In today’s article, we will be learning about this framework in detail. We will show you the method of checking all the disk volumes that your LVM can manage. Finally, we will state some benefits of using LVM, followed by the conclusion of our article.
A Detailed Explanation on LVM:
As we have already mentioned that the concept of using LVM is very much similar to virtualization; therefore, its working is also more or less the same as virtualization. We will try to understand the working of LVM by creating an example scenario. Generally, we have a physical device that is divided into multiple partitions. All these partitions have a file system installed on them which can be used to manage these partitions.
However, we know that we can have multiple physical devices as well rather than having just a single physical device. In this case, each of these physical devices has its own partitions and the respective file systems. The management of all of these partitions can become a mess if handled as it is. This is where the concept of logical volume management comes into play. It allows you to aggregate all the partitions of different physical devices into a single logical volume group from where they can be managed centrally.
This volume group is a combination of used and unused disk space. From this volume group, you can extract multiple logical volumes depending upon your requirements. Moreover, the exact space allocated to each logical volume can also be increased or decreased depending upon your needs. Then you can have separate file systems for each of these logical volumes. In this way, you can manage the overall storage space more efficiently and can assign the unused space to all those users that ask for it without any problem.
Before logically partitioning your physical disk, you need to have the knowledge about all the volumes that your LVM can access and manage. Therefore, we will explain to you the method of checking all the volumes that LVM can manage in the following section of this article.
Note: We are using Linux Mint 20 to demonstrate this method.
Method of checking all the Volumes that LVM can manage:
For checking all the disk volumes that LVM can manage, you will need to run a disk scan which can be done in the following manner:
First, we will launch the terminal in our desired Linux distribution which in this case is Linux Mint 20. Its terminal is displayed in the image below:
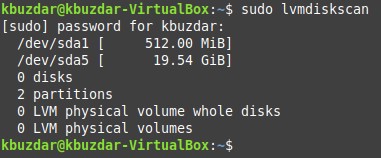
Now we will run the disk scan command in the terminal in the following manner:
The disk scanning process requires root user privileges. For that, you must make use of the “sudo” keyword before this command. However, if you are already logged in to the root user account, then you are allowed to omit this keyword.
Once you run this command in your terminal, the details of all the disk volumes will appear on your screen as shown in the image below:
Benefits of LVM:
The following are some of the biggest advantages of using logical volume management or LVM:
- It allows you to efficiently manage and utilize your physical disk space.
- It is capable of creating such logical volumes whose capacity can be increased or decreased depending upon your requirements.
- If you intend to keep backups of your data on multiple logical volumes, then this increases the availability of your data.
- A new physical device can easily be added below the volume group with zero downtime and without any service disruption.
- LVM allows you to partition a single physical device into multiple logical partitions as well as it also allows you to integrate multiple physical devices into a single volume group.
Conclusion:
This article provided you with a brief overview of logical volume management which is a very important framework of the Linux operating system. Without this framework, we have very limited options for managing our storage space. Also, these options fail to resolve the conflicts between the varying storage needs of multiple users. That is why LVM is considered as an essential component of the Linux based systems.