In this write-up, we will explain what a schema is, how it works, and what are the differences between the schema and database.
What is schema
A database schema is an architecture of the database which holds the information about the pattern of how the data should be placed in the table but it should be clear that a schema has no association with the data itself, it just tells the possible ways in which a data should be placed in the database. We can define, the schema as the structure of any database that tells us about the representation of the table, it also defines the number of rows, columns of the table, the primary and foreign keys associated with the tables, and also defines the datatypes of the data to be inserted in the tables.
Mostly in companies, Database Administrators, are responsible for providing a proper schema for any database, according to which Database Developers, develop the databases.
Comparison Between Database and Schema
| Database | Schema |
|---|---|
| Stores the data in the tables | Provides the logical representation of a database on basis of tables |
| DML (data modification language) is used to manage data in the database | DDL (data definition language) is used to manage the representation of tables |
| Data can be edited at any time | Modifications are not supported |
| It includes tables, schemas, and all other constraints of the database | It includes only structures of tables and privileges related to tables |
| It occupies memory on the server | It occupies no memory |
What are the types of Schema
Schema can be divided into two types on the basis of their functions as shown in the chart below.
Physical Schema: It is the type of Schema that can be viewed by the users, it deals with the methods of storing the data and how they can be represented in the database.
Logical Schema: It is the type of schema which tells us about the concept behind the creation of the database, it explains the formation of tables, the relationship of tables with each other in a database, and the keys used in the tables which can be the primary key as well as a foreign key. Assume the above example of “school_record_of_students”, now this defines the number of rows and columns of the table and it also links it with the other tables, let’s say, “record_of_grade_2_students” with the help of primary and foreign keys.
How schema works in MySQL
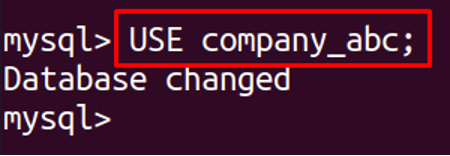
We will try to create the database, named,”company_abc” and a schema, named, “school_abc”, we will create the tables and try to insert data in both tables and observe the results, but before the creation of tables we will create a database as
Use this database to create the table:
Create a table and name it “employees_data”.
Insert data in the table:
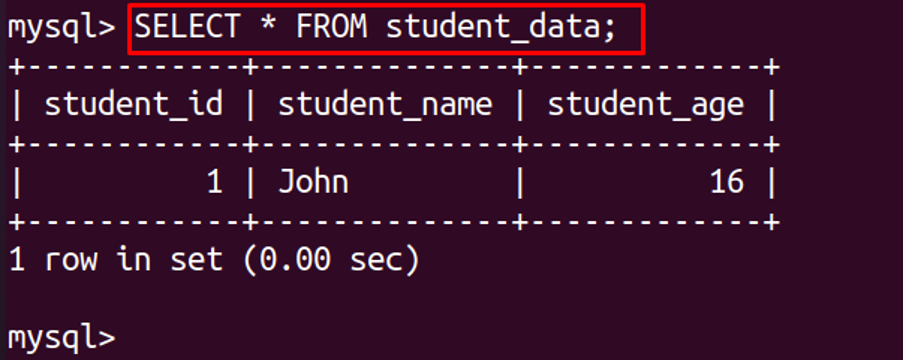
To display the table:
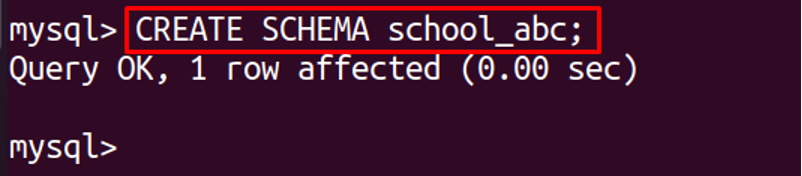
Similarly, we will create a schema ”school_abc”:
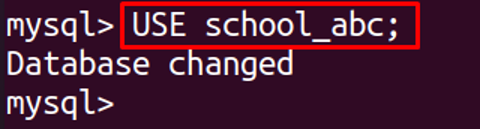
Use the newly created schema:
Create a table in schema school_abc,
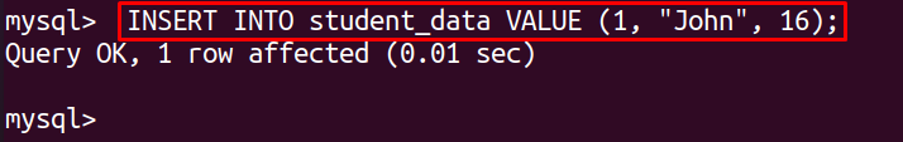
Now insert the data in the table:
To display the table:
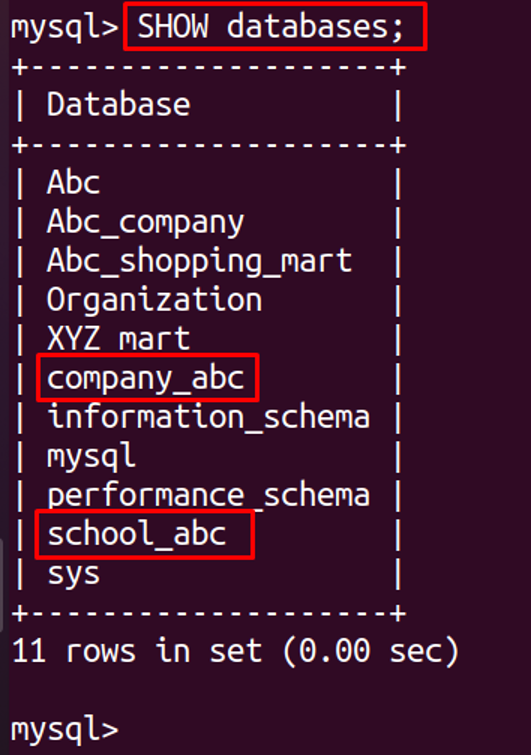
To show the databases.
We can observe that in MySQL not only is Schema created and displayed in the same way as Database has been created but also the table has been created in both schema and database.
Conclusion
Schema is the structure that can help the developers in creating many databases following a single schema. In this article, we have learned that schema is a logical representation of the database and it differs from the database as it doesn’t occupy any space whereas the database occupies some space on the server, but with the help of examples we have deduced the results that in MySQL, the schema is just a synonym of database and can perform the same functions which a database can perform.