This blog will cover the enlisted content:
Overview of Oracle NVL
The Oracle NVL function is a built-in Oracle database function that aids users to replace null values with a specified default value to avoid any error in calculations or reports. It takes two arguments as input and checks the first argument to see whether it is null or not, in the case of the null value it replaces it with the second value. However, if the data type is different for both arguments it implicitly converts the data type of the second argument.
Syntax
In the above syntax, the “NVL” function can take only two arguments. The “expr” (stands for expression) should be checked if it is null or not. In the case of null, it should be replaced by a second argument (replacement_value).
Practical Implementation
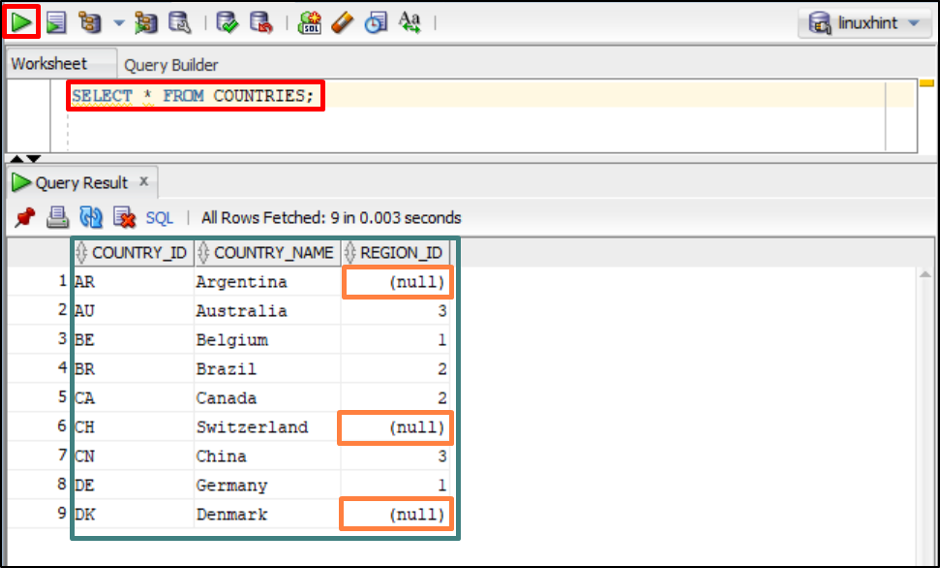
For the practical implementation, let’s first show the values of a table named “COUNTRIES” using this command:
The above command lists all values stored in the “COUNTRIES” table.
Output
The output depicts the values of the table, users can see null values stored in the column name “REGION_ID”.
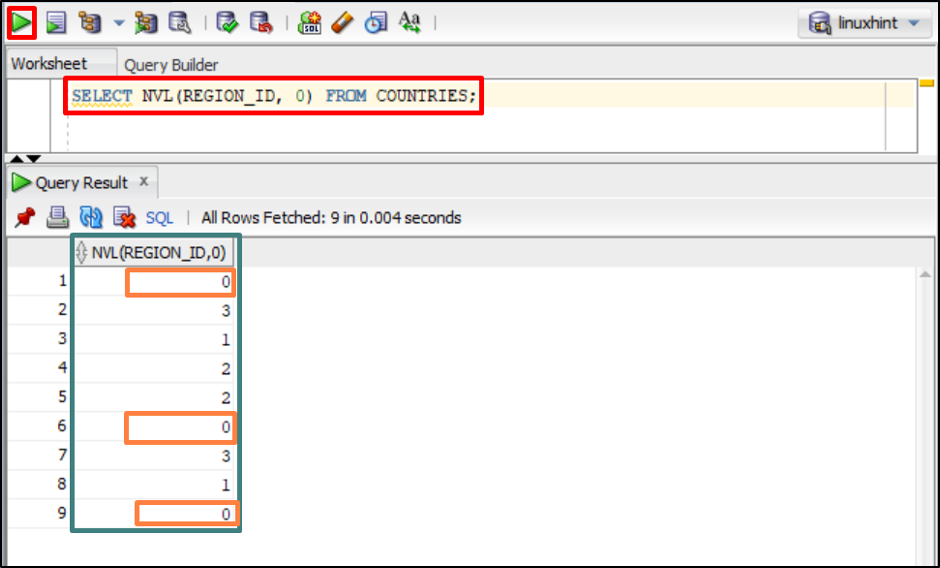
It’s time to run the provided command to replace the null values of column “REGION_ID” in the table “COUNTRIES” with the value “0”:
The above command passed two arguments “REGION_ID” which will be checked for null values and “0” which will be replaced with null values.
Output
The output returned a column with the value “0” in place of null values.
Overview of Oracle Coalesce
The Oracle Coalesce function (use the “short-circuit evaluation” feature) is a built-in Oracle database function that aids the user to replace the null values with the first not null value from the specified multiple arguments. However, if all the input arguments will be null, the user will get the null output.
Syntax
In the above syntax, the “Coalesce” can take multiple arguments. The “expr” argument checks for being null or not. In case it is null, it will be replaced with the first not null “replacement_value”.
