To start with the “taskset” command, first, we need to know about process affinity. Process affinity is the scheduler property that helps to bind or unbind the process so that the process will run only with the allotted CPU.
In Linux-like systems, there are multiple tools to set the affinity of the CPU of a process. One of the popular utilities is the “taskset” command that seems difficult, but breaking it with different steps makes it easier.
With the help of the “taskset” command tool, the user can fetch or set the CPU affinity of a particular process with its given process id (PID). Not only this, but it also helps the user to assign CPU cores manually.
Through this utility, one can perform two functions with the process affinity; first, you can set CPU affinity for the programs that are to be launched. Second, to set the CPU affinity for the programs already in a running state.
The important thing to keep in mind that CPU affinity is signified as Bitmask but using the “taskset” options, you can display it numerically. You can specify the Bitmask list in a hexadecimal format (with or without 0x).
For example:
0x00000003 represents to processor 0 and 1
0x00000007 represents to processor 0, 1 and 2
And so on..
The syntax of the “taskset” command is:
(Run a command with given affinity mask)
(Set the affinity of CPU of an existing task)
(fetch the affinity of CPU of an existing task)
Taskset Commands Options:
The “taskset” command tool supports the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -a, –all | Used to set the CPU affinity of all tasks for the given PID |
| -c, –cpu-list | Allows specifying processors in a numerical list instead of a bitmask having multiple items that can be set by comma or ranges |
| -p, –pid | Works on the existing PID and doesn’t allow to launch the new task |
| –help | Print the help message and exit |
| –version | Print the version of the command and exit |
How to Use “taskset” Command Options:
Through the multiple options of the “taskset” command, the user can perform various operations with the given processes:
Fetch the CPU Affinity of a Process:
The “taskset” command is used to display the affinity of the CPU of a process that is already running.
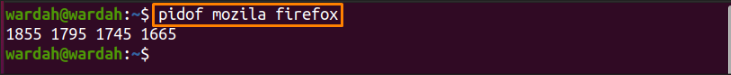
Before getting started with it, we need to get the PID of that specific process:
Now, use the PID to get CPU affinity in a terminal:
Display the CPU range:
To get the CPU range of a process in a terminal, execute the mentioned command:
Change CPU Affinity:
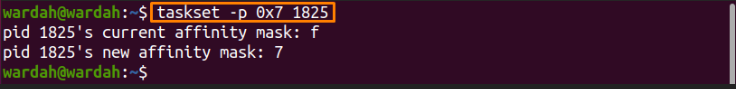
You can change the CPU affinity of a process by assigning the new value to the PID of the existing process through the command:
(As you can see, I set the affinity value 7, and it has been changed, you can set according to the requirement)
To check the current value of CPU affinity, use the same command we have executed above. You will get the updated value:
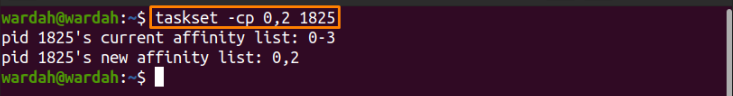
Change CPU range:
CPU affinity of a running process can also be allocated using the mentioned command:
Using the “taskset” command, the user cannot only set the CPU affinity or range, but the user can also assign the CPU core to the process.
In UNIX systems, cores numbers starting from 0, which means the first core of the system would be 0, and 2nd core would be 1, and so on.
Assigning a core means you want to run that process on that particular core. You can also allocate multiple cores to a single process.
So, the syntax for this process is:
Let’s perform an example, set the CPU core to the firefox using the command mentioned below:
The command will assign core 3 and core 5 to firefox and open it:
There is another way to set core; for instance, if you want to set the core from core 3 to core 5. You will use the hyphen “–” instead of a comma:
Top Command:
The “top” command is used to show all the running processes with their PID that is considered a quick way to get the list on the terminal. You don’t need to find the complex setup to monitor applications.
Type the “top” in the terminal to get the names of all running programs:
Conclusion:
In this writing, we have discussed the “taskset” command tool and its options to set the CPU affinity of a given process. The “taskset” command is a Linux tool that helps to assign the CPU core to a process to execute and run only on the designated CPU cores. We have also checked how to set CPU affinity for the process in a running state.