I am going to show you how to do that now.
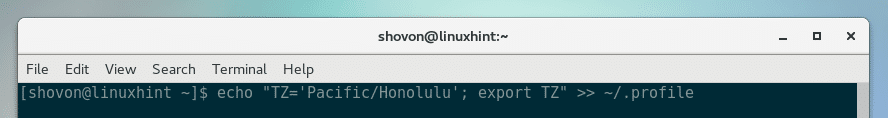
Now run the following command to append line as marked line in the previous screenshot to ~/.profile file:
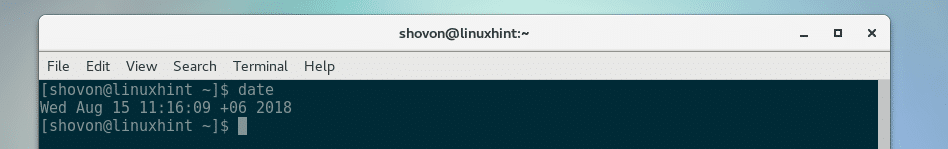
Before you reboot, check your current date & time with the following command:
Now reboot your computer with the following command:
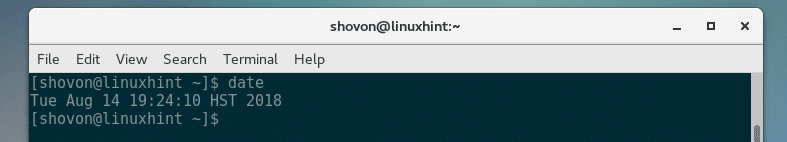
Once your computer boots, run the following command to check your date & time again:
As you can see, the timezone is changed.
The change is also reflected in the GNOME panel as you can see from the screenshot below.
Setting Timezone using timedatectl:
To set timezone using timedatectl, you have to know the timezone string of the timezone you want to set. The timezone string is something like ‘Asia/Dhaka’. I showed you how to list timezones using timedatectl in the Listing Available Timezones using timedatectl section of this article above.
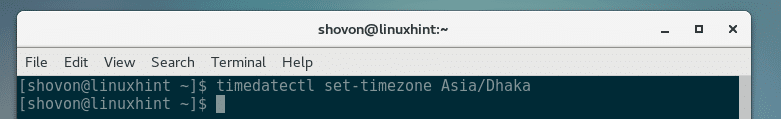
Pick a timezone of your choice and run the following command to set the timezone using timedatectl:
NOTE: Replace Asia/Dhaka with your own timezone.
Before rebooting your CentOS machine, check the current date & time with the following command:
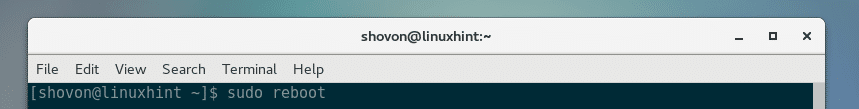
Now reboot your computer with the following command:
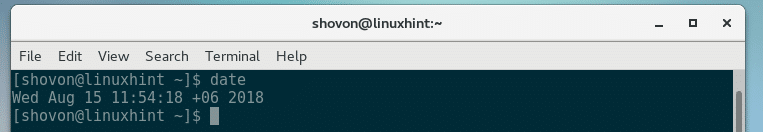
The timezone should be set as you can see from the output of the date command:
Set Timezone using Graphical User Interface:
If you have any desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE installed on your CentOS machine, then you can easily set timezone using graphical softwares.
