A Special Interest group of Fedora Project known as EPEL group is accountable for maintaining the EPEL repository. This repository is responsible for developing and managing a high-quality set of extra packages. The packages present in the EPEL repository can be the software not added to the core repository, or sometimes their updates are not released.
Why you should use EPEL repository on CentOS
Here is a list of some of the benefits of using the EPEL repository:
- EPEL is a freely available, open-source repository.
- There are no compatibility issues with the packages in the EPEL repository.
- You can utilize dnf and yum to install open-source packages from the EPEL repository.
- EPEL group is accountable for EPEL packages management.
Now, we will demonstrate how to install the EPEL repository on a CentOS system. So, let’s start!
How to install EPEL repository on CentOS
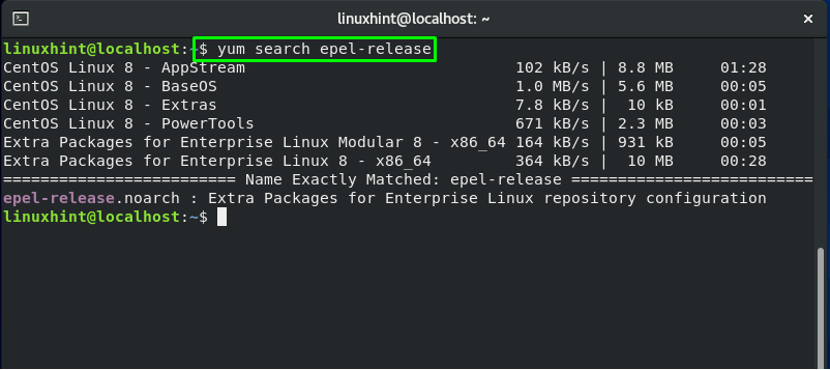
Open up your CentOS terminal by pressing “CTRL+ALT+T“. You have to log in as a root user or superuser in the terminal. Now, search for the “epel-release” repository by utilizing the below-given command:
