This blog will discuss using and implementing the arrow operator “->” in Java.
How to Use/Apply the Arrow Operator, “->”, in Java?
The arrow operator “->” is utilized to create/define lambda expressions. It is such that it separates the arguments from an expression.
Syntax
Example 1: Applying the Arrow Operator “->” in Java
This example applies the arrow operator to create a lambda expression such that the interface function gets invoked and the allocated integer value is returned:
public void age();
}
public class Arrowoperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 18;
Sample x = ()->{
System.out.println("Age -> "+age);
};
x.age();
}}
In the above code snippet:
- Firstly, define an interface and contain the stated function in it.
- In the “main()” method, initialize the stated integer.
- After that, create a lambda expression invoking the age, and lastly, access the defined function in the interface.
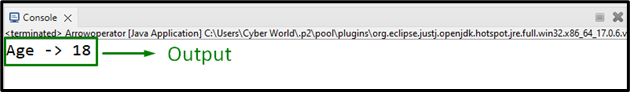
Output
In this output, it can be seen that upon invoking the interface function, the initialized value of age is returned appropriately with the help of a created lambda expression via the arrow operator.
Include the below-provided packages in the next example first to work will all the classes within the “java.util” package and with “Stream”, respectively in the next example:
import java.util.stream.Stream;
Example 2: Applying the Arrow Operator “->” in Java Collection(ArrayList)
In this particular example, the arrow operator can be applied to the Java collection i.e., “ArrayList” to filter out the list values based on a condition:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
Stream<Integer> extract = list.stream().filter(p -> p > 1);
extract.forEach(value -> System.out.println(value));
}}
In the above code block:
- First of all, create an ArrayList of the “Integer” type and add the stated integer values via the associated “add()” method.
- Now, apply the combined “stream()” and “filter()” methods along with a created lambda expression based on which the list values will get filtered.
- Lastly, apply the “forEach()” method with a lambda expression again to print out the filtered values based on the specified condition.
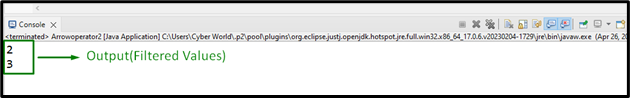
Output
In this output, it can be observed that the list values are retrieved based on the applied condition in the lambda expression.
Example 3: Applying the Arrow Operator “->” in Java Thread
This demonstration applies the arrow operator to implement the “run()” method of the “Runnable” interface:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable x = ()-> {
System.out.println("Thread is executing...");
};
Thread tr = new Thread(x);
tr.start();
}}
According to the above lines of code, perform the following steps:
- Likewise, create a lambda expression comprising an arrow operator with the help of the “Runnable” interface.
- Now, create a Thread object via the “new” keyword and the “Thread()” constructor and pass the instance of Runnable as its(constructor) argument.
- Finally, associate the “start()” method that invokes and returns the lambda expression statement.
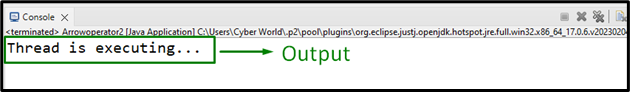
Output
In this outcome, it can be analyzed that the instance of the “Runnable” interface is executed as a thread accordingly.
Conclusion
The arrow operator “->” is used to create/define lambda expressions. It is such that it separates the arguments from the expression. Also, it assists in referencing the functionalities, thereby making their access convenient. This blog discussed using and implementing the arrow operator “->” in Java.