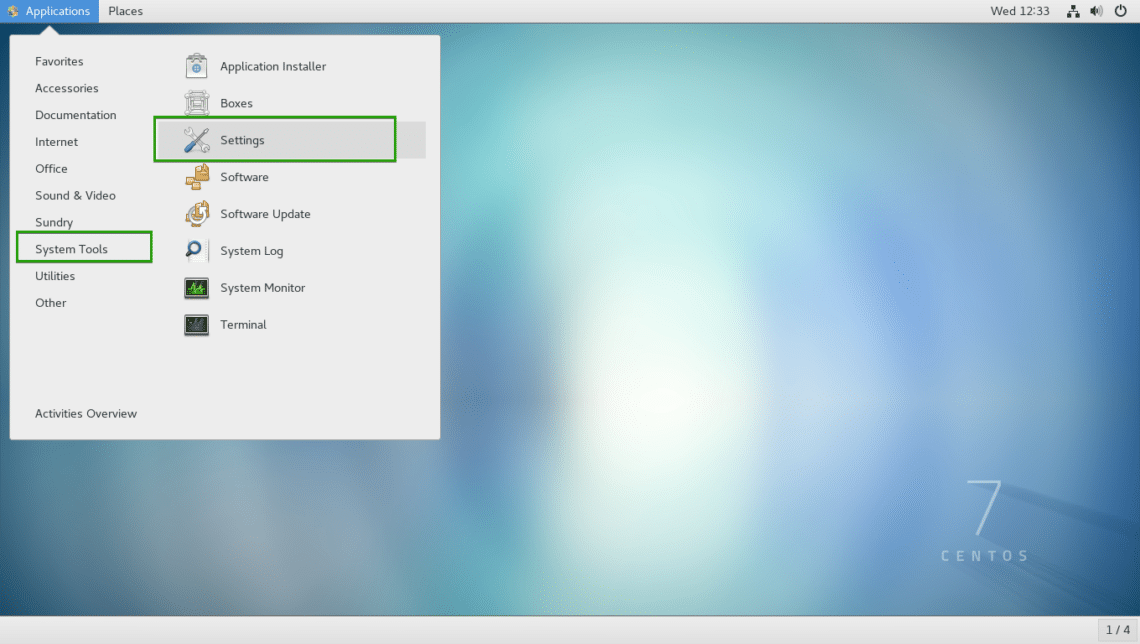
First open Settings app from Application Menu > System Tools > Settings
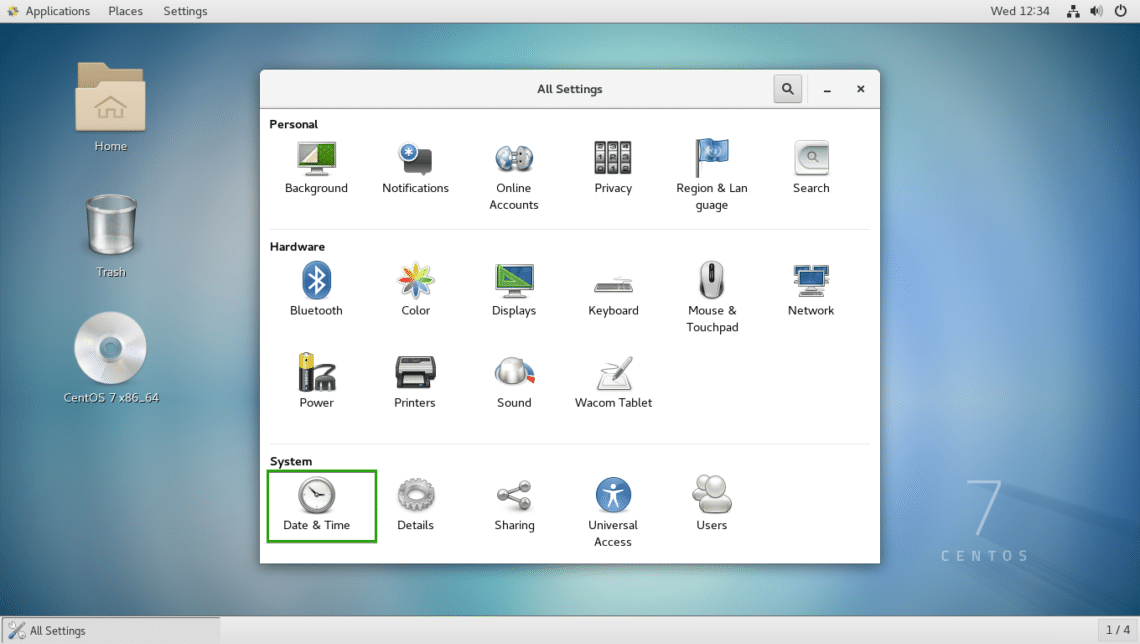
Now from the Settings app, click on Date & Time as marked in the screenshot below.