Practical Implementation
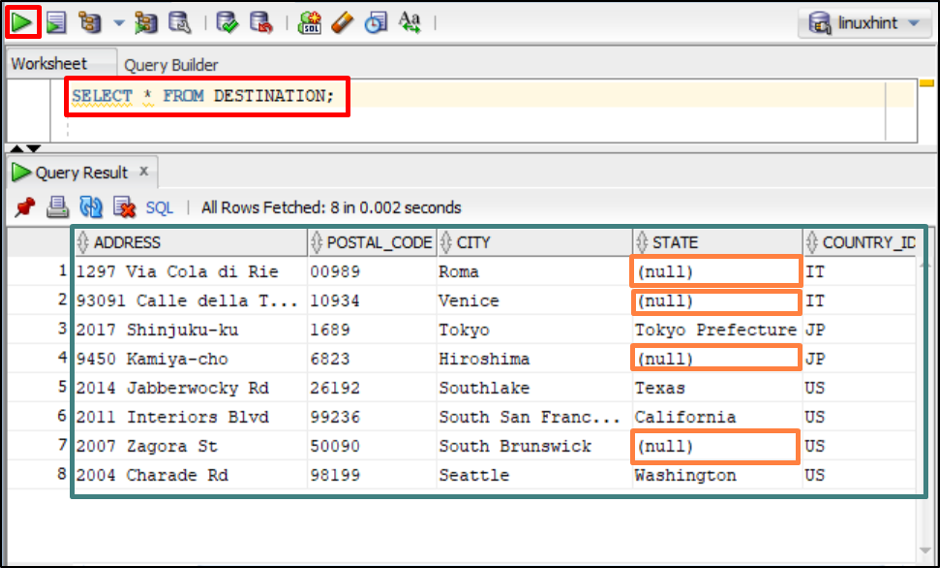
Let’s use a “DESTINATION” table for the practical implementation of the “Coalesce” function. But before that, execute the below command to enlist all the stored values of this table:
The above command depicts the stored values of the “DESTINATION” table.
Output
The output displayed the table values and here users can see the column “STATE” with some null values.
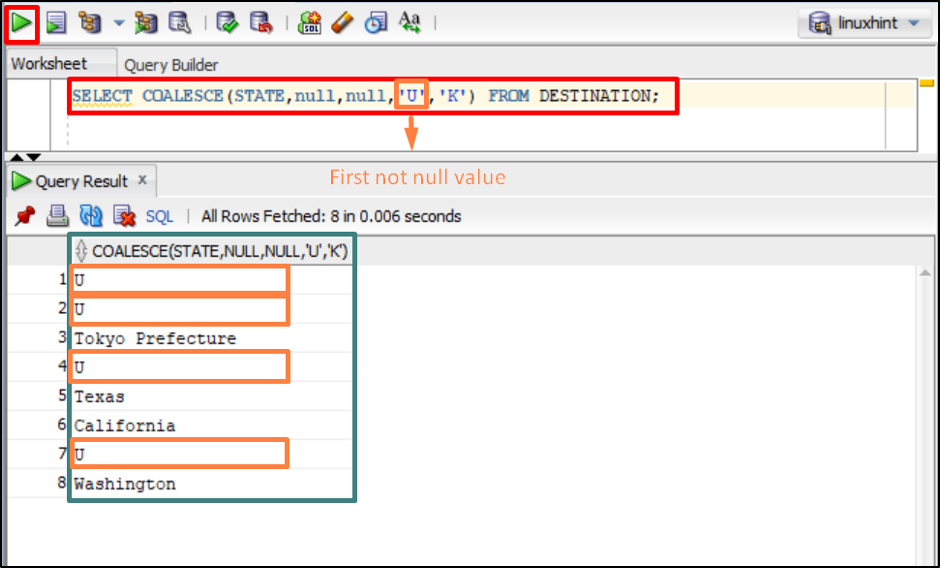
Execute the given command to utilize the “COALESCE” function to replace the null values:
The above command comprises multiple arguments which replace the null values of the “STATE” column with the first non-null argument.
Output
The output returns a column where the null values of the “STATE” column have been replaced by the first not null value which is “U”.
Difference Between Oracle NVL and Coalesce
Let’s discuss the differences between the Oracle NVL and Oracle Coalesce functions:
| Parameters | Oracle NVL | Oracle Coalesce |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Arguments | It accepts only two arguments as input for the function. | It can take two or more arguments as input for the function. |
| Return Type | It always returns the same data type as the first argument. If the data type is changed it implicitly changes the data type of the second argument. | It returns the data type of the first non-null argument encountered. |
| Evaluation of Arguments | It checks the first argument and in case it is null the second argument is returned | It checks each argument starting from the second position until a non-null value is found and replaces it with the null value of the first argument. |
| Performance | If the requirement is to check only two arguments the NVL is faster than coalesce. | If the requirement is to handle multiple arguments, then coalesce is faster than NVL as it only evaluates each argument until a non-null value is found |
Conclusion
Oracle NVL and Oracle Coalesce are useful Oracle database functions for handling null values to prevent calculation errors and make reports more meaningful. NVL is a simpler and faster function for handling two arguments while coalesce is a more versatile and efficient function when the user wants to handle multiple arguments. This post has discussed Oracle NVL, Oracle Coalesce, and their differences.