In PowerShell, the “Get-Acl” cmdlet is used to get the security descriptor for a resource including a registry key or a file and is only available for Windows. The security descriptor in PowerShell includes the “ACL” resource access control lists. It specifies the permissions to the users or user groups who need to access the resource.
In this blog, we will demonstrate the usage of the “Get-Acl” cmdlet in PowerShell.
How to Use the Get-Acl (Microsoft.PowerShell.Security)?
As it is described earlier that the “Get-Acl” cmdlet is responsible for getting the security descriptor for a specific resource.
Let’s have a look at the following examples for a better understanding.
Example 1: Use the “Get-Acl” Cmdlet to Retrieve Folder’s ACL
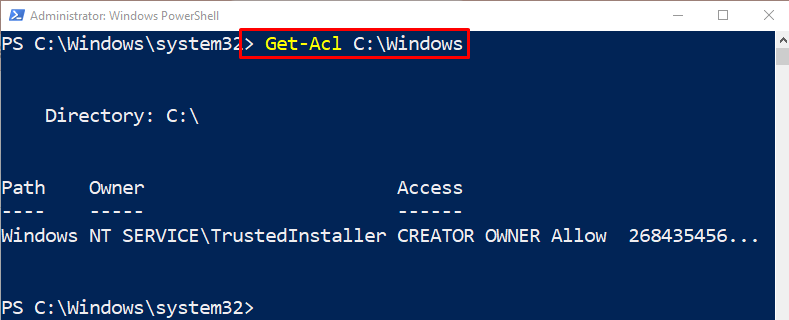
Execute the below-stated code to get the ACL for a folder:
As you can see, we have retrieved the folder ACL:
Example 2: Use the “Get-Acl” Cmdlet to Retrieve an ACL for a Directory Using Wildcard
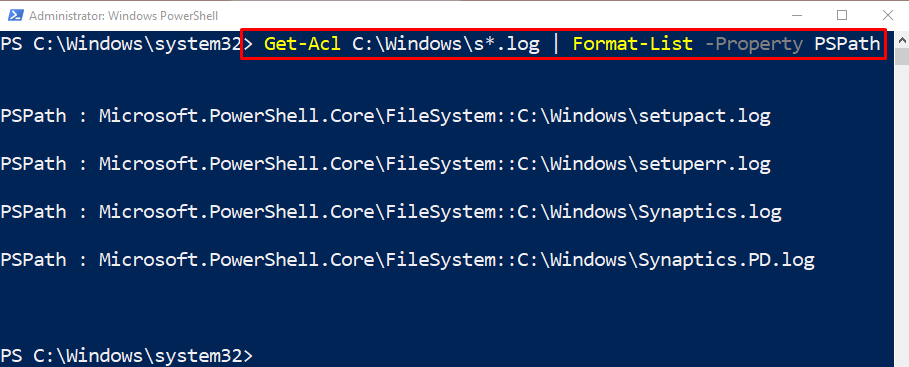
To retrieve an ACL for a specific folder, execute the below-mention command:
In the above-stated code:
-
- First, mention the cmdlet “Get-Acl” along the stated path and the “|” pipeline.
- Next, write the cmdlet “Format-List”.
- Lastly, specify the “-Property” parameter and assign the stated value:
Example 3: Use the “Get-Acl” Cmdlet to Get an ACL for a Registry Key
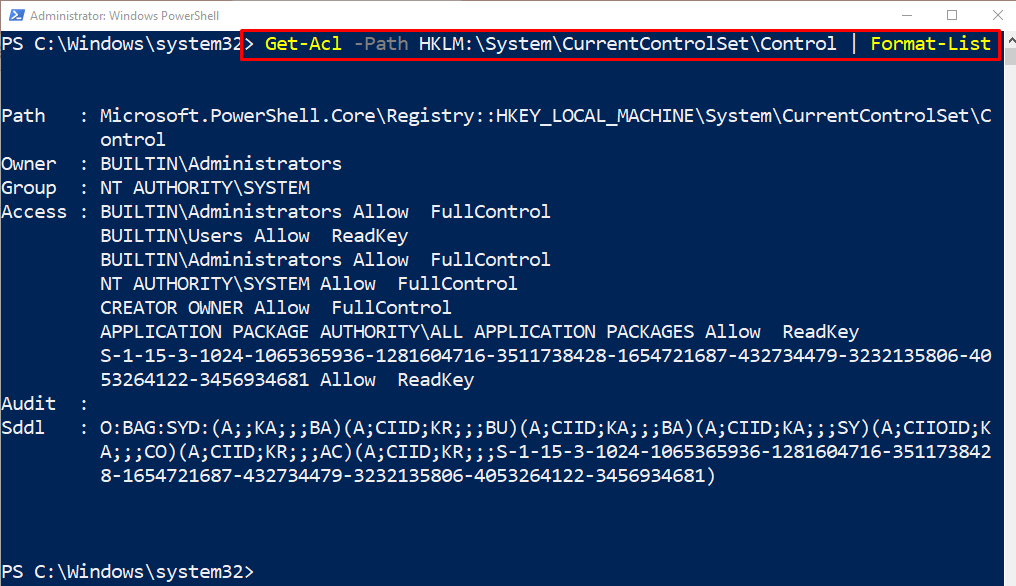
Run the below-given command to retrieve an ACL for a specific registry key:
According to the above code, first, mention the “Get-Acl” cmdlet and the “-Path” parameter having the stated registry path assigned to it. Then, add the “|” pipeline and the “Format-List” cmdlet:
That’s it! The “Get-Acl” cmdlet has been explained in detail.
Conclusion
The cmdlet “Get-Acl” is used to retrieve the security descriptor for a resource including a file and a registry key. It specifies the permissions that the user or user groups need to access the resource. This particular tutorial has demonstrated the “Get-Acl” cmdlet with the aid of various examples.