What Is time.Sleep() Function in Golang
In Golang, a program’s execution can be paused for a set amount of time using the time.Sleep() function. The amount of time to suspend the running of the program is the single argument that the time.Sleep() function accepts, below is the syntax for it:
Where d is the time duration and time-unit can be seconds, or milliseconds.
How to use time.Sleep() function in Golang
The time.Sleep() is employed to make delays in the execution process of the Golang program. It is necessarily used to limit the rate of a certain amount of time in program exceptions. Now let’s see the examples of time.Sleep() function in Golang programming.
Example 1: Golang time.Sleep() Function (Seconds)
The following Golang code suspends the program execution for three seconds:
In the main function using fmt.Println() function strings are displayed. After that time.Sleep() function is called with the value of 3 in seconds. After 3 seconds the following instructions will execute displaying the respective strings.
Example 2: Golang time.Sleep() Function (Milliseconds)
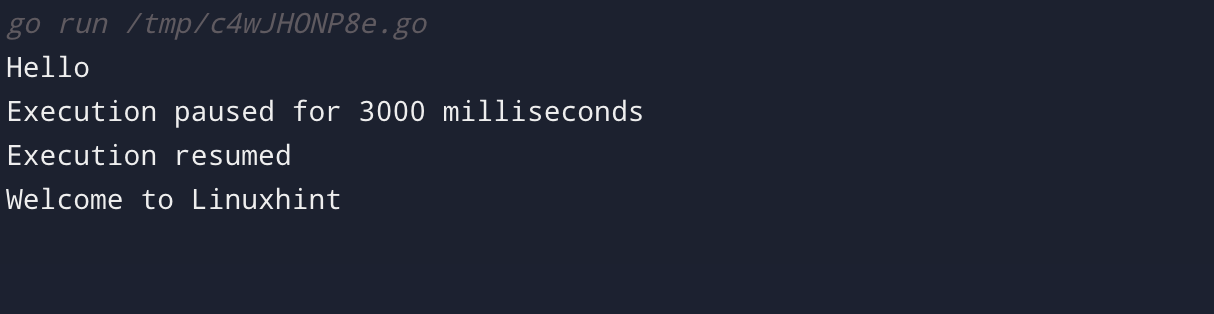
The following example application utilizes a time.Sleep() function to stop the execution for a given amount of time, measured in three thousand milliseconds:
When the main function execution started, it printed Hello using fmt.Println() then, this example prints Execution paused for 3000 milliseconds to the console. Once the execution is resumed it prints the message Execution resumed and then executes the next instruction.
Conclusion
The time.Sleep() function is often employed in Go scripts to add pauses in the code execution. This article explained the time.Sleep() function with the help of examples that makes some pauses in seconds and milliseconds.