In programming, void is a keyword used in C, C++, and C# which refers to the absence of a value. It is a data type that does not hold any value or memory allocation. Instead, it is used as a placeholder or a marker for functions that do not return a value or when it is designed to simply terminate the program.
Follow this article’s guidelines to know about void use in C, C++, and C#.
What Does void Mean in C, C++, and C#
The void meaning in C, C++ and C# is the same but its use may vary depending on which programming language you use.
Void in C
In C, you use the void to declare a function that does not return any value (no return argument). For instance, a function that displays a message or performs a task without producing a result is usually declared void. An example of such a function in C is shown below:
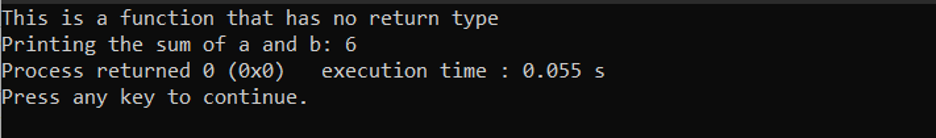
In the above code, we are using a void function sum() to print a message and sum of two variables, and sum() is then called in the main() function.
Output
In some cases, a pointer may not have any memory location to point to, and in such cases, we use the void pointer. A void pointer is a special type of pointer that holds the address of any data type or object, regardless of its type or size. However, the void pointer cannot be dereferenced directly as it does not point to any specific data type or object.
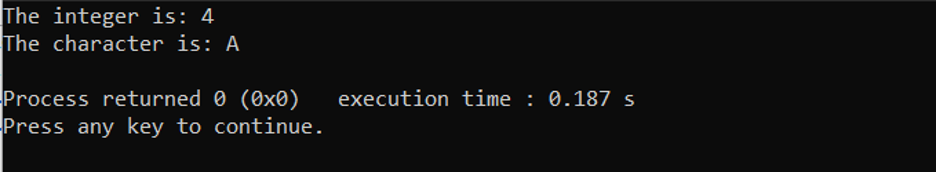
In the C code above, we are using a void pointer in the main() function and the pointer is pointed towards the variable a which is an integer, and prints its value. The pointer is then pointed to the variable b which is a character, and the value is printed then.
Output
Void Keyword in C++
In C++, the use of void in C is not limited to functions and pointers only. It can also be used as a type for function parameters, which indicates that the specific argument passed to the function does not have any specific data type or value. For instance, the main() function in C++ does not need any arguments and can be declared void. An example is shown below:
using namespace std;
void message (void)
{
cout << "I'm a function!";
}
int main (void)
{
message ();
}
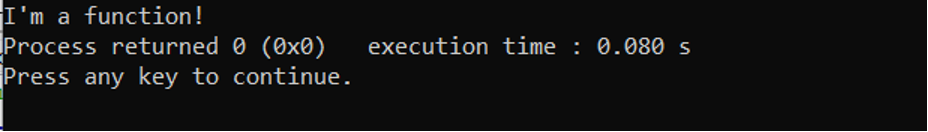
In the C++ code above, we are using void as a function parameter for the function message(). The output will then be printed when the function message() is called from the void main() function.
Output
Void Keyword in C#
In C# void is used as a return type for methods that do not return anything. This includes functions that return no value, as well as constructors, destructors, and event handlers. When a method has a void return type, it cannot be assigned to a variable or used in an expression. An example of a void method in C# is shown below:
class GFG {
public void Text()
{
Console.WriteLine("Linuxhint");
}
public void sum(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("multi = " + (a * b));
}
};
class Prog {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
GFG ex = new GFG();
ex.Text();
ex.sum(5, 20);
}
}
In the C# code above, two void functions Text() and sum() are declared, and then these functions are called from the void main() function.
Output
Conclusion
Void is a keyword used in programming languages like C, C++, and C# to indicate the absence of a value. It is used to declare functions and methods that do not return anything, and specifically as a function parameter in C++. Understanding how to use void correctly is essential for writing efficient and functional code.