The network manager is responsible for the administration, detection, and connection of the server with internet connectivity. It is a tool that assists the user in automatically connecting the Arch Linux operating system with the network. You can also opt for the netctl utility that comes along the Arch Linux server. An effective network manager puts up your system defenses against unknown connectivity bugs. Arch Linux is a complex system, so it requires an efficient network-manager to oversee the secure connection. This guide provides a detailed understanding of downloading and using the network manager in Arch Linux.
Installation Process
To get the network manager for your system, there are only two steps that you need to follow:
- Step 1: Installation
- Step 2: Configuration
Once the network manager is working effectively on your server, you can use the manager to connect to your network. After the successful installation of the network manager, you can opt for various command-line tools to maximize the efficacy and ease of operationality of this tool.
Prerequisites
The essential components for installing the network manager in Arch Linux include a sudo user and the Pacman package manager.
Installing the Network Manager
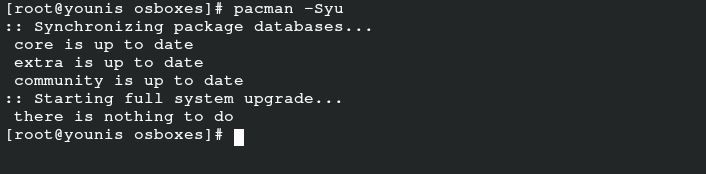
First, input the following command to update and sync any existing system packages:
This command will sync, refresh, and update packages that are already available in your Arch Linux official database. It is very easy to install the network manager in Arch Linux because it comes in the Arch repository packages.
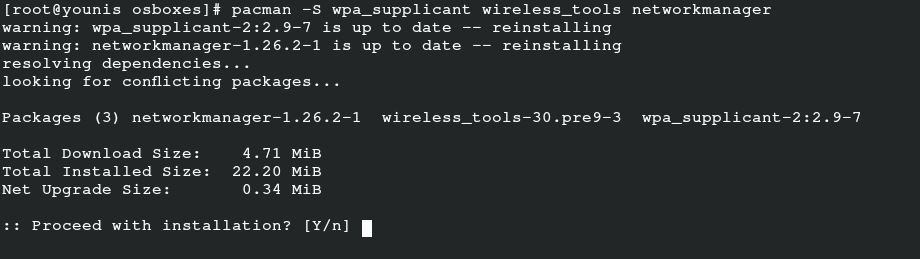
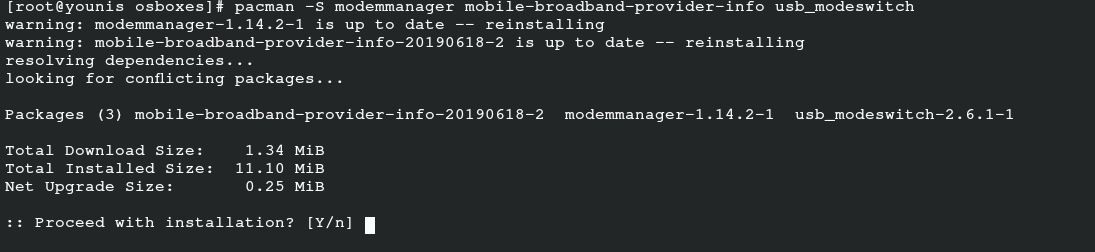
To install a network-manager for your mobile device, run the following command for the additional installation of the related package:
To obtain the respective packages for PPPoE support, issue the following command:
This last command allows you to obtain the respective packages to support the UI. Installing any of these packages depends on your preferences.
Configuration
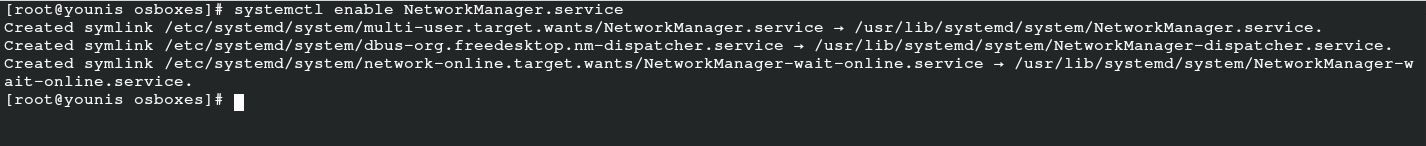
Enabling the network manager will assist you in setting up the network manager as the main package for network connectivity after booting the system.
Disable the default dhcpcd service to avoid conflict over network management by issuing the following command:
You may also need to enable some supportive services. Run the following command to enable supportive services:
Lastly, input the following command to start the network manager and reboot the system to bring the changes into effect:
Using Network Manager
Now, you can use the network manager on your Arch Linux system with the netctl utility or some other command-line tool. The priority is to get the list of networks that are nearby your system. Enter the cli command below to list out the networks. I am using a Virtual box here, so it will not display any devices, as I am using the host machine connection as ethernet.
You can also input the following command using netctl:
Once you have selected your preferable network, proceed with connectivity via the following command:
Input the network and its respective password to connect the network to your server via the following command:
This command will visualize all the hidden networks available to your system.
If you are curious about the connected network details, then input the following command:
The above command will present a list onscreen of all connected networks on your system, along with their respective details. After checking the network, you can also check the available device connected with that network. You can add your interface to the wireless network before disconnecting it via the following command:
Visualize the network to reconnect to it using UUID.
The next phase is to edit the connection. You can save the settings in the respective repository of the network via the following command:
To alter the settings of the respective file, execute the following cli command:
The last step is to reload the server to ensure that the changes have been made successfully. To do so, issue the following:
Using Network Manager nmti
Using the nmti network manager is comparatively easy because it applies the user interface to select the options, instead of running the command. Nmti is a command-line UI tool, and you can navigate the network manager after launching this tool.
Select the “Edit a connection” option in the window visible on your screen and hit “OK.” Select the connection and click “Edit.” You can delete any networks that you do not need and add those that you wish to edit. Type the details of the network you are editing and press “OK.” You can also activate and deactivate the connection in this way.
Desktop Environment
If you are using a desktop environment like GNOME or KDE, then you can integrate the network manager with the desktop environment. You can manage settings on GNOME with the GNOME plug-in. You can also use the following command in KDE Plasma to configure the settings:
Conclusion
Using the network manager in Arch Linux can save you a lot of trouble. This tool makes managing your internet connection swift and easy. You can secure your network devices and also get detailed information about the network with the network manager. Moreover, you do not need to concern yourself with network issues anymore. The network manager allows automatic connection with your preferred networks. You can connect to your server and also mobile networking through the network manager.
This guide shares the complete details of the Arch Linux network manager, from its installation to its uses. This way, even if you are a beginner, you can still effectively ace the operations of the network manager in Arch Linux.