Read this article to know how you can use the split command.
Linux Split Command Syntax
The basic syntax for the split command is given as follow:
Linux Split Command Options
You have different options while using split command, you can use these options to perform different operations:
| Option/Flag | Description |
| -a | Set suffix length. |
| -b | Identify size per output file. |
| -C | Maximum size of the file can be determined. |
| -n | Generates a specific number of output files. |
| -e | Omits creating empty output files. |
| -l | Creates files with a specific output line. |
| -d | Change suffixes into numeric values. |
| –verbose | Displays a detailed output. |
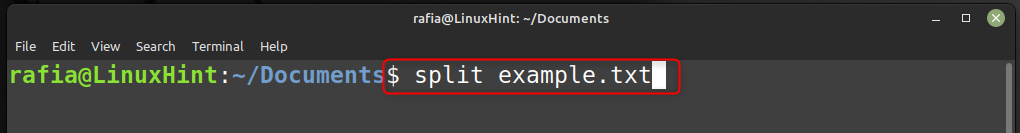
To split a file into smaller files, use the command syntax given below:
For demonstration I have used the above syntax to split the file example.txt into smaller files:
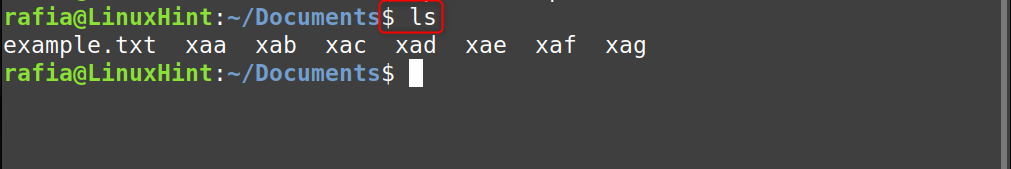
By executing the below command, you can check the smaller files into which the file s converted:
Note: By default, the split command uses the “x” prefix to name the splitted files.
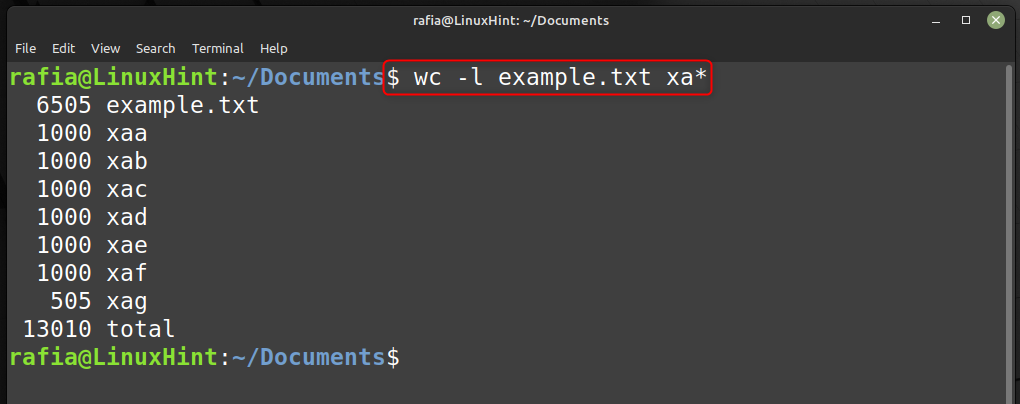
Run the command given below to get the number of lines per file and you can see it is 1000 by default:
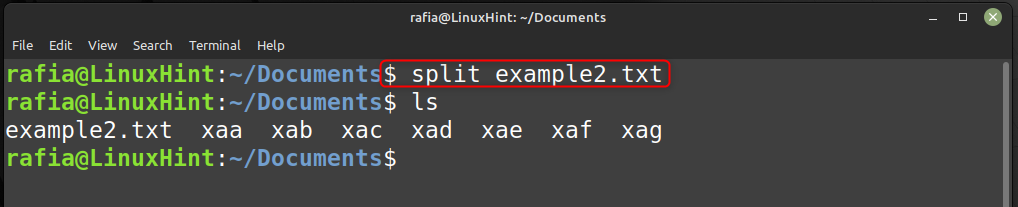
Now split a smaller file into the files via the following command given below:
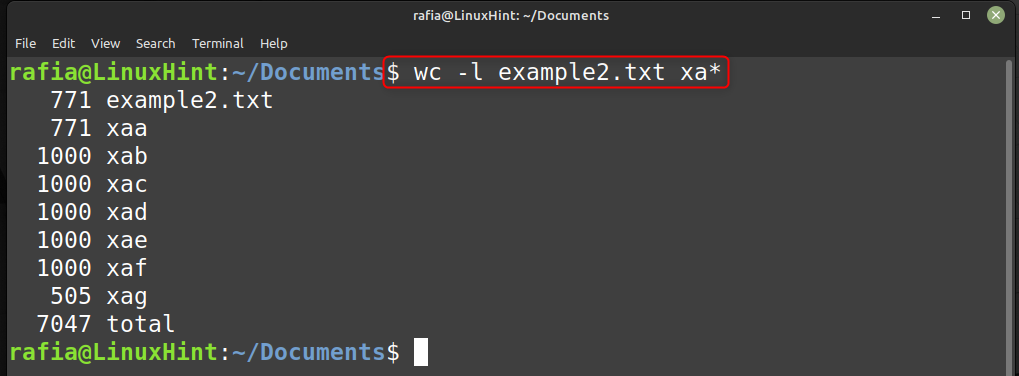
Run the command given below to check the smaller files created for file example2.txt.