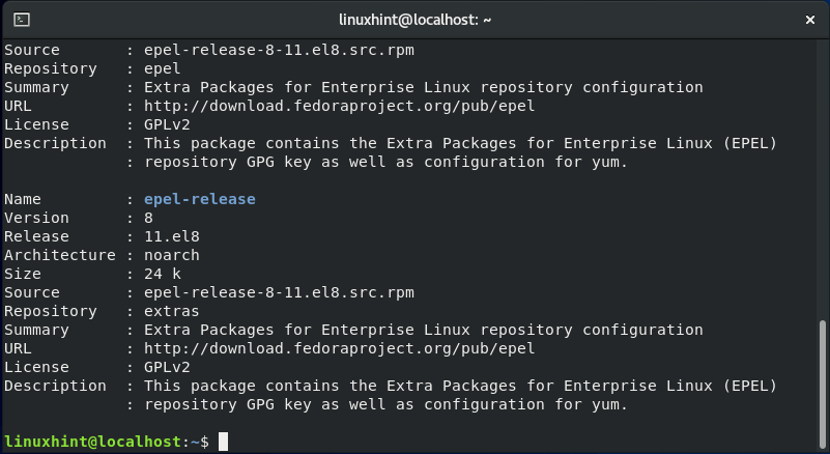
To know more about the EPEL repository, such as its version, architecture, size, source, write out the “yum info” command as follows:
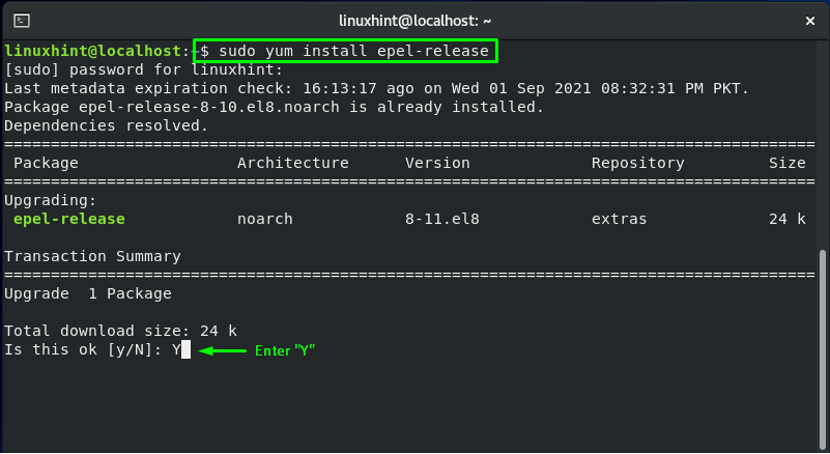
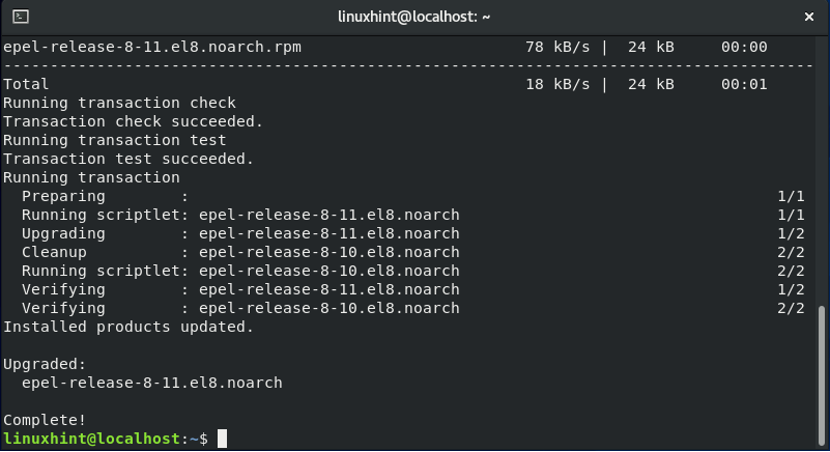
The last step is to execute the below-given command for installing the EPEL repository on your system:
How to verify EPEL repository installation on CentOS
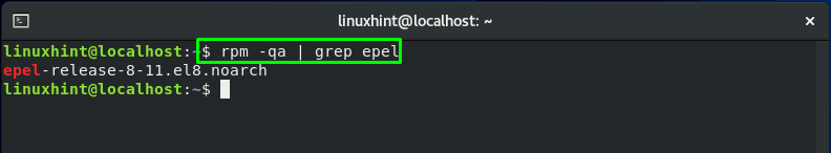
The error-free output declares that the EPEL repository is successfully installed on the CentOS system. To confirm its existence, we will search for “epel” in the rpm, which is the Red Hat Package Manager. In CentOS, this utility permits users to update, verify, query, install, uninstall any package. We will add the “-qa” option to perform the “query all installed packages” operation in rpm. Next, we will direct the output of “rpm -qa” to the “grep epel” command using the “[|]” pipe. As a result, it will verify if the EPEL repository is installed or not:
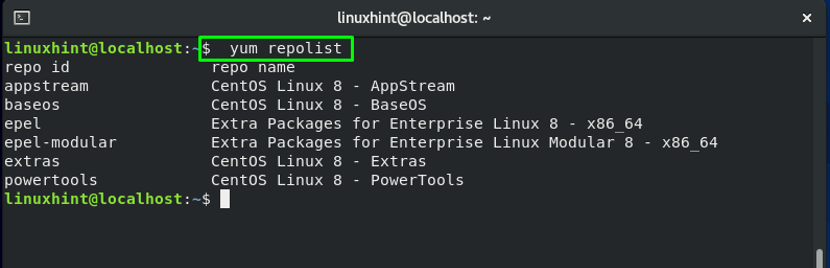
How to list all active repositories on CentOS
