Syntax:
The syntax of the ternary operator is given below:
‘?’ and ‘:’ symbols are used to define the ternary statement. The first part of this statement contains the conditional statement. If the conditional statement returns true, statement-1 will be executed, otherwise, the statement-2 will be executed.
Example 1: Use of the ternary operator in the pace of if-else statement
The following example shows the way to compare the if-else statement and the ternary operator for implementing the conditional logic to find a number that is even or odd. Create a PHP file with the following script.
Here, the $number variable is initialized with an integer number. At first, the if-else statement is used to check if the $number is even or odd. Next, the same logic is implemented by using the ternary operator.
//Define a number
$number = 24;
//Check the number is even or odd using if-else
if ($number % 2) {
$result = 'Odd';
} else {
$result = 'Even';
}
//Print the result
echo "The $number is $result. (The output of if-else statement)<br />";
//Check the number is even or odd using ternary operator
$result = ($number % 2) ? 'Odd' : 'Even';
//Print the result
echo "The $number is $result. (The output of ternary operator)<br />";
?>
Output:
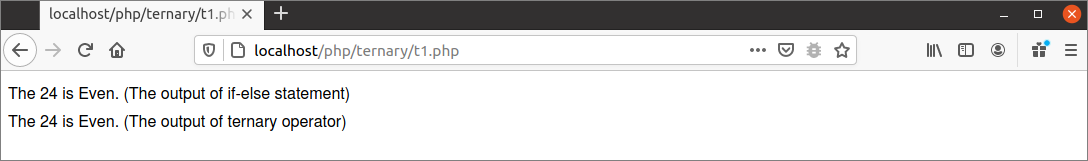
The following output will appear after running the script from the server. According to the script, 24 is even and both outputs generate the same result.
Example 2: Use of the ternary operator with $_GET variable
The following example shows how the ternary operator can be used to check if the $_GET variable is initialized or not and read the value of this variable. Create a PHP file with the following script.
If the value of the ‘id’ and ‘marks’ are provided by using the URL query string, then the script will print the values of $_GET[‘id’] and $_GET[‘marks’], otherwise, it will print an error message.
Output:
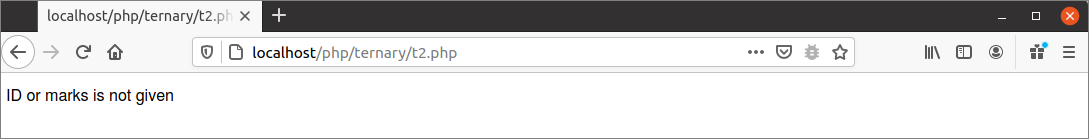
The following output will appear if the script is executed without providing any query string.
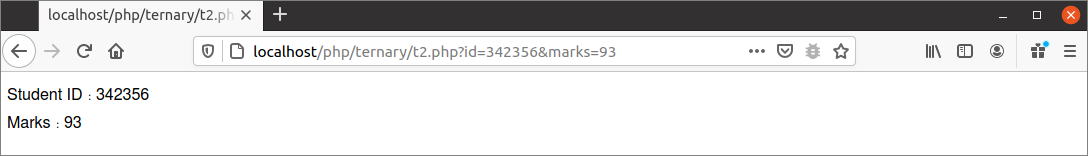
The following output will appear if the script is executed with two query strings. In the output, 342356 is given as an id value and 93 is given as marks value. So, both values are printed as the output.
Example 3: Use of ternary operator with $_POST[] variable
The following example shows the use of the ternary operator to read the values of the $_POST variable. Create a PHP file with the following script.
An HTML form is used in the script to take two integer numbers from the user. The ternary operator is used to check if the numbers are numeric or not, and calculate the sum of the numbers. If any number is not numeric, the script will print the error message, and if both numbers are numeric, then the sum of these numbers will be printed.
//Check the form values
if(isset($_POST['n1']) && isset($_POST['n2']))
{
//Use the ternary operator to check the submitted values are numeric or not
$number1 = is_numeric($_POST['n1']) ? $_POST['n1'] : "<p style='color:red'>Enter the numeric value.</p>";
$number2 = is_numeric($_POST['n1']) ? $_POST['n2'] : "<p style='color:red'>Enter the numeric value.</p>";
//Calculate the addition if both field values are numeric
$result = is_numeric($number1) && is_numeric($number2) ? $number1 + $number2 : $number1;
//Print the output
if(is_numeric($result))
echo "<p style='color:green'> The value after addition: $result.</p>";
else
echo $result;
}
?>
<!-- Design a HTML form with POST method -->
<html>
<head>
<title>Use of ternary operator</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="#">
<table>
<tr><td>Enter the first number: </td><td><input type="text" name="n1"></td></tr>
<tr><td>Enter the second number: </td><td><input type="text" name="n2"></td></tr>
<tr><td></td><td><input type="submit" name="submit" value="ADD"></td></tr>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output:
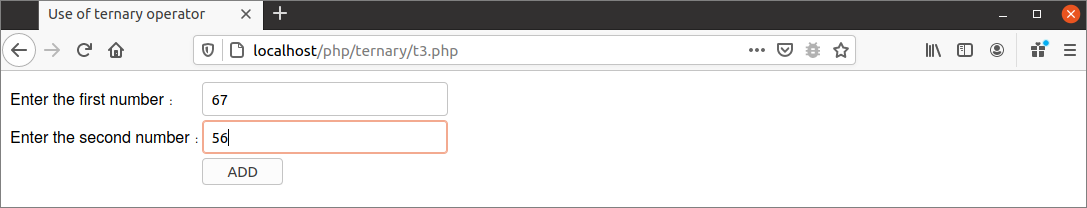
The following form will appear if the script is executed from the server. In the output, 67 and 56 are given as the number values.