Run the command given below to get the number of lines per file and you can see it is 1000 by default:
Set Number of Lines per File
Use the -l command with split to override the default 1000-line restriction. split -l command is used to adjust lines number in the file.
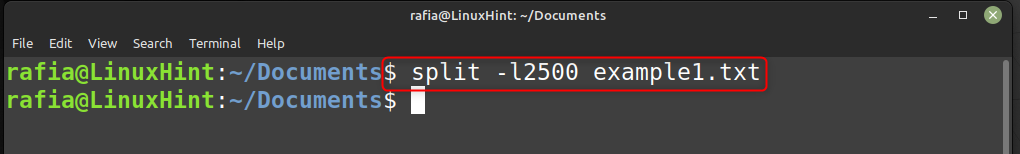
For example, I have split a file into smaller files by setting the lines per file equal to 2500:
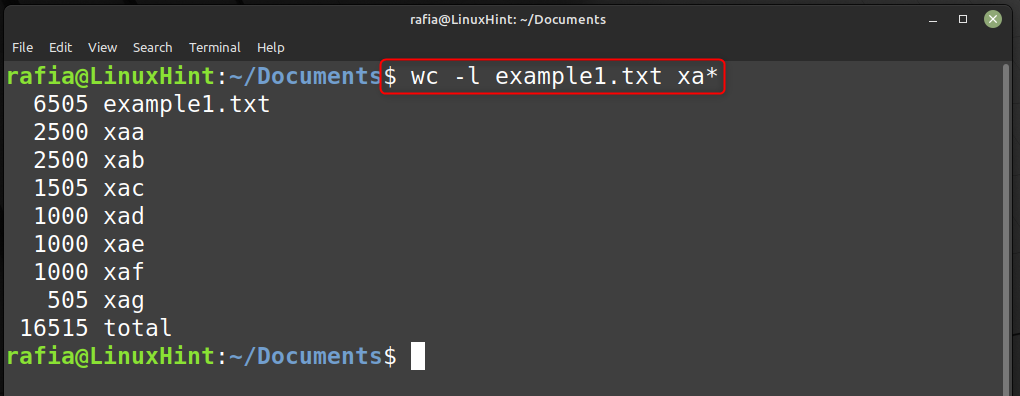
Run the below command to check the number of lines per file:
Run the command given below to split the text into 500-line files:
Run the below command to check the number of lines per file that you have set:
Choose File Size
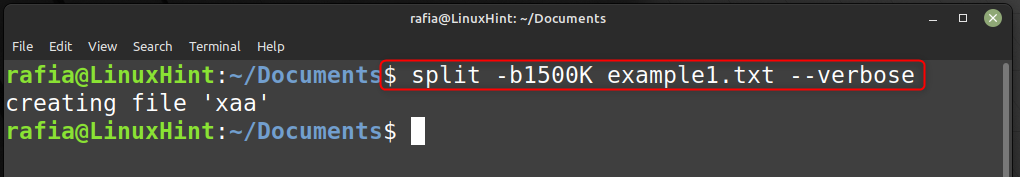
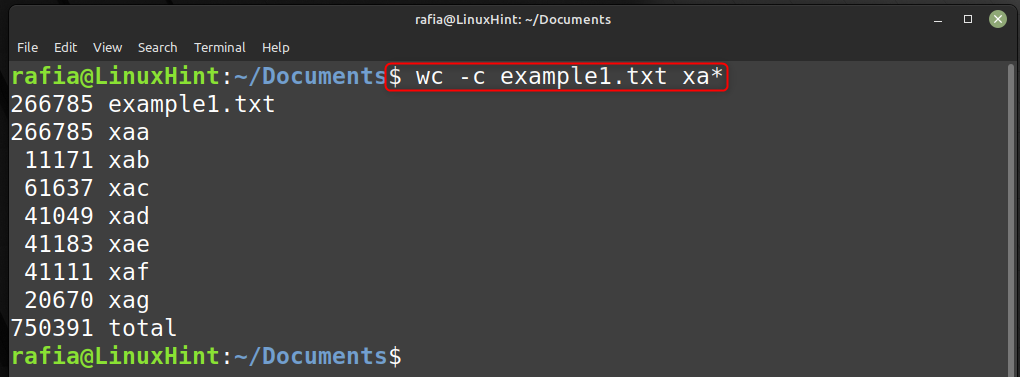
You can split files based on their size using command split -b. For example, to create 1500 kb file using the file example1.txt run the command given below:
Run the command given below to check the file size:
Specify Maximum Size
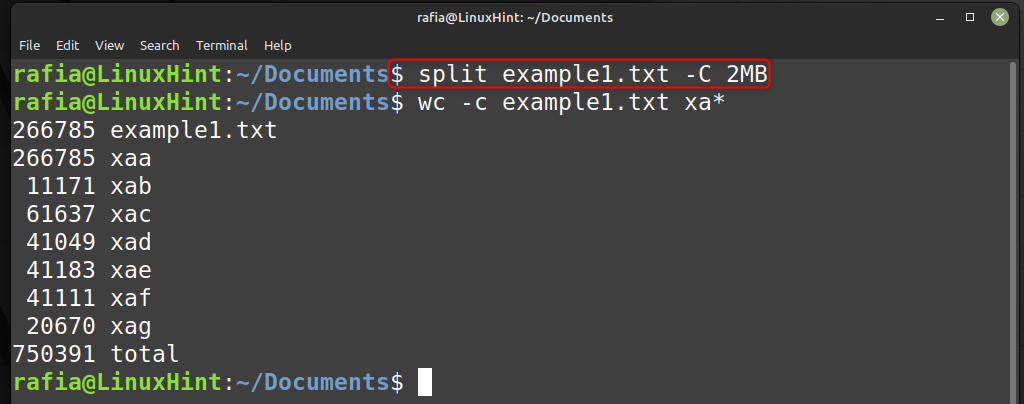
You can also specify the maximum file size using the split command:
To specify a maximum output file size, use the -C command. For illustration, split example1.txt and provide a 2MB output size by using:
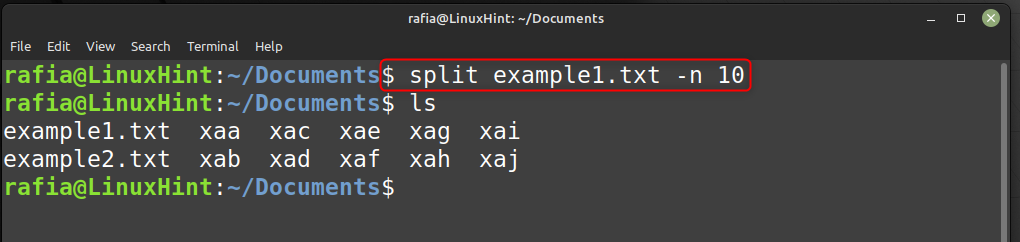
Set Number of Output Files
Use the -n option to set the numbers of output of your file. For instance, divide example.txt into 10 sections by running the following command:
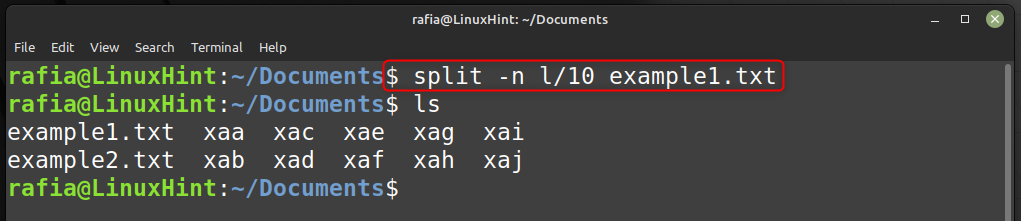
Split a File at the End of a Line
Another way to use the -n option is splitting a file at the end of a whole line.
To do this, combine -n and l. For instance, divide the large text file into 10 files, each of which must conclude with the following entire line:
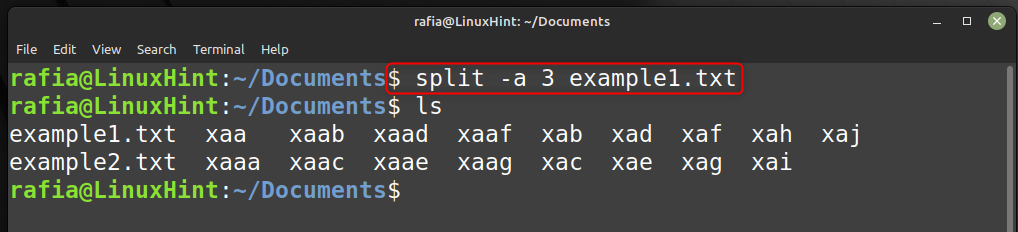
Set Suffix Length
You can generate files with a two-letter default suffix using the split command. The -a flag with the split command is use to change the length. For example, to make the suffix three characters long run the command given below:
For further help, use the man command to open the split command manual on the terminal.
Conclusion
This article focused on using split commands in Linux systems. By default, the split command divides a file into 1000-line pieces, each of which is divided into multiple files. You can use the split command to divide large files into smaller files. The above instruction shows you how to divide the files based on specific features using several split commands in Linux.