The Enumerated or ENUM data type is used to select one value from the list of multiple values. The particular value will be selected from the drop-down list for the ENUM data type. The ENUM values are static, unique, and case-sensitive. So, the users have to select any value from the ENUM values. The input value that does not match with any ENUM value can’t be inserted into the ENUM field. This data type takes 4 bytes to store in the table. The ENUM data type is useful for storing those types of data that are not required to change in the future. It helps to insert valid data only. The uses of ENUM data type in PostgreSQL have been shown in this tutorial.
Pre-requisites:
You have to install the latest version of PostgreSQL packages on the Linux operating system before executing the SQL statements shown in this tutorial. Run the following commands to install and start the PostgreSQL:
$ sudo systemctl start postgresql.service
Run the following command to login to PostgreSQL with root permission:
Uses of ENUM data type:
Before creating any table with the Boolean data type, you have to create a PostgreSQL database. So, run the following command to create a database named ‘testdb’:
The following output will appear after creating the database:
Create and read the ENUM type:
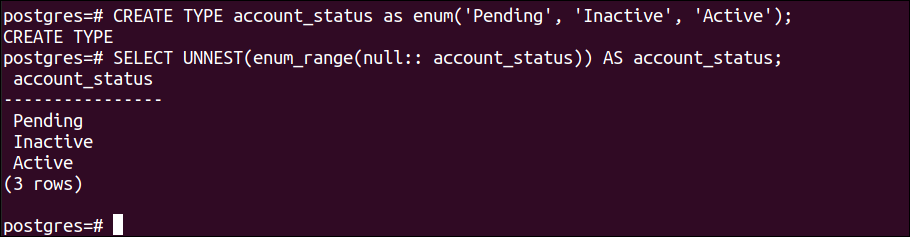
Run the following CREATE command to create an ENUM type named account_status with three values:
Run the following SELECT command to print the values of ENUM type that has been created before:
The following output will appear after executing the above commands:
Rename the ENUM Type:
Run the following command to change the name of the ENUM type from ‘account_status’ to ‘status’:
Create a table using the ENUM data type:
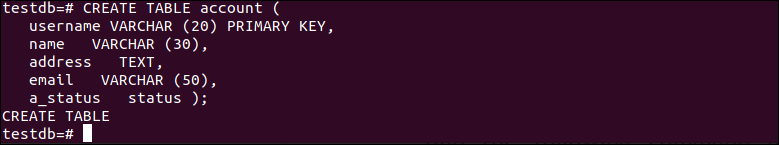
Create a table named ‘account’ in the current database with three fields. The first field name is the username that is the primary key of the. The second field name is the name and the data type is VARCHAR (30). The third field name is address and the data type is TEXT. The fourth field name is email and the data type is VARCHAR (50). The fifth field name is a_status and the data type is ENUM that has been created earlier.
username VARCHAR (20) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (30),
address TEXT,
email VARCHAR (50),
a_status STATUS );
The following output will appear after executing the above command:
Insert data into the table:
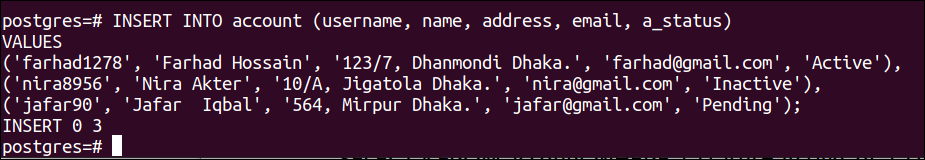
Run the following INSERT query to insert three records into the account table. All values of the ENUM field are valid here:
VALUES
('farhad1278', 'Farhad Hossain', '123/7, Dhanmondi Dhaka.', '[email protected]', 'Active'),
('nira8956', 'Nira Akter', '10/A, Jigatola Dhaka.', '[email protected]', 'Inactive'),
('jafar90', 'Jafar Iqbal', '564, Mirpur Dhaka.', '[email protected]', 'Pending');
The following output will appear after executing the above query:
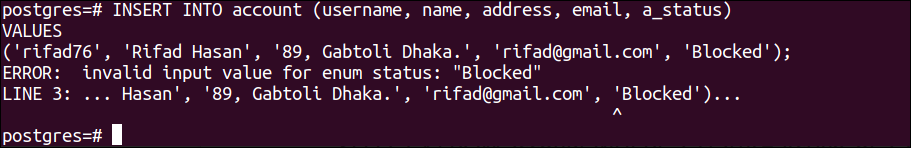
Run the following INSERT query to insert a record into the account table but the value given for the ENUM field does not exist in the ENUM type:
VALUES
('rifad76', 'Rifad Hasan', '89, Gabtoli Dhaka.', '[email protected]', 'Blocked');
The following output will appear after executing the above query. The error has occurred in the output for giving an ENUM value that does not exist in the ENUM type.
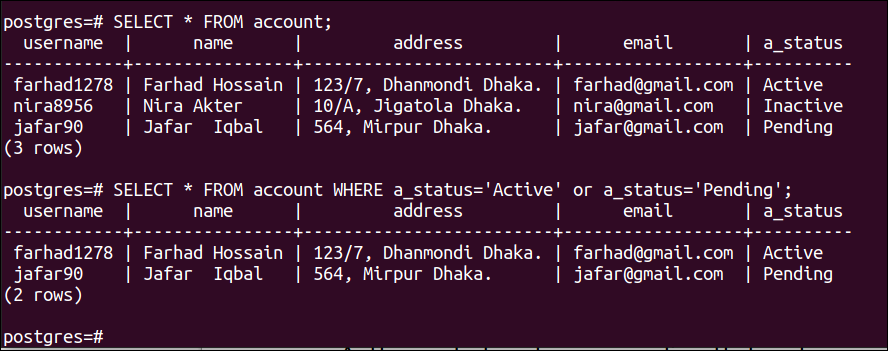
Run the following SELECT command to read all records from the account table:
Run the following SELECT command to read those records of the account table that contain the ‘Active’ or ‘Pending’ value in the ENUM field:
The following output will appear after executing the above SELECT queries:
Change the ENUM value:
If any existing value of the ENUM type is changed then the ENUM field value of the table where that ENUM has been used will be changed also.
Run the following ALTER command to change ENUM value ‘Active’ to ‘Online’:
Run the following SELECT command to check the records of the account table after changing the ENUM value:
The following output will appear after executing the above commands. There was one record in the table that contains the ENUM value, ‘Active’. The output shows that the ‘Active’ value has been changed to ‘Online’ after changing the ENUM value.
Add new value to an existing ENUM data type:
Run the following ALTER command to add a new item into the ENUM type named status:
Run the following SELECT query that will print the list of ENUM types after adding the new value:
The following output will appear after executing the above query:
A new value can be inserted before or after the particular value of an existing ENUM type. Run the first ALTER command to add the new value, ‘Blocked’ before the value ‘Inactive’. Run the second ALTER command to add the new value, ‘Blocked’ after the value ‘Inactive’.
# ALTER TYPE STATUS ADD VALUE ' Blocked' AFTER 'Inactive';
Delete ENUM data type:
You have to delete the table where the ENUM type is used before removing the ENUM type. Run the following command to remove the table:
Run the following command to remove the ENUM type after removing the table:
Conclusion:
The ways to create, update, and delete ENUM data types in PostgreSQL and the uses of ENUM data types in the PostgreSQL table have been shown in this tutorial that will help the new PostgreSQL users to know the purpose of using ENUM data types properly.