The following output will appear after clicking the submit button. If the submit button is pressed by keeping any field empty, then an error message will be displayed.
Example 4: Use of chaining ternary operator
The following example shows the use of the chaining ternary operator to define the multiple conditions using multiple ternary operators. This type of task can be done using the if-else-if statement. Create a PHP file with the following script.
An HTML form is used in the script to select a name from the dropdown list. Check the submitted value using the chaining ternary operator and print the output based on the matching condition.
<html>
<head>
<title>Use of ternary operator</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="#">
<table>
<tr><td>Name: </td><td><select name='name'>
<option>Select Name</option>
<option>Mohammed Ali</option>
<option>Nila Chowdhury</option>
<option>Meher Afroz</option>
</select>
</td></tr>
<tr><td></td><td><input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit"></td></tr>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<?php
//Check the submitted value
if(isset($_POST['name']))
{
//Set the value
$name = $_POST['name'];
//Set the color based on the chaining ternary operator
$result = ((strcmp($name,'Mohammed Ali') == 0) ? 'Blue' :
((strcmp($name,'Nila Chowdhury') == 0) ? 'Pink' :
((strcmp($name,'Meher Afroz') == 0) ? 'Green' : 'None')));
//Print the output
echo $result != 'None' ? "<p style='color:blue'>The favorite color of $name is <b>$result</b></p>" : "<p style='color:red'>No name is selected.</p>";
}
?>
Output:
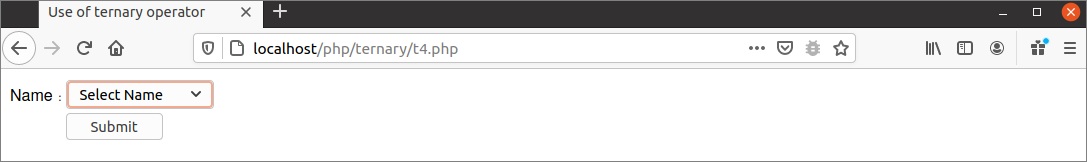
The following output will appear after running the script from the server.
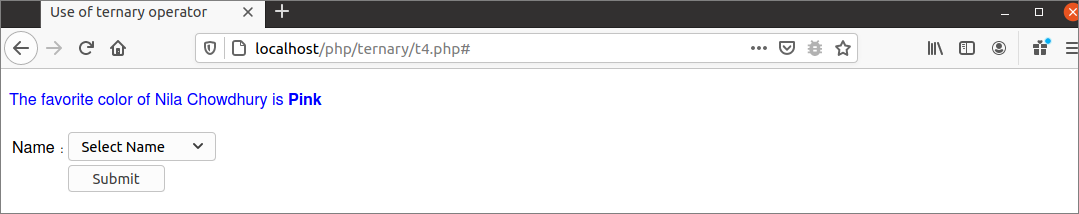
The following output will appear if ‘Nila Chowdhury’ is selected from the dropdown list.
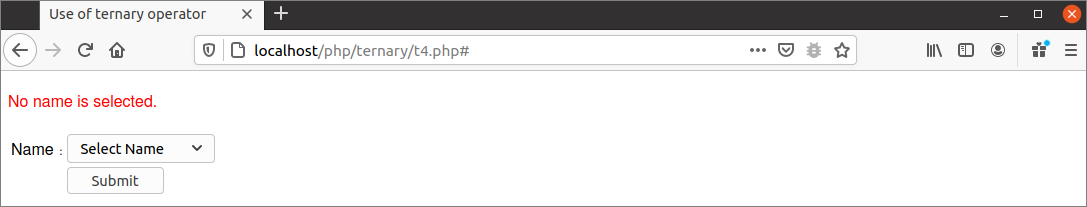
The following output will appear if the submit button is pressed without selecting any value from the dropdown list.
Conclusion
The various uses of the ternary operator have been explained in this tutorial using simple examples to help new PHP coders. Null Coalescing operator can be used as the alternative of the ternary operator in PHP 7+.