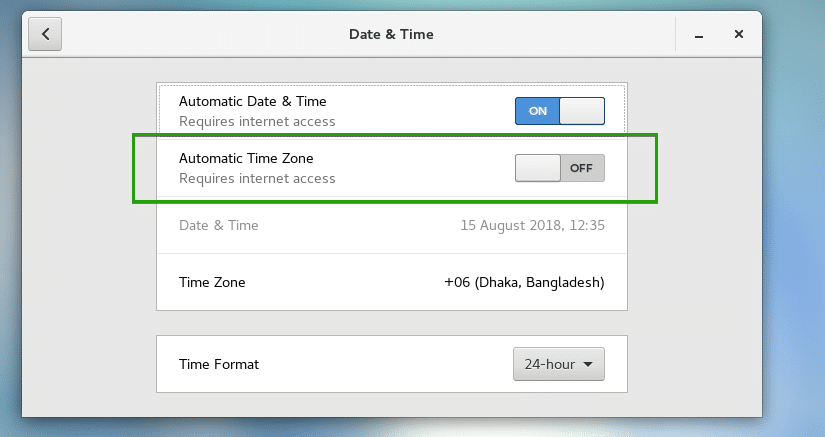
From here, you can toggle the Automatic Time Zone switch and your timezone should be automatically set. It requires internet connection.
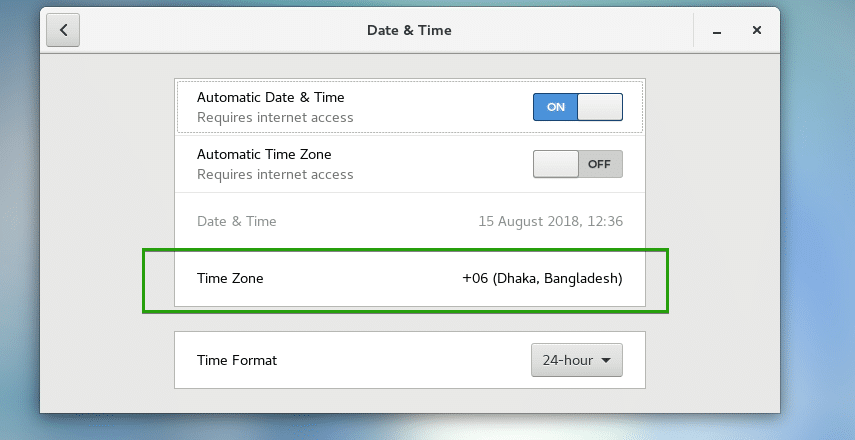
You can also click on Time Zone to change your timezone manually.
A map should appear. Search and select your timezone from here.
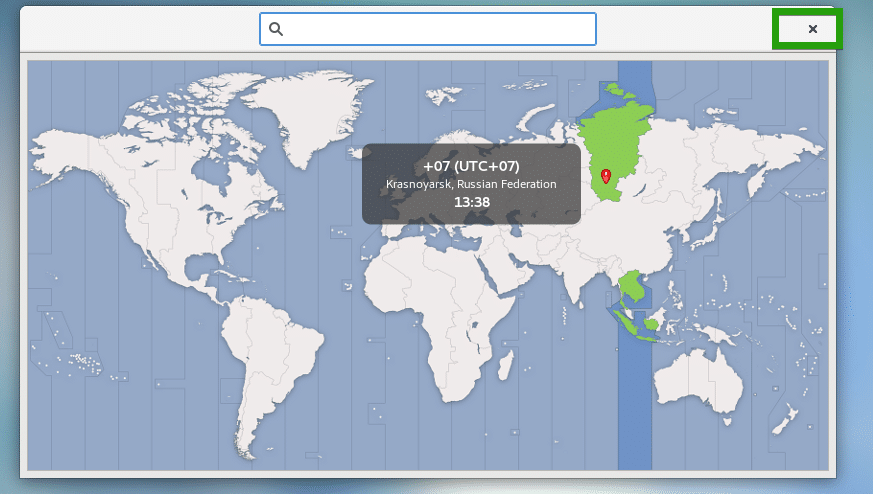
I selected a random timezone. Once you’re happy, click on the x button as marked in the screenshot below.
Your desired timezone should be set.
Unlike the command line approach, this will update the date & time of your CentOS machine instantly. You won’t have to reboot the system manually as you can see in the screenshot below.
So that’s how you set timezone on CentOS using the command line interface and graphically. Thanks for reading this article.