Using variable from command line or terminal
You don’t have to use any special character before the variable name at the time of setting value in BASH like other programming languages. But you have to use ‘$’ symbol before the variable name when you want to read data from the variable. You can set and get data from a variable from the terminal in the following way.
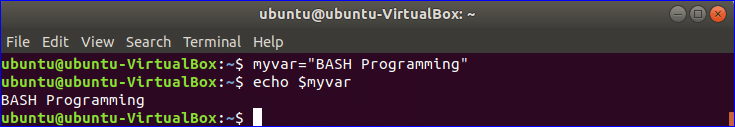
Example-1: Declaring and reading string data using variable
Run the following commands from the terminal.
$ echo $myvar
Output:
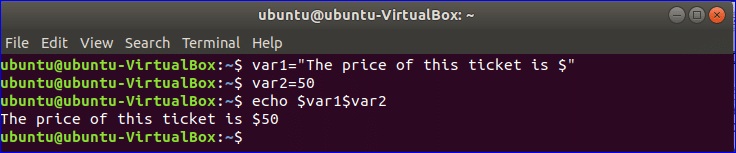
Example-2: Combining two string variables
You don’t have to use any operator to combine two or more strings like other languages. Here, $var1 is used to store string value and $var2 is used to store a numeric value. Run the following commands from the terminal to combine two variables $var1 and $var2.
$ var2=50
$ echo $var1$var2
Output:
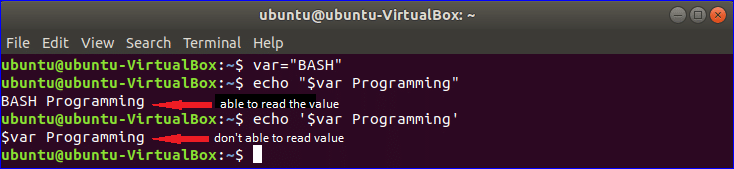
**Note: You can print the value of the variable without any quotation but if you use quotations then you have to use double quotations.
Example-3: Concatenating strings with variables
Double quotation can be used to read the value of the variable. In this example, single quotation is used on one echo statement and double quotation is used on another echo statement. Run the following commands from the terminal to check the output.
$ echo "$var Programming"
$ echo '$var Programming'
Output:
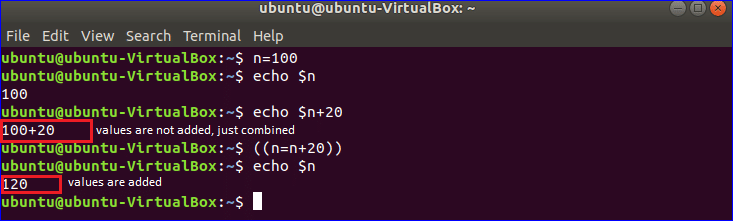
Example-4: Declaring and reading numeric data using variables
One of the major limitations of Bash programming is that it can’t perform arithmetic operations like other programming languages. Numeric values are taken as strings in BASH. So no arithmetic operation can be done by normal expression and it just combines the numeric values. If you write the expression with double first bracket then the arithmetic operation works properly. Run the following commands from the terminal.
$ echo $n
$ echo $n+20
$ ((n=n+20))
$ echo $n
Output:
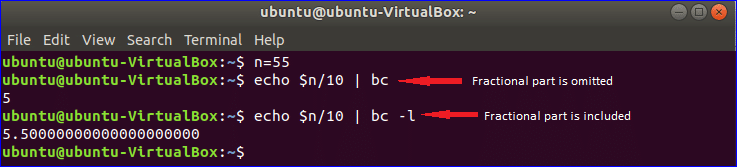
Example-5: Doing arithmetic operation using bc command
bc command is another way to do arithmetic operation in BASH. Run the following commands from the terminal. When you use bc command only for doing any arithmetic operation then fractional parts are omitted from the result. You have to use -l option with bc command to get the result with fractional value.
$ echo $n/10 | bc
$ echo $n/10 | bc -l
Output:
Using variables in bash file
You can define variable in bash file by the same way which are mentioned in above examples. You have to create file with .sh or .bash extension to run bash script.
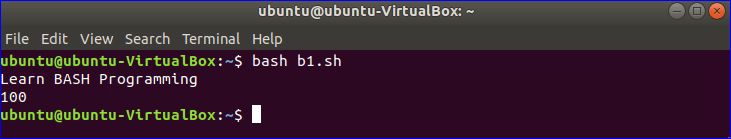
Example-6: Creating simple bash script
Copy the following code in a text editor and save the file with bash extension. In this script, one string and one numeric variables are declared.
#print string value
echo $str
num=120
#subtract 20 from numeric variable
(( result=$num-20))
#print numeric value
echo $result
Output:
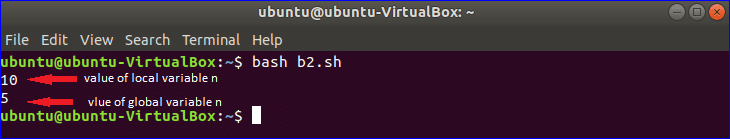
Example-7: Using global and local variables
In the following script, one global variable n and two local variables n and m are used.
When the function addition() is called then the value of the local variable n is taken for calculation but global variable n remains unchanged.
n=5
function addition()
{
local n=6
local m=4
(( n=n+m ))
echo $n
}
addition
echo $n
Output:
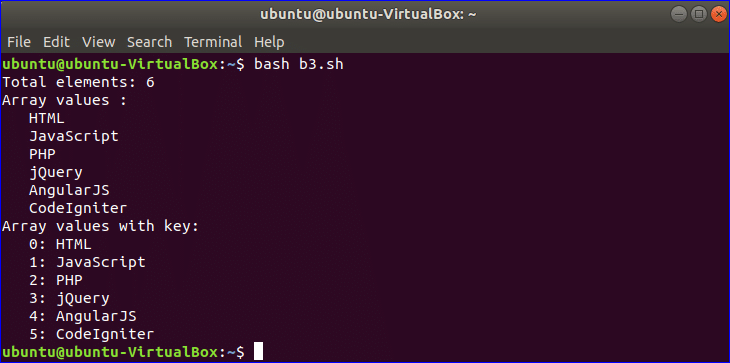
Example-8: Using array variable
Array variable is used to store a list of data. The following example shows how you use of array variable in bash script. The elements of any array are separated by space in BASH. Here, an array of 6 elements is declared. There is no built-in function or property to count the total elements of the array. # with * is used to count total elements. All elements are indicated by *. For loop is used here to iterate the array values. Reading array values and array values with key are shown in the next part of this script.
myarr=(HTML JavaScript PHP jQuery AngularJS CodeIgniter)
#Count total number of elements of the array
total=${#myarr[*]}
echo "Total elements: $total"
#Print each element value of the array
echo "Array values :"
for val in ${myarr[*]}
do
printf " %s\n" $val
done
#Print each element value of the array with key
echo "Array values with key:"
for key in ${!myarr[*]}
do
printf "%4d: %s\n" $key ${myarr[$key]}
done
Output:
To use BASH variables properly you need a clear concept on the declaration and use of variables. This tutorial will help you to get a clear idea on BASH variables. After exercising the above examples properly you will be able to use variables more efficiently in your bash scripts.