Now, check that the EPEL repository is enabled on your system by listing all active repositories in your CentOS system:
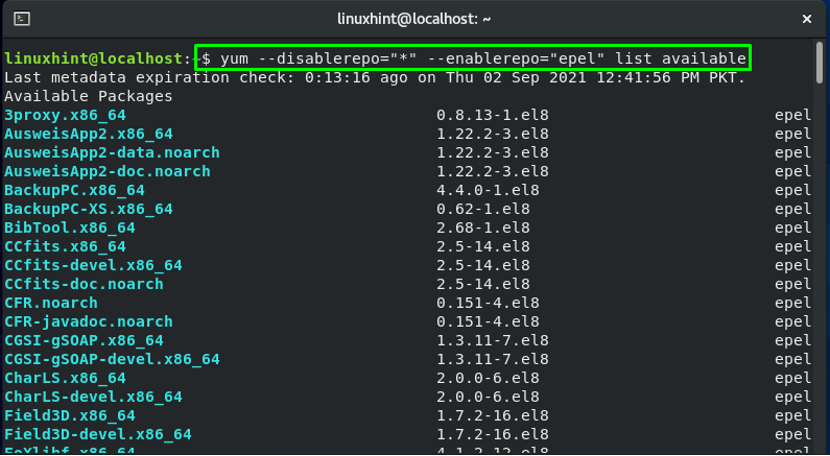
How to list packages of EPEL repository on CentOS
In your CentOS terminal, you can view a list of packages that EPEL comprises by executing the below-given command:
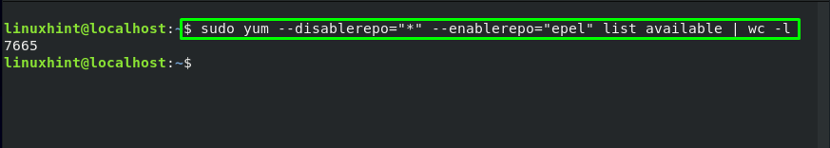
How to count packages of EPEL repository on CentOS
The “wc” is an acronym for “word count”. The “wc” command is used to count characters, lines, and words. In the “wc” command, the “-l” option is added to print the number of lines. If you want to count the packages in your EPEL repository, then utilize this command:
How to search a package in EPEL repository on CentOS
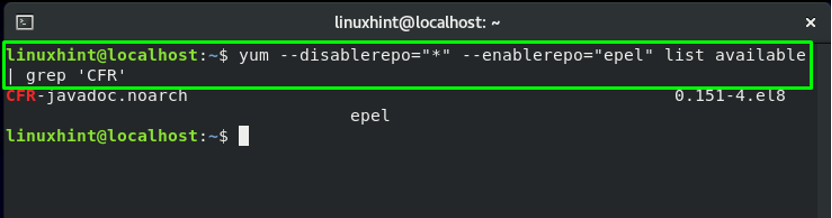
The command that is used for searching a package in the EPEL repository is divided into two parts. The first part of the command will get a list of packages present in the EPEL repository, and in the next part, we will utilize the “grep” command to search for a specific package in the retrieved list. Pipe “[|]” is used for redirecting the packages list to the “grep” command.
In our EPEL repository, we will search for “CFR,” a Java decompiler that decompiles the modern Java features. To do so, we will execute this command in the CentOS terminal:
How to install a package from EPEL repository on CentOS
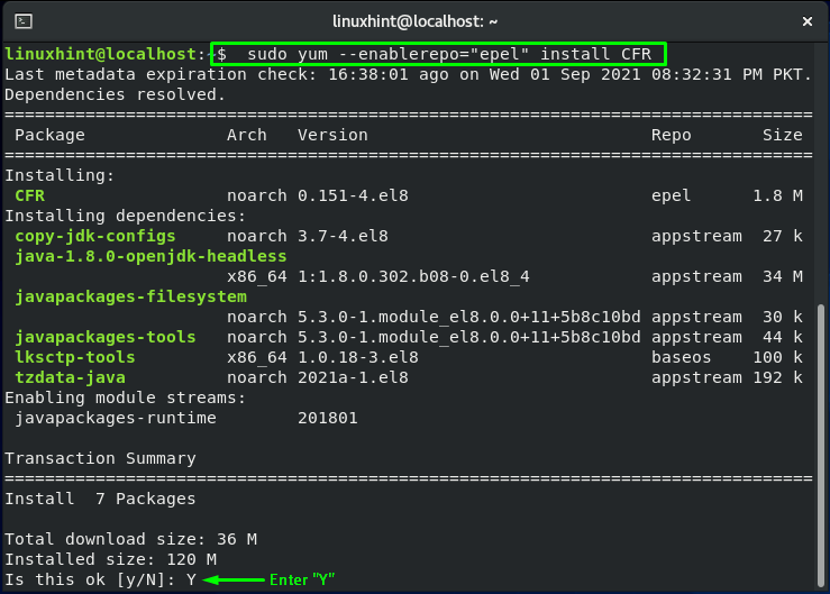
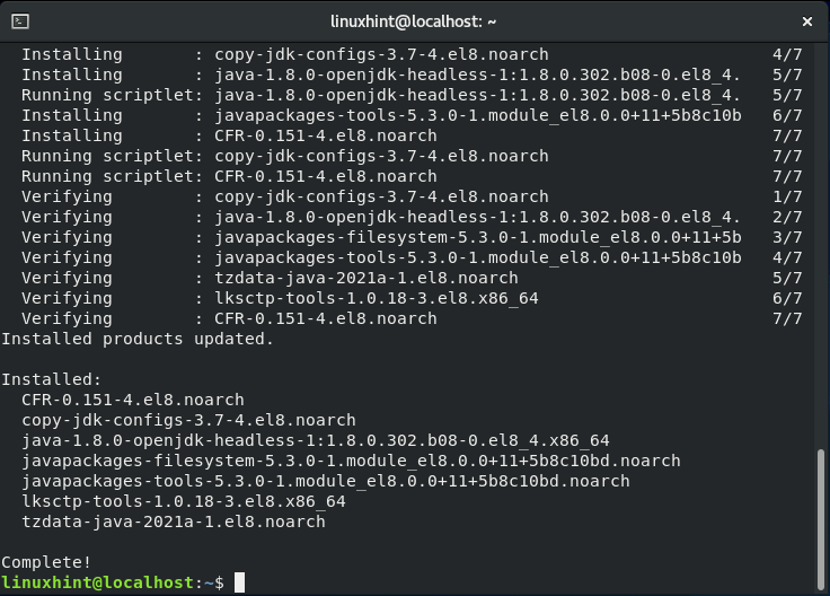
Now, we will install the “CFR” package from our EPEL repository by executing the command given below:
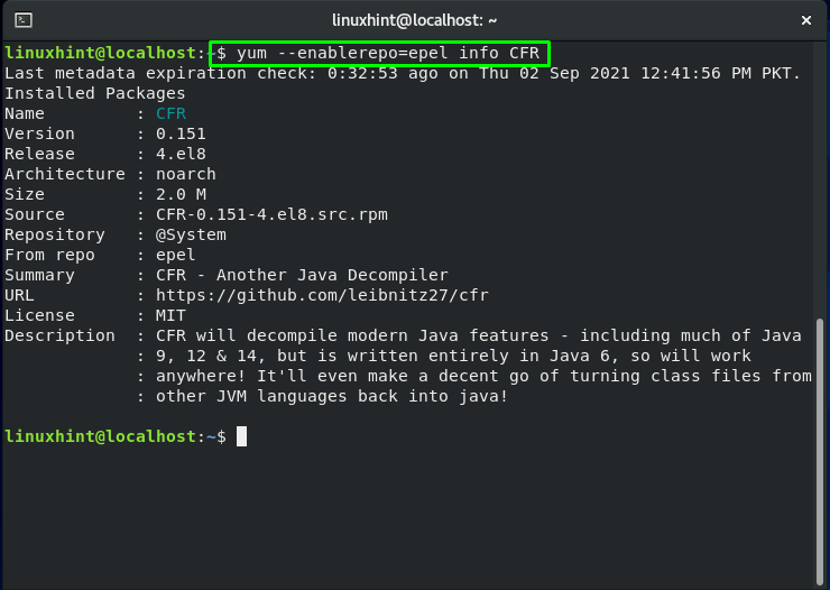
You can also check the information related to the CFR package:
The command mentioned above will show you the name, version, architecture, size, and many other details about the “CFR” package:
How to remove EPEL repository on CentOS
You can erase the EPEL repository by executing the command given below:
Conclusion
EPEL is a software package repository maintained by the EPEL group for Linux-based operating systems such as CentOS. This repository has a lot of additional packages that the core repositories do not have. You have learned about how to install the EPEL repository on CentOS in this post. Moreover, the procedure of installing and enabling any package from the EPEL repository is also provided.